What Is The Molecular Mass Of C2h6
Juapaving
May 09, 2025 · 5 min read
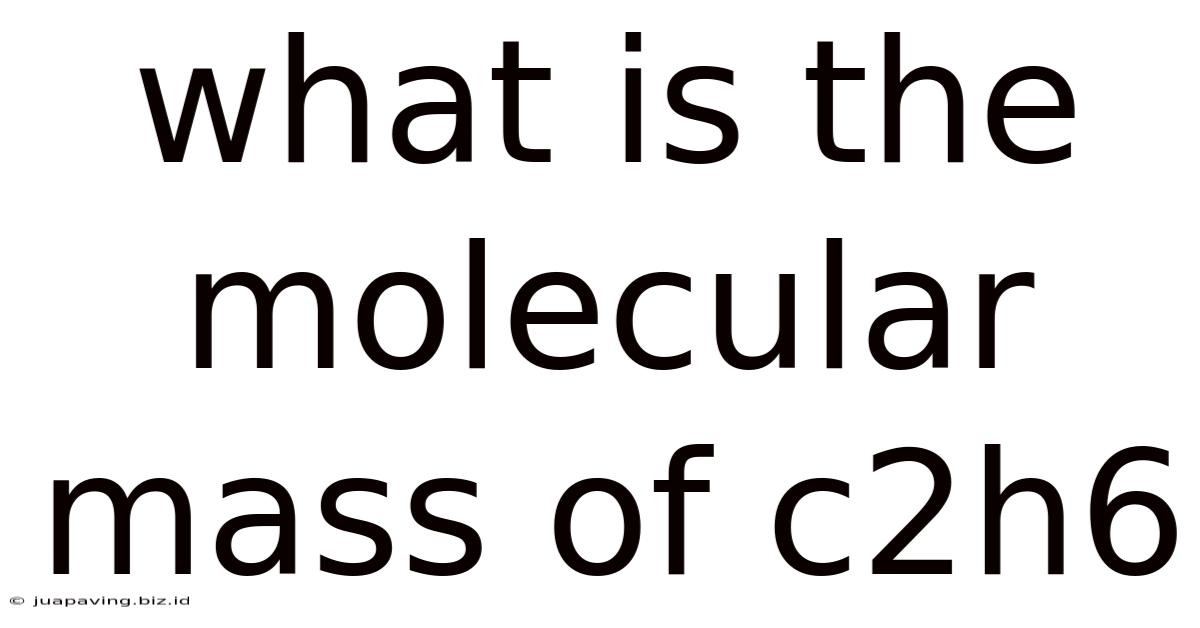
Table of Contents
What is the Molecular Mass of C₂H₆? A Deep Dive into Ethane
Ethane, a simple yet crucial hydrocarbon, plays a significant role in various industrial processes and natural gas composition. Understanding its molecular mass is fundamental to various chemical calculations and applications. This article will delve deep into determining the molecular mass of C₂H₆ (ethane), exploring the underlying principles and providing a comprehensive understanding of the concept. We'll also touch upon related concepts and applications.
Understanding Molecular Mass
Before we calculate the molecular mass of ethane, let's clarify the concept. Molecular mass, also known as molecular weight, is the mass of a molecule. It's expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or Daltons (Da). Unlike molar mass, which refers to the mass of one mole of a substance (6.022 x 10²³ molecules), molecular mass focuses on the mass of a single molecule. To calculate the molecular mass, we need to consider the atomic masses of the constituent elements and their respective numbers in the molecule.
Atomic Mass: The Building Blocks
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of its isotopes, weighted by their relative abundance in nature. These values are readily available in the periodic table. For our calculation of ethane's molecular mass, we need the atomic masses of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H).
- Carbon (C): Approximately 12.01 amu
- Hydrogen (H): Approximately 1.01 amu
These values might slightly vary depending on the source due to the different rounding off practices, but the differences will be negligible for most calculations.
Calculating the Molecular Mass of C₂H₆ (Ethane)
Ethane (C₂H₆) consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. To calculate its molecular mass, we simply multiply the atomic mass of each element by its number of atoms in the molecule and then add the results together.
Molecular Mass (C₂H₆) = (2 × Atomic Mass of C) + (6 × Atomic Mass of H)
Substituting the atomic masses:
Molecular Mass (C₂H₆) = (2 × 12.01 amu) + (6 × 1.01 amu)
Molecular Mass (C₂H₆) = 24.02 amu + 6.06 amu
Molecular Mass (C₂H₆) = 30.08 amu
Therefore, the molecular mass of ethane (C₂H₆) is approximately 30.08 amu. This value is crucial in various chemical calculations, including stoichiometry, determining the empirical formula, and understanding the behavior of ethane in chemical reactions.
Distinguishing Molecular Mass from Molar Mass
It's essential to differentiate between molecular mass and molar mass. While both relate to the mass of a substance, they operate on different scales:
- Molecular Mass: The mass of a single molecule. Expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or Daltons (Da).
- Molar Mass: The mass of one mole (6.022 x 10²³ molecules) of a substance. Expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
For ethane, the molar mass is numerically equal to its molecular mass but expressed in grams per mole. Therefore, the molar mass of ethane is approximately 30.08 g/mol. This molar mass is highly useful in practical laboratory settings, allowing for the conversion between mass and moles of ethane.
Applications of Ethane's Molecular Mass
Knowing the molecular mass of ethane is critical in numerous applications:
1. Stoichiometric Calculations:
In chemical reactions involving ethane, the molecular mass is vital for calculating reactant and product quantities. For instance, if you need to determine how much oxygen is needed to completely combust a specific amount of ethane, you'll utilize its molecular mass to convert the mass of ethane to moles, enabling you to use stoichiometric ratios from the balanced chemical equation.
2. Gas Law Calculations:
Ethane's molecular mass plays a role in gas law calculations, especially when dealing with ideal gas behavior. The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) uses the number of moles (n), which can be calculated from the mass of ethane using its molar mass.
3. Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas:
The molecular mass helps differentiate between empirical and molecular formulas. The empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound, while the molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms. Knowing the molecular mass allows for the determination of the molecular formula from the empirical formula.
4. Mass Spectrometry:
In mass spectrometry, the molecular mass of ethane can help identify the molecule in a mixture. Mass spectrometry separates ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The mass of the ethane ion (after ionization) directly relates to its molecular mass.
Isotopic Variations and Their Impact
The atomic masses used in our calculation are average values, taking into account the natural abundance of isotopes. Carbon has two main isotopes, ¹²C and ¹³C, while hydrogen has two main isotopes, ¹H and ²H (deuterium). These variations can slightly affect the molecular mass of ethane. However, the variation will be minimal for most practical purposes due to the dominance of ¹²C and ¹H. More precise calculations would require considering the isotopic abundances and their respective masses.
Conclusion
The molecular mass of ethane, C₂H₆, is approximately 30.08 amu. This fundamental value is crucial in various chemical calculations and applications, including stoichiometry, gas law calculations, and determining empirical and molecular formulas. Understanding the distinction between molecular mass and molar mass is essential for accurate calculations and interpretations. While isotopic variations can introduce minor changes, the average molecular mass remains a valuable tool for understanding and working with ethane in various chemical and industrial contexts. This detailed explanation provides a solid foundation for anyone needing to understand and utilize the molecular mass of ethane in their work or studies. Remember that accurate calculations rely on using reliable sources for atomic masses and paying close attention to units.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not Matter
May 11, 2025
-
What Is 2 5 Cm In Mm
May 11, 2025
-
Time Is A Vector Or Scalar
May 11, 2025
-
Cardiac Action Potential Phases 0 4
May 11, 2025
-
Center Of Mass Of A Semicircle
May 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molecular Mass Of C2h6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.