What Is The Lcm For 6 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
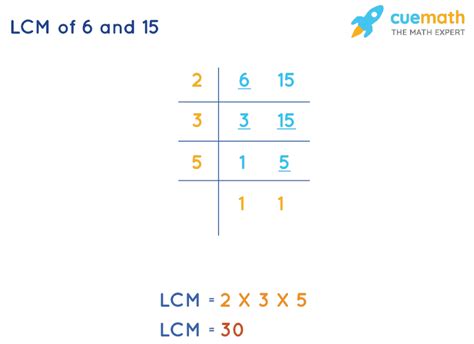
Table of Contents
What is the LCM for 6 and 15? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications ranging from simple fraction addition to complex scheduling problems. This article will explore the LCM of 6 and 15, not just providing the answer but delving into the underlying principles, different methods of calculation, and real-world examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also touch upon the relationship between LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD), enhancing your overall grasp of number theory.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers in the set as factors. For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer divisible by both 2 and 3.
Understanding the LCM is vital for several reasons:
- Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding a common denominator for adding or subtracting fractions requires determining the LCM of the denominators.
- Scheduling Problems: The LCM is used to determine when events will occur simultaneously. For example, if two buses leave a station at different intervals, the LCM helps find when they'll depart together again.
- Modular Arithmetic: LCM plays a crucial role in solving problems involving modular arithmetic, a system where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying repeating patterns and cycles often involves finding the LCM.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 6 and 15
There are several ways to calculate the LCM of 6 and 15. Let's explore the most common methods:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, ...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, ...
The smallest number appearing in both lists is 30. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 15 is 30.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the concept. We first find the prime factorization of each number.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations and multiply them together.
- Highest power of 2: 2¹ = 2
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
LCM(6, 15) = 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
3. Using the GCD (Greatest Common Divisor)
The LCM and GCD are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, let's find the GCD of 6 and 15 using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
- Prime factorization method for GCD:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 15 = 3 x 5
- The common factor is 3. Therefore, GCD(6, 15) = 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(6, 15) = (6 x 15) / GCD(6, 15) = (90) / 3 = 30
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization directly might be more challenging.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The LCM isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields:
- Construction: Determining the optimal length of tiles or bricks needed to cover a specific area involves finding the LCM of the tile/brick dimensions.
- Music: The LCM is used to calculate the least common period of two musical notes played simultaneously, determining when they will both be at the beginning of their respective cycles again.
- Manufacturing: In a manufacturing process with multiple machines operating at different cycles, the LCM helps determine when all machines will complete a cycle at the same time.
- Calendars: Determining when specific days of the week will coincide (e.g., when will a Tuesday and a Friday both fall on the 15th of the month?) involves the concept of LCM.
LCM and its Relationship with GCD
As demonstrated earlier, the LCM and GCD are intrinsically linked. They are inversely related; a higher GCD implies a lower LCM and vice-versa. Understanding this relationship simplifies calculations, particularly for larger numbers. The formula LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b is a powerful tool in number theory.
Extending the Concept to More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, we simply consider all prime factors of all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the listing multiples method, we list out the multiples for all numbers until a common multiple is found. However, the process becomes more computationally intensive as the number of integers increases.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM
Understanding the least common multiple is essential for various mathematical applications and real-world problems. Whether you use the listing multiples, prime factorization, or GCD method, the key is to choose the approach best suited to the numbers involved. This article aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the LCM, its calculation methods, its relationship with the GCD, and its significance in diverse fields. By mastering the LCM, you unlock a crucial tool for solving problems across various disciplines. Remember to practice these methods with different numbers to build confidence and fluency in your calculations. The more you practice, the easier it will become to identify and solve problems involving LCM effectively. The exploration of LCM extends beyond simple arithmetic; it opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving strategies. Embrace the challenge, and you'll find yourself more proficient in number theory and its numerous applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Liters In 50 Gallons
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Are Benefits Of Monsoon Winds
Mar 21, 2025
-
Where Are Metals Located On The Periodic Table
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Hours Is In 7 Days
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Stalk That Connects The Leaf To The Stem
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm For 6 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
