What Is The Lcm Of 11 And 5
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 4 min read
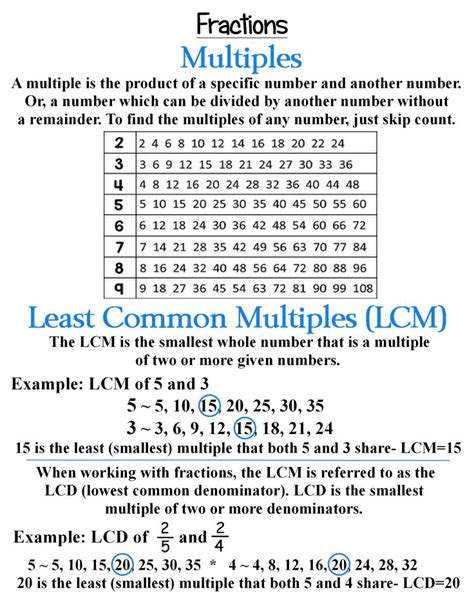
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 11 and 5? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but understanding the underlying concepts and exploring different methods to solve it opens doors to a deeper appreciation of number theory and its applications. This article will not only answer the question "What is the LCM of 11 and 5?" but also delve into the broader context of LCMs, exploring various methods for calculation, practical applications, and the connection to the greatest common divisor (GCD).
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. This concept is fundamental in various areas, from simplifying fractions to solving problems involving cyclical events.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18...
The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM(2, 3) = 6.
Finding the LCM of 11 and 5
Now, let's address the question at hand: What is the LCM of 11 and 5?
Since 11 and 5 are both prime numbers (meaning they are only divisible by 1 and themselves), finding their LCM is particularly straightforward. Let's explore two common methods:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method is to list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 11: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, ...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60...
As we can see, the smallest common multiple of 11 and 5 is 55. Therefore, LCM(11, 5) = 55.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is particularly useful for larger numbers or when dealing with more than two numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 11: 11 (11 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
Since 11 and 5 are both prime and distinct, their LCM is simply their product: 11 * 5 = 55. Therefore, LCM(11, 5) = 55.
The Relationship between LCM and GCD
The greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. The LCM and GCD are closely related through the following formula:
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two integers.
Let's apply this to 11 and 5:
- Since 11 and 5 are prime numbers and have no common factors other than 1, their GCD is 1.
- GCD(11, 5) = 1
- Therefore, LCM(11, 5) * GCD(11, 5) = 11 * 5
- LCM(11, 5) * 1 = 55
- LCM(11, 5) = 55
This confirms our earlier findings using the other methods.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has numerous applications in various fields:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions involves finding the LCM of the denominators.
-
Scheduling Problems: Determining when two cyclical events will coincide (e.g., two buses arriving at the same stop simultaneously) involves finding the LCM of their cycles.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanical engineering, LCM is used to calculate gear ratios and determine the optimal speeds and rotations of gears.
-
Music Theory: LCM is used in music to determine the least common multiple of the different rhythmic durations, enabling the creation of harmonious musical phrases.
-
Computer Science: LCM finds its use in algorithms related to scheduling and synchronization in multi-processing systems.
Advanced Techniques for Finding LCM
While the methods described above are sufficient for smaller numbers, more efficient algorithms exist for larger numbers, particularly when dealing with many numbers simultaneously. These include:
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This algorithm is highly efficient for finding the GCD of two numbers, and since we know the relationship between LCM and GCD, we can easily calculate the LCM afterward.
-
Using the Prime Factorization Theorem: For larger numbers, using the prime factorization and efficiently finding the highest powers of each prime factor present provides a systematic and faster approach.
Conclusion: The Simplicity and Significance of LCM(11, 5)
The seemingly simple question, "What is the LCM of 11 and 5?", leads us to explore the rich world of number theory and the practical applications of the least common multiple. While the answer, 55, is easily obtained through various methods, the underlying concepts and their broader applications highlight the significance of this fundamental mathematical concept in diverse fields. Understanding LCM extends beyond simple arithmetic; it’s a key component in solving complex problems across numerous disciplines, underscoring its importance in mathematics and beyond. The exploration of LCM, even in its simplest forms, provides a valuable foundation for further mathematical studies and problem-solving skills. This deep dive into the LCM of 11 and 5 showcases the beauty and power of seemingly basic mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Boiling Point Of Water Kelvin Scale
Mar 21, 2025
-
150 Cm Is How Many Inches
Mar 21, 2025
-
120 Sq Mt To Sq Ft
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 19 25 As A Percent
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Mm Is 7 Cm
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 11 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
