Where Are Metals Located On The Periodic Table
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
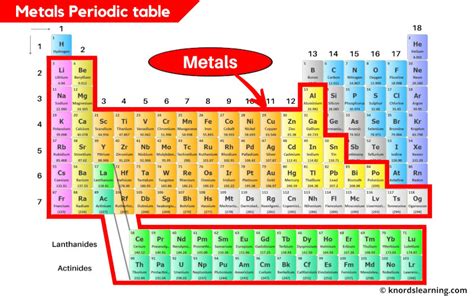
Table of Contents
Where are Metals Located on the Periodic Table? A Comprehensive Guide
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, organizes elements based on their atomic structure and properties. One of the most fundamental classifications of elements is their categorization as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids. Understanding the location of metals on the periodic table is crucial for comprehending their chemical behavior, applications, and overall importance in various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the precise location of metals, delve into their properties, and examine specific metal groups within the table.
The Broad Location of Metals
Metals occupy the vast majority of the periodic table. They are predominantly located to the left and center of the table. A zig-zag line, generally starting from Boron (B) and extending downwards, acts as a visual separator between metals and nonmetals. Elements to the left of this line are typically metals, while those to the right are generally nonmetals. The elements directly bordering this line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals, hence their classification as metalloids or semimetals.
Key Properties of Metals
Before diving into specific metal locations, it's crucial to understand the properties that define a metal. These characteristics contribute significantly to their widespread use in various applications:
-
Conductivity: Metals are excellent conductors of both heat and electricity. This property stems from the ease with which electrons can move freely within their metallic structure. This is why metals are frequently used in electrical wiring and heat sinks.
-
Malleability and Ductility: Metals can be easily hammered into thin sheets (malleability) and drawn into wires (ductility). These properties are directly related to the arrangement of metal atoms in a lattice structure, allowing for deformation without fracturing.
-
Luster: Metals generally possess a characteristic shiny appearance, often described as metallic luster. This results from the interaction of light with the free electrons in their structure.
-
Hardness: While some metals are softer than others, many exhibit significant hardness, meaning resistance to indentation or scratching. This makes them suitable for construction and manufacturing applications.
-
Density: Metals typically have relatively high densities, meaning they have a large amount of mass packed into a small volume. However, there's considerable variation in density among different metals.
-
Melting and Boiling Points: Most metals possess high melting and boiling points, requiring substantial energy to transition from solid to liquid or liquid to gas phases. This is a direct consequence of the strong metallic bonding.
Exploring Specific Metal Groups on the Periodic Table
The periodic table isn't just a random arrangement; it reflects underlying chemical trends and similarities. Metals are organized into several groups, each exhibiting unique properties and applications:
1. Alkali Metals (Group 1): The Most Reactive Metals
Located in the first column of the periodic table, alkali metals (Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, and Francium) are highly reactive metals. Their reactivity stems from their single valence electron, readily lost to form a +1 ion. They are soft, silvery-white metals that react violently with water, making them unsuitable for many everyday applications. However, their reactivity is harnessed in various industrial processes.
2. Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2): Moderately Reactive Metals
The second column houses the alkaline earth metals (Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, and Radium). Less reactive than alkali metals, they have two valence electrons, forming +2 ions. These metals are also silvery-white, but their reactivity is less pronounced than that of alkali metals. Magnesium, for example, is widely used in lightweight alloys and construction. Calcium plays a vital role in biological systems.
3. Transition Metals (Groups 3-12): A Diverse and Important Group
The central block of the periodic table comprises the transition metals. This large group contains elements like Iron, Copper, Gold, Platinum, and many others. They are characterized by their variable oxidation states, meaning they can lose different numbers of electrons to form ions with varying charges. This contributes to their diverse chemical behavior and wide range of applications. Transition metals are essential components in catalysts, alloys, and numerous industrial processes. Their varied colors and magnetic properties make them useful in pigments, magnets, and electronics.
4. Post-Transition Metals: Bridging the Gap
Elements like Aluminum, Tin, and Lead are classified as post-transition metals. They are located to the right of the transition metals. While they exhibit some metallic properties, they are generally less conductive and harder than typical transition metals. Their reactivity lies somewhere between transition metals and metalloids.
5. Lanthanides and Actinides: The Inner Transition Metals
Located at the bottom of the periodic table, the lanthanides and actinides are often referred to as the inner transition metals or f-block elements. They are characterized by their partially filled f-orbitals. Lanthanides, often used in high-tech applications like magnets and lighting, are found naturally together and are challenging to separate. Actinides are mostly radioactive and are used in nuclear reactors and weapons.
6. Other Metals Scattered Across the Periodic Table
While the groups mentioned above represent the major classifications of metals, some metals are found interspersed across the periodic table, particularly in the p-block. Examples include Gallium, Indium, Thallium, and others. While exhibiting metallic properties, their behavior often reflects characteristics of neighboring metalloids and nonmetals.
Importance of Metal Location on the Periodic Table
Understanding the precise location of metals on the periodic table allows us to:
-
Predict their properties: The position of an element on the table provides clues to its reactivity, conductivity, and other characteristics.
-
Understand chemical trends: The periodic arrangement helps in identifying trends in properties as you move across periods or down groups.
-
Design new materials: Knowledge of metal location aids in designing new alloys and compounds with specific properties for various applications.
-
Analyze chemical reactions: The location of elements helps predict the outcome of chemical reactions involving metals.
-
Explore industrial applications: Knowing the properties of metals based on their location allows us to choose suitable materials for various engineering and technological applications.
Conclusion: Metals - The Backbone of Modern Society
Metals form the backbone of modern society. Their widespread use in various applications, from construction and transportation to electronics and medicine, highlights their significance. Understanding their location on the periodic table and their associated properties is paramount for chemists, materials scientists, engineers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the material world around us. The periodic table, with its systematic arrangement of elements, serves as an invaluable tool for unraveling the mysteries and complexities of chemical behavior and material science. Further exploration of the periodic table, with a focus on the properties of specific metal groups and their individual elements, will lead to a more comprehensive understanding of this fascinating and indispensable class of materials.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Unit For Power
Mar 21, 2025
-
Explain The Ptv Stick In Your Own Words
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Tall Is 80 Inches In Feet
Mar 21, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple 9 And 12
Mar 21, 2025
-
Paragraph Writing About Mangoes 5 Line
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Where Are Metals Located On The Periodic Table . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
