What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
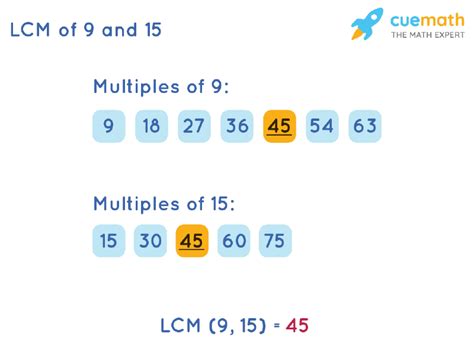
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 9 and 15? A Deep Dive into Finding LCMs
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding LCMs is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving problems involving ratios and proportions, and even in more advanced mathematical concepts. This article will delve deep into the question: What is the least common multiple of 9 and 15? We'll explore several methods for calculating the LCM, explain the underlying principles, and illustrate how this seemingly simple calculation has broader applications.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 9 and 15, let's establish a solid foundation. The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into without leaving a remainder.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM
There are several efficient methods to determine the LCM of two or more numbers. We'll explore three common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples
This method is straightforward but can become cumbersome for larger numbers. It involves listing the multiples of each number until you find the smallest multiple that's common to both.
Let's apply this to 9 and 15:
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120...
Notice that 45 appears in both lists, but 45 is not the smallest common multiple. The smallest common multiple is 45. Therefore, the LCM(9, 15) = 45.
This method is suitable for smaller numbers but becomes less practical as numbers increase in size.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all the prime factors present.
Let's find the prime factorization of 9 and 15:
- 9 = 3² (9 is 3 multiplied by 3)
- 15 = 3 x 5 (15 is 3 multiplied by 5)
The prime factors involved are 3 and 5. The highest power of 3 is 3² (or 9), and the highest power of 5 is 5¹. Therefore, the LCM is 3² x 5 = 9 x 5 = 45.
This method is generally more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method utilizes the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. We can find the GCD using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
First, let's find the GCD of 9 and 15 using prime factorization:
- 9 = 3²
- 15 = 3 x 5
The common prime factor is 3, and the lowest power is 3¹. Therefore, the GCD(9, 15) = 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(9, 15) = (|9 x 15|) / GCD(9, 15) = 135 / 3 = 45
This formula provides a concise and efficient way to calculate the LCM once the GCD is known.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has widespread applications across various fields:
1. Fraction Addition and Subtraction
Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires finding the LCM of the denominators. For example, to add 1/9 + 2/15, you would find the LCM of 9 and 15 (which is 45) and rewrite the fractions with a common denominator of 45 before adding them.
2. Scheduling and Timing Problems
LCMs are crucial in solving problems involving repeating events. For instance, if two buses leave a station at different intervals, the LCM of the intervals determines when both buses will depart at the same time again.
3. Music Theory
Musical intervals and harmonies are often related to LCMs. The frequencies of notes are expressed as ratios, and the LCM helps to determine when those ratios align, creating harmonious sounds.
4. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Engineering
Gear ratios in machinery and engineering often rely on the concept of LCM to ensure smooth operation and efficient energy transfer.
5. Computer Science and Algorithms
LCMs are used in various algorithms and data structures, such as finding the least common multiple of array elements or optimizing memory allocation.
Conclusion: The LCM of 9 and 15 is 45
Through the various methods explored – listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the GCD formula – we've conclusively determined that the least common multiple of 9 and 15 is 45. This seemingly simple calculation highlights a fundamental concept with far-reaching applications across numerous mathematical and practical fields. Understanding LCMs is a valuable skill that extends beyond basic arithmetic, providing a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving. Mastering this concept opens doors to more complex applications and a deeper understanding of numerical relationships. Remember to choose the method that suits your needs and the complexity of the numbers involved. The prime factorization method often proves most efficient for larger numbers, while the GCD formula offers a concise alternative once the GCD is known.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 5
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Common Denominator Of 50 And 40
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Are The Factors For 23
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is 2 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is 23 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
