What Is The Lcm Of 14 And 6
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
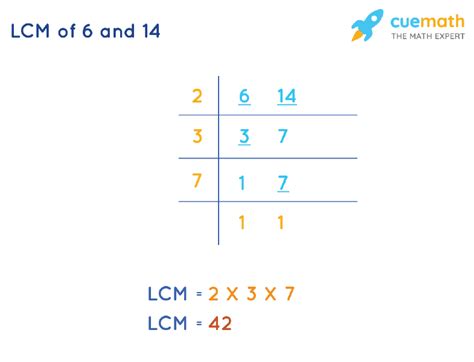
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 14 and 6? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but understanding the concept and its various methods of calculation opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will explore the LCM of 14 and 6, delving into the underlying principles, different approaches to solving the problem, and showcasing its real-world applications. We'll go beyond a simple answer and equip you with a thorough understanding of LCMs.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before diving into the specifics of finding the LCM of 14 and 6, let's establish a firm grasp of what LCM actually means. The least common multiple of two or more numbers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21...
The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM
Several methods can be used to determine the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's examine the most common and effective approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. You simply list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest multiple common to both.
Let's apply this to find the LCM of 14 and 6:
- Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70, 84, 98, 112, 126...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78, 84, 90...
Notice that 42 and 84 appear in both lists. However, 42 is the smallest number present in both lists, making it the LCM of 14 and 6.
While this method is simple for smaller numbers, it becomes less efficient as the numbers increase in size.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a more systematic approach. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
Let's find the LCM of 14 and 6 using prime factorization:
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
The prime factors present are 2, 3, and 7. We take the highest power of each prime factor:
- Highest power of 2: 2¹ = 2
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 7: 7¹ = 7
Multiplying these together: 2 x 3 x 7 = 42
Therefore, the LCM of 14 and 6 is 42. This method is significantly more efficient than listing multiples for larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method uses the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula states:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
where:
- a and b are the two numbers.
- GCD(a, b) is the greatest common divisor of a and b.
First, we need to find the GCD of 14 and 6. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (14) by the smaller number (6): 14 ÷ 6 = 2 with a remainder of 2.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (6) and the smaller number with the remainder (2): 6 ÷ 2 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
- The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 2.
Now, we can apply the formula:
LCM(14, 6) = (14 x 6) / 2 = 84 / 2 = 42
This method is also efficient and provides an alternative approach to finding the LCM.
Real-World Applications of LCM
Understanding LCMs extends beyond theoretical mathematics; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine you have two events that repeat at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when both events will coincide. For example, if one event occurs every 14 days and another every 6 days, the LCM (42) tells you that both events will happen on the same day every 42 days.
-
Fractions: Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. The LCM of the denominators becomes the common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
-
Music: In music theory, LCM is used to calculate the least common multiple of the note values in a rhythmic pattern, helping to determine the overall length and structure of the musical phrase.
-
Construction: When working with materials that have different lengths, knowing the LCM helps determine the optimal size for cutting or joining them efficiently, minimizing waste.
-
Manufacturing: In a factory assembly line, if different machines have varying cycle times, the LCM can help synchronize their operations to optimize production efficiency.
Conclusion: The LCM of 14 and 6 is 42
Through various methods – listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the GCD – we've definitively established that the least common multiple of 14 and 6 is 42. Understanding the concept of LCM and mastering its calculation methods empowers you to solve more complex problems across diverse fields, showcasing the practical utility of this fundamental mathematical principle. Remember, the best method to use depends on the complexity of the numbers involved. For smaller numbers, listing multiples might suffice, while prime factorization is more efficient for larger numbers. The GCD method provides a powerful alternative, especially when you already know the GCD. Now you're well-equipped to tackle LCM problems with confidence!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 14 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
