What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 25
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
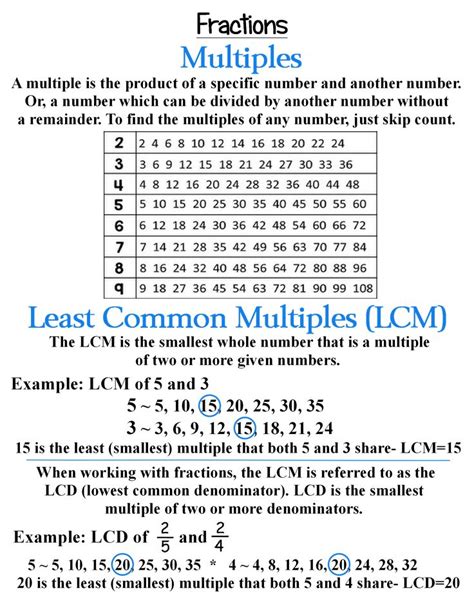
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 10 and 25? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts reveals its importance in various mathematical fields and practical applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calculating the LCM of 10 and 25, exploring different methods and expanding on the broader significance of LCMs in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCMs)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's a fundamental concept in number theory, with applications spanning diverse areas, from scheduling to music theory. Think of it as the smallest common "meeting point" of multiples of the given numbers.
For example, let's consider the multiples of 4 and 6:
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36... Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36...
The common multiples of 4 and 6 are 12, 24, 36, and so on. The smallest of these is 12, therefore, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Calculating the LCM of 10 and 25: Three Proven Methods
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 10 and 25. We can employ several methods:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method involves listing the multiples of both numbers until we find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70... Multiples of 25: 25, 50, 75, 100...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 50. Therefore, the LCM(10, 25) = 50. This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We start by finding the prime factorization of each number:
- 10 = 2 × 5
- 25 = 5 × 5 = 5²
Next, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The highest power of 2 is 2¹
- The highest power of 5 is 5²
Finally, we multiply these highest powers together:
LCM(10, 25) = 2¹ × 5² = 2 × 25 = 50
This method is generally more efficient and less prone to errors than the listing method, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula connecting LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
First, we find the GCD of 10 and 25 using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization. Let's use prime factorization:
- 10 = 2 × 5
- 25 = 5 × 5
The common prime factor is 5, and its lowest power is 5¹. Therefore, GCD(10, 25) = 5.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(10, 25) = (10 × 25) / GCD(10, 25) = (250) / 5 = 50
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization might be more time-consuming.
The Significance of LCMs in Various Applications
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Its applications are surprisingly diverse:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two machines that perform a specific task. Machine A completes the task every 10 minutes, and Machine B every 25 minutes. If both machines start simultaneously, when will they complete the task at the same time again? The answer is the LCM(10, 25) = 50 minutes. This principle is crucial in scheduling repetitive tasks or events.
2. Music Theory
LCM plays a role in determining rhythmic patterns and harmonies in music. The LCM helps to find the smallest time interval at which different rhythmic patterns repeat simultaneously.
3. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical systems with gears, the LCM determines the smallest number of rotations required for the gears to return to their initial relative positions.
4. Construction and Architecture
LCM finds application in laying out repeating patterns of tiles or bricks in construction projects. Ensuring uniformity and minimizing waste involves calculating the LCM of the dimensions of the construction materials.
5. Computer Science and Algorithms
LCM appears in various algorithms related to modular arithmetic, cryptography, and synchronization in concurrent programming.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Advanced Concepts
The LCM forms a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Here are a few examples:
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM is crucial in solving congruence equations in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with widespread applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concept of LCM can be generalized to more abstract algebraic structures, such as rings and ideals.
-
Number Theory Research: LCM continues to be a subject of active research in number theory, with ongoing investigations into its properties and relationships with other mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: The Power of a Simple Concept
While finding the LCM of 10 and 25 might seem trivial, the underlying concept holds significant weight across diverse fields. The ability to efficiently calculate LCMs and understand their implications is invaluable in many practical applications and further mathematical explorations. Whether you're scheduling tasks, designing machines, or delving into abstract algebra, the LCM remains a fundamental tool in the mathematician's and engineer's toolbox. The different methods presented here equip you with the skills to tackle LCM calculations effectively, regardless of the complexity of the numbers involved. Mastering these methods not only enhances your mathematical skills but also opens doors to a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Blood A Mixture Or Compound
Mar 19, 2025
-
Composition Of Functions Examples With Answers
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Neon A Metal Or Nonmetal
Mar 19, 2025
-
Write 63 As The Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 19, 2025
-
Where Does Dark Reaction Take Place
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 25 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
