What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 11
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
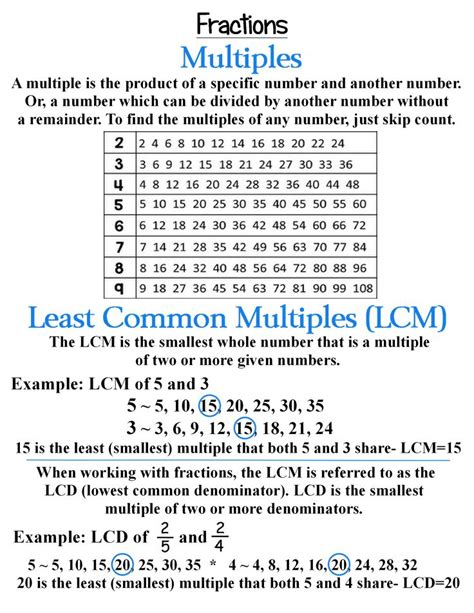
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 5 and 11? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts reveals a fascinating glimpse into number theory. This article will explore the LCM of 5 and 11, not just by providing the answer, but by delving into the methods of calculation, their applications, and the broader mathematical context. We'll also touch upon related concepts like the greatest common divisor (GCD) and their importance in various fields.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6, because 6 is the smallest positive integer divisible by both 2 and 3.
The LCM is a fundamental concept in various areas of mathematics, including:
- Fraction arithmetic: Finding the LCM of denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions.
- Modular arithmetic: LCM plays a vital role in solving congruence problems.
- Scheduling problems: Determining when events will occur simultaneously often involves finding the LCM.
Calculating the LCM of 5 and 11
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 5 and 11. Since 5 and 11 are both prime numbers (meaning they are only divisible by 1 and themselves), calculating their LCM is particularly straightforward.
Method 1: Prime Factorization
This method involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM by taking the highest power of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (since 5 is a prime number, its prime factorization is simply 5)
- Prime factorization of 11: 11 (similarly, 11 is a prime number)
Because 5 and 11 are both prime and distinct, their LCM is simply their product.
Therefore, the LCM of 5 and 11 is 5 x 11 = 55.
Method 2: Listing Multiples
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. While effective for smaller numbers, it becomes less practical for larger numbers.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60...
- Multiples of 11: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66...
The smallest common multiple in both lists is 55.
Therefore, the LCM of 5 and 11 is 55.
The Relationship Between LCM and GCD
The least common multiple (LCM) and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are intimately related. The GCD of two integers is the largest integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. For example, the GCD of 12 and 18 is 6.
The relationship between LCM and GCD is expressed by the following formula:
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
where 'a' and 'b' are the two integers.
Let's apply this to our example:
- a = 5
- b = 11
Since 5 and 11 are both prime numbers and have no common factors other than 1, their GCD is 1.
Using the formula:
LCM(5, 11) * GCD(5, 11) = 5 * 11
LCM(5, 11) * 1 = 55
LCM(5, 11) = 55
This confirms our previous calculation.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of the least common multiple finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses depart from the same station. One bus departs every 5 minutes, and the other every 11 minutes. The LCM (55 minutes) tells us when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
-
Task Synchronization: Consider two machines in a factory completing different tasks. One takes 5 minutes per cycle and the other takes 11 minutes. The LCM helps determine when both machines will be at the beginning of their cycles at the same time.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanical engineering, the LCM can be used to calculate optimal gear ratios to synchronize the rotations of different shafts.
-
Music and Rhythm: In music composition and theory, the LCM is used to find the least common denominator of rhythmic patterns, ensuring harmonious combinations of musical phrases.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. To find the LCM of multiple numbers, you can use the prime factorization method. Find the prime factorization of each number, and then take the highest power of each prime factor that appears in any of the factorizations. Multiply these highest powers together to obtain the LCM.
For instance, to find the LCM of 3, 5, and 11:
- Prime factorization of 3: 3
- Prime factorization of 5: 5
- Prime factorization of 11: 11
The LCM would be 3 x 5 x 11 = 165.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper, several advanced concepts are related to LCM and GCD:
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This efficient algorithm is used to compute the GCD of two integers. Knowing the GCD allows you to easily calculate the LCM using the formula mentioned earlier.
-
Modular Arithmetic and Congruences: The LCM is crucial in solving problems involving modular arithmetic and congruences, which have significant applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concepts of LCM and GCD extend to more abstract algebraic structures, such as rings and ideals.
-
Number Theory Theorems: Many theorems in number theory are related to LCM and GCD, providing a deeper understanding of the properties of integers.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding LCM
The least common multiple, while seemingly a simple arithmetic concept, has significant implications across various fields. Understanding its calculation methods, relationship with the GCD, and its applications in real-world problems is essential for anyone interested in mathematics, computer science, engineering, or music. The LCM of 5 and 11, being 55, serves as a clear and simple example to illustrate these profound mathematical principles. This article has hopefully provided a comprehensive overview of this fundamental concept, inspiring further exploration and a deeper appreciation of the beauty and utility of number theory. The seemingly mundane task of finding the LCM of 5 and 11 opens the door to a vast and fascinating world of mathematical exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Stereoisomers Are Possible For
May 09, 2025
-
14 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Si Unit For Distance
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does H Have
May 09, 2025
-
18 Inches Equals How Many Feet
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 5 And 11 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.