What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 4 min read
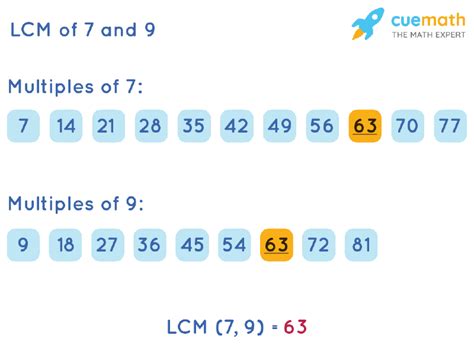
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 9 and 7? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly useful in simplifying fractions, solving problems involving ratios and proportions, and understanding rhythmic patterns in music. This article will explore the LCM of 9 and 7, providing multiple methods to calculate it and explaining the underlying mathematical principles. We'll also delve into the broader context of LCMs, showcasing their practical applications beyond the simple calculation.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before jumping into the specific calculation of the LCM of 9 and 7, let's solidify our understanding of the concept. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple is 6.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 9 and 7
There are several ways to find the LCM of 9 and 7. Let's examine the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers like 9 and 7. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72... Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
Notice that 63 appears in both lists. Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 7 is 63.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
LCM(9, 7) = 3² x 7 = 9 x 7 = 63
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) of two numbers are related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. This relationship can be expressed as:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, let's find the GCD of 9 and 7 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide 9 by 7: 9 = 1 x 7 + 2
- Divide 7 by 2: 7 = 3 x 2 + 1
- Divide 2 by 1: 2 = 2 x 1 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 1, so the GCD(9, 7) = 1.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(9, 7) = (9 x 7) / GCD(9, 7) = 63 / 1 = 63
Why is understanding LCM important?
The seemingly simple calculation of the LCM has far-reaching implications in various fields:
1. Fraction Simplification
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. By converting the fractions to equivalent fractions with a common denominator (the LCM of the denominators), we can easily perform the addition or subtraction.
For example, to add 1/9 + 1/7, we find the LCM of 9 and 7, which is 63. Then we rewrite the fractions:
1/9 = 7/63 1/7 = 9/63
1/9 + 1/7 = 7/63 + 9/63 = 16/63
2. Ratio and Proportion Problems
LCMs are instrumental in solving problems involving ratios and proportions. For instance, consider a recipe that calls for a ratio of 9 parts flour to 7 parts water. If you want to increase the recipe proportionally, finding the LCM helps determine the smallest whole number amounts of flour and water to maintain the ratio.
3. Cyclic Events and Scheduling
LCMs are essential in determining when cyclic events coincide. For example, if two machines operate on different cycles (one every 9 hours, the other every 7 hours), finding the LCM helps determine when both machines will be at the beginning of their cycle simultaneously. This is crucial in scheduling maintenance or coordinating tasks.
4. Music Theory
In music, rhythms are often expressed as fractions. The LCM is vital for determining the least common denominator when working with different rhythmic values, facilitating the creation of complex and synchronized musical patterns.
5. Modular Arithmetic
LCM plays a significant role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography and computer science.
Conclusion
The LCM of 9 and 7, calculated using various methods, is 63. While seemingly a simple calculation, understanding LCMs is essential for solving a wide range of mathematical problems across various disciplines. From simplifying fractions to coordinating complex schedules, the concept of LCM provides a powerful tool for problem-solving and analysis. Mastering LCM calculations, therefore, is not just a mathematical skill but a valuable asset for practical applications in numerous fields. The versatility and importance of LCM highlight its enduring relevance in mathematics and its applications beyond the classroom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
