What Is The Lcm Of 4 And 18
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
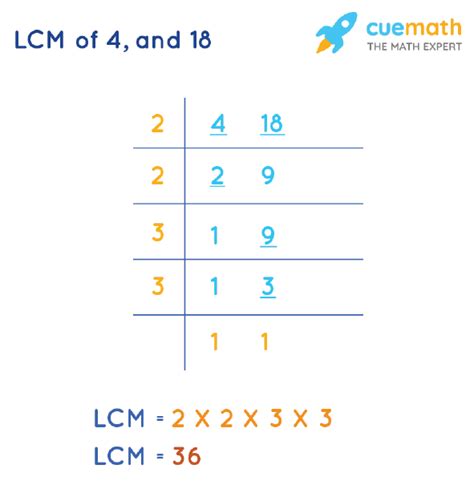
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 4 and 18? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in arithmetic and algebra. It's a skill used frequently in various fields, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. This article will explore the LCM of 4 and 18 in detail, providing multiple methods to calculate it and highlighting the broader implications of understanding least common multiples. We'll also delve into the practical applications of LCMs in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 4 and 18, let's establish a firm understanding of what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly without leaving a remainder.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, ... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, ... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple, therefore, is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. Let's apply it to find the LCM of 4 and 18:
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40...
- Multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54, 72...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in both lists is 36. Therefore, the LCM of 4 and 18 is 36.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the mathematical relationship between the numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves.
- Prime Factorization of 4: 4 = 2 x 2 = 2²
- Prime Factorization of 18: 18 = 2 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3²
Next, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9
To find the LCM, we multiply these highest powers together: 4 x 9 = 36. Therefore, the LCM of 4 and 18 is 36.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) of two numbers are related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. This means:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
We can use this relationship to find the LCM if we know the GCD.
-
Find the GCD of 4 and 18: The divisors of 4 are 1, 2, and 4. The divisors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The greatest common divisor is 2.
-
Apply the formula: LCM(4, 18) x GCD(4, 18) = 4 x 18 LCM(4, 18) x 2 = 72 LCM(4, 18) = 72 / 2 = 36
Therefore, using this method, we again find the LCM of 4 and 18 to be 36.
Comparing the Methods
Each method has its advantages:
- Listing Multiples: Simple and intuitive for small numbers, but becomes cumbersome for larger numbers.
- Prime Factorization: Efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of number relationships.
- Using GCD: Elegant and efficient if the GCD is already known or easily calculated. It leverages the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD.
Real-World Applications of LCM
Understanding LCMs isn't just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses leave a station at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when they will depart simultaneously again. For example, if one bus leaves every 4 hours and another every 18 hours, they will depart together again after 36 hours.
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions is equivalent to finding the LCM of the denominators.
-
Project Management: If different tasks in a project have varying cycle times, the LCM helps determine the earliest point at which all tasks can be completed simultaneously.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanical engineering, the LCM is used in calculating gear ratios and determining the synchronization of rotating components.
-
Music: The LCM plays a role in understanding musical intervals and harmonies, particularly in determining when different musical phrases will coincide rhythmically.
-
Construction: Determining the appropriate lengths of materials for repetitive patterns or designs often involves using the LCM to ensure consistent spacing and alignment.
Beyond Two Numbers: Finding the LCM of Multiple Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, you simply include all prime factors raised to their highest powers. For the listing method, it becomes progressively more challenging, highlighting the efficiency of prime factorization for larger sets of numbers.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
The ability to calculate the least common multiple is a crucial skill with far-reaching applications. Whether you are solving simple arithmetic problems or tackling complex engineering challenges, understanding LCMs provides a valuable tool for problem-solving. This article has demonstrated multiple effective methods for calculating the LCM, specifically focusing on the LCM of 4 and 18, emphasizing the importance of understanding the underlying mathematical principles. By mastering these methods, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for various mathematical and real-world applications. Remember to choose the method best suited to the specific problem at hand, balancing simplicity and efficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does An Amoeba Obtain Food
Mar 22, 2025
-
Square Root Of 200 In Simplest Radical Form
Mar 22, 2025
-
Why Are Metals Good Conductors Of Electric Current
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Atp Molecules Are Produced In Electron Transport Chain
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Makes Metal A Good Conductor
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 4 And 18 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
