What Is The Lcm Of 18 And 9
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
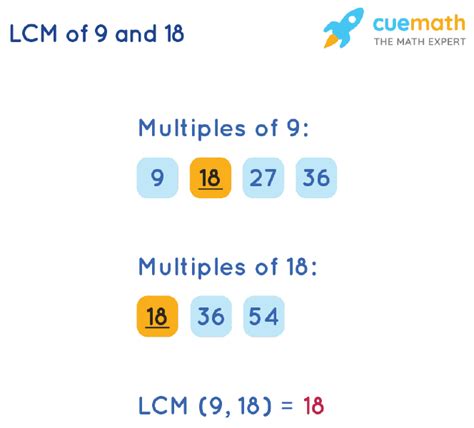
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 18 and 9? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly crucial in areas like fractions, algebra, and even music theory. This article will not only answer the question "What is the LCM of 18 and 9?" but also provide a comprehensive understanding of LCMs, exploring various methods for calculating them and illustrating their practical applications. We'll delve into the theory behind LCMs, examine different approaches to finding them, and explore why understanding LCMs is essential in various mathematical contexts.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCMs)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 18 and 9, let's establish a solid understanding of what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly without leaving a remainder.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... Notice that 6 and 12 are common multiples of both 2 and 3. However, the least common multiple is 6 because it's the smallest positive integer that appears in both lists.
Key Characteristics of LCMs:
- Positive Integer: The LCM is always a positive whole number.
- Smallest Common Multiple: It's the smallest number that satisfies the condition of being a multiple of all the given numbers.
- Multiple of all Input Numbers: Every number in the input set divides evenly into the LCM.
Methods for Finding the LCM
There are several effective methods for determining the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially useful for smaller numbers. You list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
Example: Finding the LCM of 4 and 6.
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20... Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 12. Therefore, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
This method becomes less efficient as the numbers get larger.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient and systematic method, particularly useful for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
Steps:
- Find the prime factorization of each number: Express each number as a product of its prime factors.
- Identify the highest power of each prime factor: For each prime factor that appears in any of the factorizations, choose the highest power.
- Multiply the highest powers together: The product of these highest powers is the LCM.
Example: Finding the LCM of 12 and 18.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² × 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 × 3²
The highest power of 2 is 2² (from 12). The highest power of 3 is 3² (from 18).
LCM(12, 18) = 2² × 3² = 4 × 9 = 36
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. That is:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
Therefore, if you know the GCD, you can easily calculate the LCM. Finding the GCD can be done using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
Example: Finding the LCM of 12 and 18 using the GCD method.
- Find the GCD of 12 and 18: Using prime factorization, the GCD(12, 18) = 6 (since 12 = 2² × 3 and 18 = 2 × 3²).
- Apply the formula: LCM(12, 18) × GCD(12, 18) = 12 × 18 LCM(12, 18) × 6 = 216 LCM(12, 18) = 216 / 6 = 36
This method is efficient because finding the GCD is often relatively quick, even for larger numbers.
Solving the Problem: LCM of 18 and 9
Now, let's apply these methods to find the LCM of 18 and 9.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36... Multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54...
The smallest common multiple is 18. Therefore, LCM(18, 9) = 18.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 × 3²
The highest power of 2 is 2¹ (from 18). The highest power of 3 is 3² (from both 9 and 18).
LCM(18, 9) = 2¹ × 3² = 2 × 9 = 18
Method 3: GCD Method
- Find the GCD of 18 and 9: The GCD(18, 9) = 9.
- Apply the formula: LCM(18, 9) × GCD(18, 9) = 18 × 9 LCM(18, 9) × 9 = 162 LCM(18, 9) = 162 / 9 = 18
All three methods consistently show that the LCM of 18 and 9 is 18.
Applications of LCMs
Understanding LCMs has practical applications across various mathematical fields and real-world scenarios:
- Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires finding the LCM of the denominators.
- Scheduling and Time Problems: Determining when events will occur simultaneously (e.g., buses arriving at a stop, machines completing cycles) often involves finding the LCM.
- Music Theory: The LCM is used in calculating rhythmic patterns and finding the least common denominator for musical phrases.
- Modular Arithmetic: LCM plays a vital role in solving congruence problems in number theory.
- Algebra and Number Theory: LCMs are utilized in various theorems and concepts within higher-level mathematics.
Conclusion
Finding the least common multiple is a fundamental mathematical skill with broad applications. This article thoroughly explained the concept of LCMs, explored different methods for calculating them, and solved the specific problem of finding the LCM of 18 and 9. Understanding LCMs is not only crucial for success in various mathematical contexts but also provides a valuable tool for solving practical real-world problems. Whether you're working with fractions, scheduling events, or exploring more advanced mathematical concepts, a strong grasp of LCMs will undoubtedly enhance your mathematical abilities. Remember to choose the method that best suits the numbers you are working with – the listing method for smaller numbers and prime factorization or the GCD method for larger numbers for efficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Multiples Of 7 Up To 100
Mar 16, 2025
-
Graphite Is Not Used In Ornaments
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Common Factor Of 35
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Element Has Four Valence Electrons
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Do You Make A Ratio Into A Percent
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 18 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
