What Is The Numerical Value Of Avogadro's Number
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
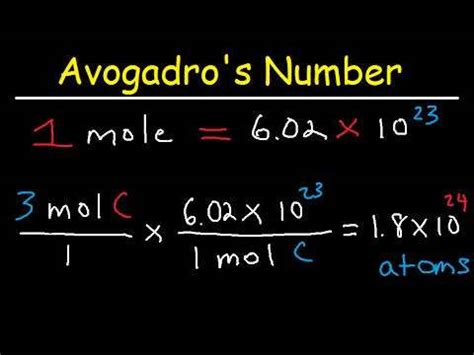
Table of Contents
What is the Numerical Value of Avogadro's Number?
Avogadro's number, a cornerstone of chemistry and physics, represents the number of constituent particles (usually atoms or molecules) in one mole of a substance. Understanding its numerical value and its significance is crucial for anyone delving into the quantitative world of chemistry and related fields. This article will delve deep into the definition, significance, historical context, and the precise numerical value of Avogadro's number.
Defining Avogadro's Number
Avogadro's number, denoted as N<sub>A</sub>, is approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup>. It's not just a random number; it's a fundamental constant that connects the macroscopic world (the world we see and interact with) to the microscopic world (the world of atoms and molecules). One mole of any substance contains Avogadro's number of particles. This means one mole of carbon atoms contains 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup> carbon atoms, one mole of water molecules contains 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup> water molecules, and so on.
This concept is incredibly important because it allows chemists and physicists to work with manageable quantities of substances, even when dealing with incredibly large numbers of atoms or molecules. Imagine trying to work with individual atoms! Avogadro's number provides a convenient scaling factor.
The Significance of Avogadro's Number
The importance of Avogadro's number extends far beyond simply counting particles. It forms the basis of several crucial concepts and calculations:
1. Molar Mass Calculations:
Avogadro's number links the atomic mass (or molecular mass) of a substance to its mass in grams. The atomic mass of an element, as found on the periodic table, represents the average mass of one atom of that element in atomic mass units (amu). One mole of that element will have a mass in grams numerically equal to its atomic mass. This is because one amu is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom, and Avogadro's number is the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12.
For instance, the atomic mass of carbon is approximately 12 amu. Therefore, one mole of carbon weighs 12 grams. This relationship allows for easy conversion between moles and grams, facilitating stoichiometric calculations.
2. Stoichiometry:
Stoichiometry, the study of quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions, heavily relies on Avogadro's number. Balanced chemical equations show the molar ratios of reactants and products. Using Avogadro's number, we can convert these molar ratios into the number of atoms or molecules involved in the reaction, which is essential for understanding reaction yields and limiting reactants.
3. Gas Laws:
Avogadro's law states that equal volumes of different gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles. This directly relates to Avogadro's number, as it implies that one mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP) occupies approximately 22.4 liters. This volume is a direct consequence of the number of particles (Avogadro's number) present in one mole.
4. Solution Chemistry:
In solution chemistry, molarity (moles of solute per liter of solution) is a frequently used concentration unit. Avogadro's number is implicitly used in molarity calculations, enabling us to determine the number of solute particles present in a given volume of solution.
The Historical Context of Avogadro's Number
While the number itself is named after Amedeo Avogadro, the Italian scientist who proposed Avogadro's hypothesis (equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules), he didn't actually determine the numerical value. The determination of Avogadro's number was a gradual process, involving contributions from multiple scientists and advancements in experimental techniques.
Early attempts to estimate the number relied on indirect methods, such as studying Brownian motion (the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid) or using electrochemical experiments. Later, precise measurements of X-ray diffraction patterns in crystals provided more accurate estimates.
The modern value of Avogadro's number is refined constantly through sophisticated experimental techniques. The most accurate determinations involve measuring the mass and volume of a highly pure silicon crystal with precise lattice spacing. This method utilizes Avogadro's number as a link between macroscopic measurements (mass and volume) and microscopic properties (lattice spacing and atomic mass of silicon).
Precise Numerical Value and Uncertainty
The current CODATA (Committee on Data for Science and Technology) recommended value of Avogadro's number is 6.02214076 x 10<sup>23</sup> mol<sup>-1</sup>. Note the inclusion of the units, mol<sup>-1</sup>, indicating the number of entities per mole. The value is now fixed, meaning it's no longer subject to experimental refinement. This fixed value is a consequence of the redefinition of the mole in 2019, which now bases the mole on the fixed value of Avogadro's constant.
The Redefinition of the Mole (2019)
Prior to 2019, the mole was defined based on the mass of carbon-12. The redefinition linked the mole to the Avogadro constant, giving it a fixed numerical value. This change simplifies measurements and improves consistency across scientific disciplines. The mole is now defined as the amount of substance containing exactly 6.02214076 × 10<sup>23</sup> elementary entities. This redefinition makes the Avogadro constant a fundamental constant, similar to the speed of light.
Conclusion
Avogadro's number, with its precise numerical value of 6.02214076 x 10<sup>23</sup> mol<sup>-1</sup>, is far more than just a large number. It's a fundamental constant that bridges the macroscopic and microscopic worlds, allowing us to perform essential calculations in chemistry, physics, and related fields. Its historical development, tied to advancements in experimental techniques, showcases the collaborative nature of scientific progress. The recent redefinition of the mole, based on the fixed value of Avogadro's constant, underscores its importance in ensuring accuracy and consistency in scientific measurements. Understanding Avogadro's number and its significance is crucial for anyone seeking to master the quantitative aspects of science.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Difference Between Zip And Bin
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is The Roman Numeral For 69
Apr 07, 2025
-
Ground State Electron Configuration For Arsenic
Apr 07, 2025
-
A Single Carbon Atom Can Form A Maximum Of
Apr 07, 2025
-
Which Is A Biotic Component Of A Marine Ecosystem
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Numerical Value Of Avogadro's Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.