What Is The Greatest Common Factor For 36
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
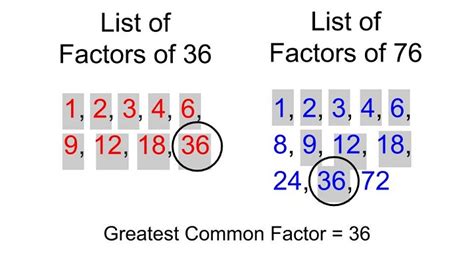
Table of Contents
What is the Greatest Common Factor for 36? A Deep Dive into Factors and Divisibility
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of a number, such as 36, might seem like a simple task at first glance. However, understanding the underlying principles of factors, divisibility rules, and prime factorization unlocks a deeper understanding of number theory and its practical applications. This article will not only answer the question "What is the greatest common factor for 36?" but also explore the broader context of GCF, offering a comprehensive guide for students and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding Factors
Before we tackle the GCF of 36, let's solidify our understanding of factors. A factor of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding all the factors of a number can be done through systematic trial and error, or by utilizing divisibility rules for specific numbers. Let's apply this to 36:
- 1: 36 divided by 1 is 36.
- 2: 36 divided by 2 is 18.
- 3: 36 divided by 3 is 12.
- 4: 36 divided by 4 is 9.
- 6: 36 divided by 6 is 6.
- 9: 36 divided by 9 is 4.
- 12: 36 divided by 12 is 3.
- 18: 36 divided by 18 is 2.
- 36: 36 divided by 36 is 1.
Therefore, the factors of 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 36.
Prime Factorization: The Key to Finding GCF
Prime factorization is a powerful tool in number theory. It involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that have only two factors: 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization provides a structured approach to finding the GCF.
Let's find the prime factorization of 36:
We can start by dividing 36 by the smallest prime number, 2:
36 ÷ 2 = 18
Now, we continue factoring 18:
18 ÷ 2 = 9
9 is not divisible by 2, but it is divisible by 3:
9 ÷ 3 = 3
3 is a prime number, so we've reached the end of our factorization. Therefore, the prime factorization of 36 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, or 2² x 3².
What is the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 36?
The greatest common factor (GCF) is the largest number that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. To find the GCF of 36, we need to consider another number. Let's assume we want to find the GCF of 36 and another number, say 24.
First, we find the prime factorization of 24:
24 ÷ 2 = 12 12 ÷ 2 = 6 6 ÷ 2 = 3
The prime factorization of 24 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3, or 2³ x 3.
Now, we compare the prime factorizations of 36 (2² x 3²) and 24 (2³ x 3):
- Both numbers have at least two factors of 2 (2² is common to both).
- Both numbers have at least one factor of 3 (3¹ is common to both).
Therefore, the GCF of 36 and 24 is 2² x 3 = 4 x 3 = 12.
Finding the GCF with Different Methods:
While prime factorization is a powerful method, especially for larger numbers, there are other ways to determine the GCF, especially for smaller numbers.
Listing Factors Method:
- List the factors of each number: List all the factors of 36 (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36) and the factors of the second number (let's say 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24).
- Identify the common factors: Find the factors that appear in both lists (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12).
- Select the greatest common factor: The largest number among the common factors is the GCF (12).
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but becomes less efficient for larger numbers.
Euclidean Algorithm:
The Euclidean Algorithm is an efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers. It involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCF.
Let's find the GCF of 36 and 24 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide the larger number (36) by the smaller number (24): 36 ÷ 24 = 1 with a remainder of 12.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (24) and the smaller number with the remainder (12): 24 ÷ 12 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 12.
Applications of GCF
The concept of GCF has various practical applications across different fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The GCF is crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 36/24 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF (12), resulting in the simplified fraction 3/2.
-
Geometry Problems: GCF is used in geometry problems involving area and volume calculations. For instance, finding the dimensions of the largest square that can perfectly tile a rectangular area involves determining the GCF of the rectangle's dimensions.
-
Real-World Applications: In everyday life, GCF might be used to solve problems related to distributing items evenly or dividing quantities into equal groups without any leftovers. Imagine dividing 36 cookies and 24 candies equally among children; the GCF (12) will determine the maximum number of children that can receive an equal share of both cookies and candies.
Conclusion
The greatest common factor of 36 itself isn't a single number; it's context-dependent. The GCF of 36 and any other number is determined by comparing their prime factorizations or using other methods like listing factors or the Euclidean algorithm. Understanding GCF goes beyond simply finding the largest common divisor; it offers a deeper understanding of number theory and has practical applications in mathematics, geometry, and real-world problem-solving. Mastering this concept lays a strong foundation for further exploration of more advanced mathematical concepts. The ability to quickly and efficiently find the GCF of numbers is a valuable skill that will undoubtedly benefit anyone exploring the world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 34 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 10, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Lists Disadvantages Of Nuclear Power
Mar 10, 2025
-
Place The Following Parts Of A Reflex Arc In Order
Mar 10, 2025
-
Five Letter Word That Ends With Er
Mar 10, 2025
-
In What Units Is Work Measured
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Factor For 36 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
