What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
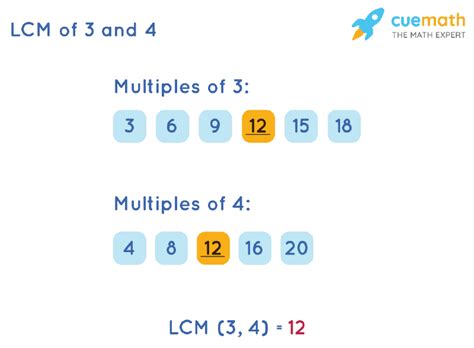
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 3 and 4? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is the least common multiple of 3 and 4?" opens a door to a fascinating realm within mathematics: number theory. While the answer itself is easily calculated, exploring the underlying concepts reveals the beauty and elegance of mathematical relationships. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader context of least common multiples, their applications, and related mathematical ideas.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors. This concept is fundamental in various mathematical fields and has practical applications in everyday life, often without us even realizing it.
For example, imagine you have two gears with 3 and 4 teeth respectively. The LCM helps determine when the gears will return to their starting positions simultaneously. This seemingly simple example highlights the practical use of LCM in areas like engineering and mechanics.
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 4
Let's tackle the initial question: What is the least common multiple of 3 and 4? We can use several methods to determine this:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method involves listing the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24…
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28…
As we can see, the smallest number that appears in both lists is 12. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We find the prime factorization of each number and then construct the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3¹
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor: 2² and 3¹. Multiplying these together gives us 2² * 3¹ = 4 * 3 = 12.
Method 3: Using the Formula
For two integers 'a' and 'b', the LCM can be calculated using the formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a * b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where GCD represents the greatest common divisor.
The greatest common divisor (GCD) of 3 and 4 is 1 (as they share no common factors other than 1). Therefore:
LCM(3, 4) = (|3 * 4|) / GCD(3, 4) = 12 / 1 = 12
This method provides a more structured approach, particularly beneficial for larger numbers where prime factorization might be more complex.
Expanding the Concept: LCM and GCD Relationships
The relationship between the LCM and GCD is fundamental. For any two positive integers 'a' and 'b':
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
This identity provides a powerful tool for calculating either the LCM or GCD if the other is known. It highlights the interconnectedness of these two important concepts in number theory.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The LCM finds its applications in various fields:
- Scheduling: Determining when events will coincide, like the return to the starting position of gears (as mentioned earlier), or scheduling recurring tasks that need to be completed simultaneously.
- Fraction arithmetic: Finding the least common denominator (LCD) when adding or subtracting fractions. The LCD is simply the LCM of the denominators.
- Music theory: Determining the frequency at which musical notes with different frequencies will sound harmonious.
- Engineering: In tasks involving gears, pulleys, or other rotating mechanisms, understanding LCM helps design systems that operate efficiently and synchronously.
- Construction: Matching the lengths of materials to ensure seamless integration and minimize waste.
Beyond the Basics: Extending LCM to Multiple Numbers
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. We can calculate the LCM of three or more integers using similar methods. For example, to find the LCM of 3, 4, and 6:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 3 = 3¹
- 4 = 2²
- 6 = 2¹ * 3¹
-
Combining Prime Factors: Take the highest power of each prime factor: 2² and 3¹.
-
Calculating LCM: 2² * 3¹ = 4 * 3 = 12
Advanced Concepts Related to LCM
The study of LCM leads to more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Modular Arithmetic: The LCM plays a crucial role in understanding modular arithmetic, which deals with remainders after division. This has significant applications in cryptography and computer science.
- Diophantine Equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions to algebraic equations, and the LCM often features in solving certain types of Diophantine equations.
- Abstract Algebra: The concept of LCM generalizes to more abstract algebraic structures, contributing to the broader understanding of mathematical systems.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding LCM
The seemingly straightforward question of finding the LCM of 3 and 4 has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of number theory. While the answer—12—is simple, the underlying concepts and applications of LCM are extensive and crucial in various fields. Understanding LCM is not only important for solving mathematical problems but also for appreciating the elegant interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their practical relevance in the real world. From scheduling tasks to designing machinery, the LCM provides a framework for understanding and optimizing numerous processes. This exploration hopefully highlights the value of delving deeper into mathematical concepts, revealing their inherent beauty and practical utility.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Shapes With 3 Lines Of Symmetry
May 09, 2025
-
Is 1 Cc The Same As 1 Ml
May 09, 2025
-
A Fully Loaded Slow Moving Freight Elevator
May 09, 2025
-
Is Potato A Root Or Stem Vegetable
May 09, 2025
-
Which Element Has The Least Metallic Character
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.