What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
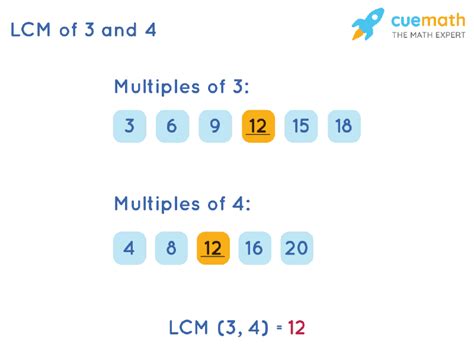
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 3 and 4? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields. This article will comprehensively explore the LCM of 3 and 4, demonstrating multiple methods to calculate it and explaining the underlying principles. We'll also delve into the broader significance of LCMs and their practical uses.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific case of 3 and 4, let's establish a clear understanding of what an LCM is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that both (or all) numbers divide into evenly.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18... The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 4: Three Effective Methods
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 3 and 4. We can employ several methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, ...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, ...
By comparing the two lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 12. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the concept. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Multiply these highest powers together: 4 x 3 = 12. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Method 3: Using the Formula (For Two Numbers)
For two numbers, 'a' and 'b', there's a handy formula relating the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD):
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 3 and 4. The GCD is the greatest number that divides both 3 and 4 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(3, 4) = 1 (because 1 is the only common divisor).
Now, we apply the formula:
LCM(3, 4) = (|3 x 4|) / GCD(3, 4) = 12 / 1 = 12
Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
The Significance of LCMs in Mathematics and Beyond
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple mathematical exercises. It plays a crucial role in various areas:
1. Fractions: Finding Common Denominators
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, we need to find a common denominator – this is typically the LCM of the denominators. For instance, to add 1/3 and 1/4, we find the LCM of 3 and 4 (which is 12), then convert the fractions:
1/3 = 4/12 1/4 = 3/12
1/3 + 1/4 = 4/12 + 3/12 = 7/12
2. Scheduling and Timing Problems
LCMs are invaluable in solving problems related to scheduling and cyclical events. Imagine two machines operating on different cycles: one every 3 hours and the other every 4 hours. To find when they'll operate simultaneously again, we calculate the LCM of 3 and 4, which is 12. They'll both operate at the same time again after 12 hours.
3. Number Theory and Abstract Algebra
LCMs are fundamental concepts in number theory and abstract algebra. They are used in various theorems and proofs related to divisibility, modular arithmetic, and other advanced topics.
4. Real-world Applications
Beyond theoretical mathematics, LCM finds applications in practical scenarios. Examples include:
- Construction: Coordinating work schedules for different teams.
- Manufacturing: Optimizing production cycles for different machines.
- Music: Determining the least common multiple of rhythmic patterns in musical compositions.
- Computer Science: Algorithm design and optimization problems often involve LCM calculations.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The principles of LCM extend to more than two numbers. To find the LCM of multiple numbers, similar methods can be applied:
- Listing Multiples: List the multiples of each number and find the smallest common multiple. This becomes less practical with a larger number of integers.
- Prime Factorization: This remains the most efficient approach. Find the prime factorization of each number, take the highest power of each prime factor present, and multiply them together.
- Formula (For More than Two Numbers): There is no single straightforward formula for more than two numbers. It often requires iterative application of the two-number formula or a more sophisticated algorithm.
Conclusion: The Power of Understanding LCMs
Understanding least common multiples is crucial for many mathematical operations and real-world applications. We've explored different methods for calculating the LCM of 3 and 4, highlighting the efficiency of prime factorization. Moreover, we've discussed the significance of LCMs in fractions, scheduling problems, and advanced mathematical fields. Mastering the concept of LCM enhances mathematical problem-solving abilities and provides a deeper understanding of number theory and its applications. The seemingly simple problem of finding the LCM of 3 and 4 serves as a gateway to a wider world of mathematical concepts and practical applications. Remember, consistent practice and exploration will solidify your grasp of this fundamental mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sodium Bicarbonate And Hydrochloric Acid Balanced Equation
May 12, 2025
-
Divides Earth Into Eastern And Western Hemispheres
May 12, 2025
-
6 Is What Percent Of 45
May 12, 2025
-
What Is Difference Between Would And Could
May 12, 2025
-
The Origin Of A Muscle Is
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.