What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
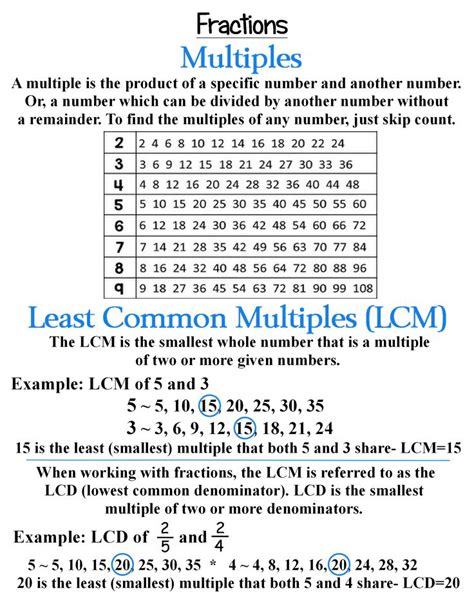
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 5 and 12? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts reveals a fascinating journey into the heart of number theory. This comprehensive guide explores the LCM of 5 and 12, delving into various methods for calculation, practical applications, and the broader significance of this concept in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the numbers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, 24, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6; therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 5 and 12: Three Proven Methods
Now, let's tackle the LCM of 5 and 12. We'll explore three common methods to arrive at the solution:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. Let's list the multiples of 5 and 12:
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, ...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120...
By comparing the lists, we find that the smallest common multiple is 60. Therefore, the LCM(5, 12) = 60.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is particularly efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Multiplying these together: 2² x 3 x 5 = 4 x 3 x 5 = 60. Therefore, the LCM(5, 12) = 60.
3. Formula Using Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two numbers are intimately related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers themselves. This relationship is expressed by the formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, let's find the GCD of 5 and 12. Since 5 is a prime number and 12 is not divisible by 5, the GCD(5, 12) = 1.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(5, 12) x GCD(5, 12) = 5 x 12 LCM(5, 12) x 1 = 60 LCM(5, 12) = 60
Why is Understanding LCM Important?
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. It has numerous practical applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two machines that complete a task in 5 and 12 hours, respectively. The LCM(5, 12) = 60 indicates that both machines will complete the task simultaneously again after 60 hours. This principle is crucial in scheduling tasks with varying cycles.
2. Fractions and Least Common Denominator (LCD)
When adding or subtracting fractions, we need a common denominator. The LCM of the denominators acts as the least common denominator (LCD), simplifying calculations and providing the most efficient solution. For example, adding 1/5 and 1/12 requires the LCD, which is the LCM(5, 12) = 60.
3. Modular Arithmetic and Cryptography
LCM plays a vital role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with significant applications in cryptography. Understanding LCM helps in solving congruence equations and analyzing cyclical patterns essential for secure communication protocols.
4. Music Theory
The LCM is used in music theory to determine the least common multiple of the durations of musical notes, facilitating the creation of harmonically consistent compositions.
5. Engineering and Construction
In engineering and construction projects, LCM can be used in tasks such as calculating the optimal timing for the repetitive operations of machines working in coordination.
Beyond the Basics: Extending the LCM Concept
The LCM concept extends to more than two numbers. For instance, to find the LCM of three numbers like 5, 12, and 15, one can utilize the prime factorization method by finding the highest power of each prime factor present in all three factorizations, and then multiplying those together. Similarly, the formula relating LCM and GCD can be extended to more than two numbers, although the calculations become more complex.
Conclusion: The Power of Simplicity
While finding the LCM of 5 and 12 might seem like a trivial exercise, it reveals a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. The various methods presented provide flexibility depending on the numbers involved, while the practical applications highlight its importance in diverse fields. Mastering LCM lays a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical explorations and problem-solving across numerous disciplines. The seemingly simple calculation of the LCM(5, 12) = 60 thus opens doors to a broader appreciation of the elegance and practicality of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between A Mixture And A Solution
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Type Of Rock Can Contain Fossils
Mar 17, 2025
-
Write The Chemical Formula For Chloric Acid
Mar 17, 2025
-
5 Letter Words With O W
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Number Of Elements In A Set Is Called The
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
