What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
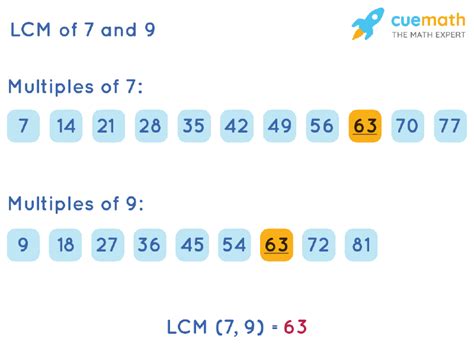
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 9 and 7? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it underpins many areas of mathematics, from simplifying fractions to scheduling events. This article will explore the LCM of 9 and 7, providing a comprehensive understanding of the concept and its applications. We'll delve into various methods for calculating the LCM, exploring the underlying mathematical principles and demonstrating the process with step-by-step examples. Beyond the specific case of 9 and 7, we’ll broaden the discussion to encompass more general strategies for determining the LCM of any two numbers.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of the numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that both numbers divide into evenly. Think of it as finding the smallest common ground between multiples of each number. For example, multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on. Multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6, hence the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 9 and 7: A Step-by-Step Guide
The numbers 9 and 7 are relatively prime, meaning they share no common factors other than 1. This simplifies the calculation of their LCM considerably. There are several methods we can use to determine the LCM of 9 and 7:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
Notice that 63 is the smallest number that appears in both lists. Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 7 is 63.
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but can become cumbersome for larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. This is a more efficient method, particularly for larger numbers.
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together. In this case, we have 3² and 7.
LCM(9, 7) = 3² x 7 = 9 x 7 = 63
This method is more systematic and works effectively for any pair of numbers.
Method 3: Using the Formula (for two numbers)
For two numbers a and b, the LCM can be calculated using the formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where GCD(a, b) represents the greatest common divisor of a and b.
Since 9 and 7 are relatively prime (their GCD is 1), the formula simplifies to:
LCM(9, 7) = (9 x 7) / 1 = 63
This method is efficient when the GCD is easily determined.
The Significance of Relatively Prime Numbers
The fact that 9 and 7 are relatively prime significantly impacts their LCM. When two numbers are relatively prime, their LCM is simply their product. This is because they share no common factors, so the smallest number that contains all their factors is simply the product of those numbers. This observation simplifies the calculation and provides a valuable insight into number theory.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond simple arithmetic exercises. It has practical applications in various fields:
Scheduling and Timing
Imagine you have two machines that cycle at different intervals. One machine completes a cycle every 9 minutes, and the other every 7 minutes. To determine when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, you need to find the LCM of 9 and 7. The LCM, 63, represents the time in minutes when both machines will be at the starting point of their cycles simultaneously. This concept is crucial in scheduling tasks, coordinating events, and optimizing processes in various industries.
Fractions and Simplifying Expressions
LCM plays a vital role in adding and subtracting fractions. To add or subtract fractions with different denominators, you need to find the LCM of the denominators. This LCM becomes the common denominator, allowing you to perform the addition or subtraction. Understanding the LCM allows for more efficient simplification of complex algebraic expressions.
Modular Arithmetic and Cryptography
The concept of LCM is fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with significant applications in cryptography. Modular arithmetic deals with remainders after division, and LCM helps in determining patterns and cycles within these systems. These patterns are crucial in the development and breaking of cryptographic algorithms.
Music Theory
Interestingly, LCM also finds its place in music theory. The concept is used in calculating the least common period for musical rhythms or patterns, helping to determine harmonic relationships between notes and rhythms.
Expanding the Concept: LCM for More Than Two Numbers
While our focus has been on the LCM of two numbers, the concept extends readily to three or more numbers. The methods of prime factorization and listing multiples can still be applied, though the process becomes more complex. For example, to find the LCM of 3, 4, and 6:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 3 = 3
- 4 = 2²
- 6 = 2 x 3
-
Finding the Highest Powers: The highest power of 2 is 2², and the highest power of 3 is 3.
-
Multiplying the Highest Powers: LCM(3, 4, 6) = 2² x 3 = 12
Therefore, the LCM of 3, 4, and 6 is 12.
Conclusion: The LCM and its Wider Implications
The seemingly simple task of finding the least common multiple of 9 and 7 opens a gateway to a richer understanding of number theory and its vast applications. From scheduling tasks to encrypting data, the LCM serves as a fundamental building block in many areas of mathematics and beyond. Understanding the various methods for calculating LCM and grasping its significance allows for a deeper appreciation of mathematical concepts and their practical relevance in the real world. The LCM of 9 and 7, 63, is more than just a number; it’s a representation of fundamental mathematical principles with far-reaching consequences.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
8 Millimeters Equals How Many Centimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Words Starting With S For Kindergarten
May 09, 2025
-
Shapes With 3 Lines Of Symmetry
May 09, 2025
-
Is 1 Cc The Same As 1 Ml
May 09, 2025
-
A Fully Loaded Slow Moving Freight Elevator
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.