What Are The Factors For 23
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
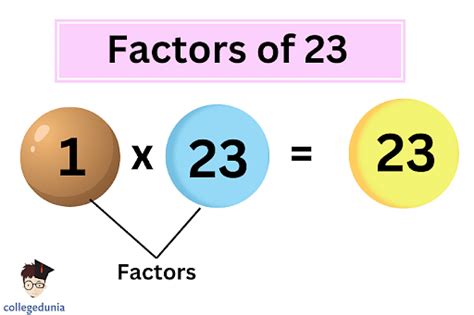
Table of Contents
What are the Factors for 23? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 23?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime numbers, and factorization. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the underlying concepts provides a solid foundation for more complex mathematical explorations.
Understanding Factors
Before we delve into the specifics of 23, let's clarify the definition of a factor. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the original number evenly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding Factors: A Systematic Approach
There are several ways to find the factors of a number. For smaller numbers, a simple trial-and-error approach works well. You systematically check each whole number, starting from 1, to see if it divides the number evenly. However, for larger numbers, this method becomes less efficient.
More advanced techniques, such as prime factorization, are crucial for larger numbers. We'll explore this further in the context of 23.
The Unique Case of 23: A Prime Number
Now, let's address the question at hand: what are the factors of 23? The answer is surprisingly simple: 1 and 23.
This simplicity stems from the fact that 23 is a prime number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself. This means it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder.
Identifying Prime Numbers: Tests and Methods
Determining whether a number is prime can be more challenging for larger numbers. Several tests exist to help identify prime numbers, including:
-
Trial Division: This involves testing for divisibility by all prime numbers less than the square root of the number. If none of these prime numbers divide the number evenly, it's prime.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is an ancient algorithm that efficiently identifies all prime numbers up to a specified limit. It works by iteratively marking the multiples of each prime number as composite (non-prime).
-
Probabilistic Primality Tests: For extremely large numbers, probabilistic tests are employed. These tests don't guarantee primality with 100% certainty but provide a high probability of correctness. The Miller-Rabin test is a commonly used example.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks in number theory. Their unique property of having only two factors makes them essential for various mathematical concepts and applications:
-
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. This is the basis for prime factorization.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are the cornerstone of modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the basis for the security of these systems.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a role in error-correcting codes, which are used to ensure reliable data transmission in various applications.
Prime Factorization: Decomposing Numbers into Primes
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number (a non-prime number) as a product of its prime factors. For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3).
This process is unique for every composite number, meaning there's only one way to represent it as a product of primes (ignoring the order of the factors). This uniqueness is a direct consequence of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Prime Factorization of 23 (Trivial Case)
Since 23 is a prime number, its prime factorization is simply 23. There are no other prime numbers that can be multiplied together to equal 23. This represents a trivial case of prime factorization.
Beyond 23: Exploring Other Numbers and their Factors
Let's briefly explore the factors of some other numbers to further solidify the concept of factorization and prime numbers:
- Factors of 10: 1, 2, 5, 10 (Prime factorization: 2 x 5)
- Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 (Prime factorization: 2³ x 3)
- Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36 (Prime factorization: 2² x 3²)
- Factors of 100: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, 100 (Prime factorization: 2² x 5²)
Notice how the prime factorization provides a concise representation of the number's factors. Every factor can be constructed by combining the prime factors in various ways.
Applications of Factorization
The ability to factor numbers has practical applications beyond pure mathematics:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator of a fraction involves factorization. This allows for simplification to its lowest terms.
-
Solving Equations: Factoring is crucial in solving polynomial equations, especially quadratic equations.
-
Computer Science: Factorization algorithms are used in various areas of computer science, including cryptography and data compression.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Factors and Prime Numbers
Understanding factors, prime numbers, and factorization is fundamental to grasping many key concepts in mathematics and computer science. While the question "What are the factors of 23?" might seem simple, its answer unlocks a deeper appreciation for the structure and properties of numbers. The seemingly simple number 23, as a prime number, holds a significant place in the mathematical world, serving as a building block for more complex mathematical structures and applications. Exploring these concepts not only sharpens mathematical skills but also illuminates the fascinating world of number theory and its practical implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Basic Building Blocks Of Matter
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Many Corners Does A Square Have
Mar 06, 2025
-
Anything That Has Mass And Occupies Space
Mar 06, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 5 And 15
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is Lv In Roman Numerals
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 23 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
