What Is The Lcm Of 4 And 14
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 4 min read
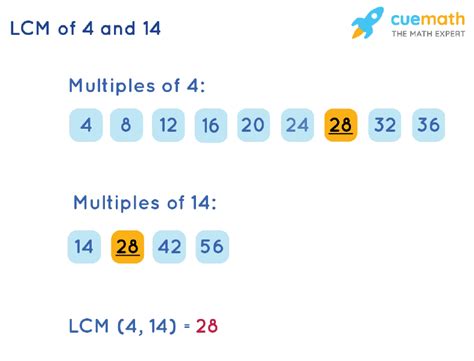
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 4 and 14? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly crucial in areas like algebra, number theory, and even real-world applications involving scheduling and rhythmic patterns. This article will comprehensively explore how to find the LCM of 4 and 14, covering various methods, explaining the underlying principles, and demonstrating its practical significance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before diving into the specific calculation for 4 and 14, let's solidify our understanding of LCM. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's essentially the smallest number that contains all the prime factors of the given numbers.
Key characteristics of LCM:
- Positive Integer: The LCM is always a positive integer.
- Divisibility: It's divisible by all the numbers in the set.
- Smallest: It's the smallest positive integer that satisfies the divisibility condition.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers, is to list the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. Let's apply this to 4 and 14:
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36... Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70...
Notice that 28 appears in both lists. Since it's the smallest number common to both sequences, the LCM of 4 and 14 is 28.
This method is intuitive but becomes less efficient with larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method offers a more systematic and efficient approach, particularly for larger numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors. The LCM is then constructed by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations.
Let's factorize 4 and 14:
- 4 = 2² (2 x 2)
- 14 = 2 x 7
The prime factors involved are 2 and 7. The highest power of 2 is 2², and the highest power of 7 is 7¹. Therefore:
LCM(4, 14) = 2² x 7 = 4 x 7 = 28
This method is more robust and easily scalable to handle larger numbers or multiple numbers.
Method 3: Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are closely related. They satisfy the following relationship:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two integers.
First, let's find the GCD of 4 and 14 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide 14 by 4: 14 = 3 x 4 + 2
- Divide 4 by the remainder 2: 4 = 2 x 2 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 2, so GCD(4, 14) = 2.
Now, using the relationship:
LCM(4, 14) = (4 x 14) / GCD(4, 14) = (56) / 2 = 28
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization can be computationally intensive. The Euclidean algorithm efficiently computes the GCD.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond theoretical mathematics; it finds practical applications in various scenarios:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses depart from the same station, one every 4 hours and the other every 14 hours. The LCM (28 hours) indicates when both buses will depart simultaneously again. This is vital for scheduling and optimizing transportation systems.
-
Rhythmic Patterns: In music, LCM helps synchronize rhythmic patterns. If one instrument has a 4-beat pattern and another has a 14-beat pattern, the LCM (28 beats) determines when both patterns will align perfectly.
-
Project Management: In project management, tasks might have different cycle times. LCM helps determine when multiple tasks will be completed simultaneously, aiding in efficient resource allocation.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
While we've focused on finding the LCM of two numbers, the concept extends to more than two numbers. The principles remain the same: find the prime factorization of each number, and the LCM will be the product of the highest powers of all prime factors involved.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Calculating the least common multiple is a fundamental mathematical skill with broad applications. We've explored three efficient methods – listing multiples, prime factorization, and the GCD method – each with its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these methods allows you to choose the most appropriate approach based on the numbers involved. The LCM's practical importance in scheduling, rhythmic patterns, and project management underscores its significance beyond theoretical mathematics, highlighting its value in solving real-world problems. By mastering LCM calculations, you equip yourself with a valuable tool applicable in various fields. Remember that understanding the underlying principles—divisibility, prime factorization, and the relationship between LCM and GCD—is key to mastering this essential concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 4 And 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
