Surface Area Of A Regular Pyramid Calculator
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
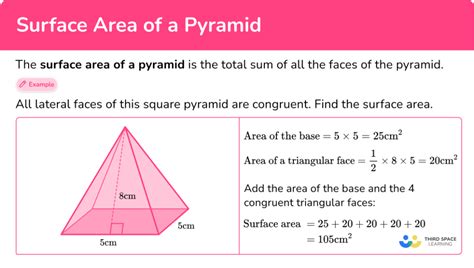
Table of Contents
Surface Area of a Regular Pyramid Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the surface area of a regular pyramid is crucial in various fields, from architecture and engineering to geometry and mathematics. This comprehensive guide will not only explain the concept but also delve into the practical application of a surface area of a regular pyramid calculator, exploring its benefits, functionalities, and limitations. We'll also discuss the underlying formulas and provide examples to solidify your understanding.
What is a Regular Pyramid?
Before we dive into calculations, let's clarify what constitutes a regular pyramid. A regular pyramid is a three-dimensional geometric shape with a polygon base and triangular faces that meet at a single point called the apex. The key characteristic of a regular pyramid is that its base is a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal), and the distance from the apex to each vertex of the base is the same. This equal distance creates congruent isosceles triangles forming the lateral faces.
Examples include:
- Square Pyramid: The base is a square.
- Triangular Pyramid (Tetrahedron): The base is an equilateral triangle.
- Pentagonal Pyramid: The base is a regular pentagon.
Understanding the Surface Area
The total surface area of a regular pyramid comprises two components:
- Base Area: The area of the polygon forming the base.
- Lateral Surface Area: The combined area of all the triangular faces.
Therefore, the total surface area (TSA) is the sum of the base area and the lateral surface area:
TSA = Base Area + Lateral Surface Area
Calculating the Base Area
The method for calculating the base area depends on the shape of the base polygon. Here are formulas for common base shapes:
- Square Base: Area = side² (where 'side' is the length of one side of the square)
- Equilateral Triangle Base: Area = (√3/4) * side² (where 'side' is the length of one side of the triangle)
- Regular Pentagon Base: Area = (5/4) * side² * cot(π/5) (where 'side' is the length of one side of the pentagon)
- Regular Hexagon Base: Area = (3√3/2) * side² (where 'side' is the length of one side of the hexagon)
And so on for other regular polygons. The formula for the area of a regular n-sided polygon is:
Area = (n * side²)/4 * cot(π/n)
Calculating the Lateral Surface Area
The lateral surface area is the sum of the areas of the triangular faces. Since all triangular faces are congruent isosceles triangles in a regular pyramid, we can calculate the area of one triangle and multiply it by the number of sides of the base polygon.
The area of one triangular face can be calculated using Heron's formula (if you know all three side lengths) or, more simply, if you know the base length (the side length of the base polygon) and the slant height (the distance from the apex to the midpoint of a base side):
Area of one triangular face = (1/2) * base * slant height
Lateral Surface Area = (number of sides) * (Area of one triangular face)
Calculating the Slant Height
The slant height is often not directly given. Instead, you might have the height of the pyramid (the perpendicular distance from the apex to the center of the base) and the apothem of the base (the distance from the center of the base to the midpoint of a side). In this case, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the slant height:
slant height² = height² + apothem²
The apothem can itself be calculated from the side length of the base polygon. The formula for the apothem (a) of a regular n-sided polygon with side length 's' is:
a = s / (2 * tan(π/n))
The Surface Area of a Regular Pyramid Calculator: Benefits and Functionalities
A surface area of a regular pyramid calculator significantly simplifies the process. It automates the calculations outlined above, saving time and reducing the risk of errors, especially when dealing with complex polygons. A good calculator will:
- Accept various input parameters: It should allow inputting different combinations of parameters like side length, slant height, height, number of sides, and apothem, depending on the available information.
- Handle different base polygon shapes: The calculator should cater to various regular polygons as bases, not just square or triangular pyramids.
- Provide step-by-step calculations: A detailed breakdown of the calculations will enhance understanding, especially for educational purposes.
- Offer clear and concise results: The final surface area should be presented clearly, along with units.
- Be user-friendly and intuitive: A well-designed calculator will be easy to navigate and use, regardless of your mathematical expertise.
Limitations of the Calculator
While calculators are invaluable tools, it's important to be aware of their limitations:
- Input Accuracy: The accuracy of the output depends entirely on the accuracy of the input. Incorrect or imprecise measurements will lead to inaccurate results.
- Regular Pyramids Only: These calculators are designed specifically for regular pyramids. They cannot be used for irregular pyramids where the base is not a regular polygon or the lateral faces are not congruent.
- Formula Dependency: The calculator relies on specific mathematical formulas. Understanding these formulas is essential to interpret the results correctly and to troubleshoot any issues.
Example Calculation: Square Pyramid
Let's consider a square pyramid with a base side length of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm. To find the total surface area:
- Base Area: Base Area = side² = 5² = 25 cm²
- Apothem: The apothem of a square is half the side length, so apothem = 2.5 cm.
- Slant Height: Using the Pythagorean theorem: slant height² = 6² + 2.5² = 42.25. Therefore, slant height = √42.25 ≈ 6.5 cm.
- Lateral Surface Area: Area of one triangular face = (1/2) * 5 * 6.5 = 16.25 cm². Lateral Surface Area = 4 * 16.25 = 65 cm² (since a square pyramid has 4 triangular faces).
- Total Surface Area: TSA = Base Area + Lateral Surface Area = 25 + 65 = 90 cm²
A surface area of a regular pyramid calculator would perform these steps automatically, given the base side length and height as input.
Practical Applications
Understanding and calculating the surface area of regular pyramids is essential in various real-world applications:
- Architecture: Determining the amount of roofing material needed for a pyramid-shaped roof.
- Engineering: Calculating the surface area of components in structures or machines.
- Packaging: Designing boxes and containers with pyramid-shaped sections.
- Construction: Estimating the materials required for constructing pyramid-shaped structures.
- Game Development: Creating realistic 3D models of pyramids in games or simulations.
Conclusion
The surface area of a regular pyramid calculator is a powerful tool that streamlines the calculation process, reducing the potential for errors and saving valuable time. By understanding the underlying formulas and principles, you can effectively utilize this tool in various applications and confidently interpret the results. Remember, however, that the calculator’s limitations should be considered to ensure accurate and reliable surface area calculations. Always double-check your inputs and understand the methodology behind the calculations to make the most of this helpful resource. This knowledge empowers you to tackle more complex geometric problems with greater confidence and efficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 25 Cm In Inches
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Describes The Process Of Globalization
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are The Greatest Common Factors Of 48
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Unit Of Energy In S I Units Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Does Temperature Relate To Kinetic Energy
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Surface Area Of A Regular Pyramid Calculator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
