What Is The Function Of Petals On A Flower
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
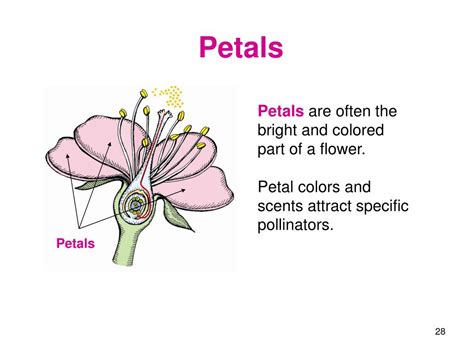
Table of Contents
What is the Function of Petals on a Flower?
Petals, those vibrantly colored and often delicately shaped structures, are a key feature of flowering plants (angiosperms). While their beauty is undeniable and often the primary reason we appreciate flowers, their function goes far beyond mere aesthetics. Petals play a crucial role in the plant's reproductive strategy, acting as essential components in the complex process of pollination. Understanding the function of petals provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationship between plants and their pollinators, as well as the remarkable evolutionary adaptations found in the floral kingdom.
The Primary Function: Attracting Pollinators
The most important function of petals is to attract pollinators. This attraction is achieved through a combination of visual and olfactory cues.
Visual Attraction: Color and Shape
The color of petals is perhaps the most immediately obvious aspect of their pollinator-attracting function. Different colors attract different pollinators. Brightly colored petals, particularly reds, oranges, and yellows, often attract pollinators with good color vision, such as birds, butterflies, and some bees. Conversely, flowers pollinated by moths or nocturnal animals often have white or pale-colored petals, which are more visible in low light conditions.
The shape of petals is also crucial. Petals can be arranged in a wide variety of patterns, from radial symmetry (like a daisy) to bilateral symmetry (like a snapdragon). The shape influences how easily pollinators can access the flower's reproductive structures (stamens and pistil). Some flowers have petals fused together, forming a tube or funnel, guiding pollinators to the nectar and pollen. Other flowers have widely separated petals, providing a landing platform for insects.
Specialized Petal Adaptations: Many flowers have evolved highly specialized petal shapes to attract specific pollinators. For instance, orchids may have petals modified into elaborate structures that mimic insects, attracting the pollinators through deception. Some flowers offer landing platforms tailored to the size and weight of their pollinator.
Olfactory Attraction: Scent and Fragrance
In addition to visual cues, many flowers use scent to attract pollinators. Floral scents are complex mixtures of volatile organic compounds, each with its own specific odor profile. These scents can attract a wide range of pollinators, from bees and butterflies to moths and beetles. Different scents are designed to attract different types of pollinators. For example, sweet, fruity scents are typically associated with flowers pollinated by bees or butterflies, while musky or pungent scents may attract carrion flies or beetles.
The timing of scent release can also be crucial. Flowers pollinated by night-flying insects often release their strongest scents in the evening. The intensity of the scent can also vary depending on the time of day or the availability of pollinators.
Nectar Guides: Many petals feature nectar guides, which are patterns of color or texture on the petals that act as visual signals directing pollinators towards the nectar source. These guides are often invisible to the human eye but are clearly visible to pollinators in the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum.
Secondary Functions of Petals: Protection and Support
While the primary function of petals is to attract pollinators, they also have several secondary functions:
Protection of Reproductive Structures
The petals often enclose and protect the reproductive organs of the flower, particularly in the bud stage. This protection is essential in preventing damage from environmental factors, such as rain, wind, and extreme temperatures. As the flower develops, the petals unfold to reveal the reproductive structures and attract pollinators. The arrangement and shape of petals aid in protecting the delicate stamens and pistil.
Support Structure
Petals, along with other floral parts like sepals, contribute to the overall structure of the flower. They provide a framework that supports the stamens and pistil, ensuring their optimal positioning for pollination. The structural support provided by petals allows for efficient pollen transfer and successful fertilization.
Thermogenesis
Some flowers, such as those in the Arum genus, exhibit thermogenesis, meaning they generate heat. The petals play a role in this process by providing insulation, maintaining a higher temperature within the flower. This higher temperature can attract pollinators or aid in volatile scent release.
Petal Diversity and Evolutionary Adaptations
The remarkable diversity of petal shapes, colors, and scents reflects the wide range of pollination strategies employed by flowering plants. Over millions of years, petals have evolved to become highly specialized structures, perfectly adapted to attract specific pollinators in their particular environment.
Co-evolution with Pollinators
The relationship between flowers and their pollinators is an excellent example of co-evolution. As pollinators have adapted to exploit different flower resources, flowers have evolved to attract those particular pollinators. This close interaction has driven the development of incredibly diverse petal morphologies and chemistries.
For example, the long, slender petals of many orchids are perfectly adapted for pollination by long-tongued moths. The vibrant colors and strong scents of many hummingbird-pollinated flowers reflect the preferences of these avian pollinators. The intricate flower structures of some flowers are specifically designed to trap pollinators, ensuring efficient pollen transfer before they are released.
Petal Loss and Anemophily
Not all flowers have brightly colored, showy petals. Many wind-pollinated flowers (anemophilous) have reduced or absent petals. In these plants, the primary focus is not on attracting pollinators, but rather on producing large quantities of lightweight pollen that can be dispersed by the wind.
Petals and Human Culture
Beyond their biological significance, petals have played a significant role in human culture for thousands of years. Flowers and their petals are used extensively in:
- Art and Decoration: The beauty and symbolism of petals have inspired artists and designers for centuries. Petals are used in floral arrangements, paintings, sculptures, and many other forms of art.
- Perfumery: The fragrant oils extracted from petals are used in the creation of perfumes and other scented products.
- Food and Medicine: Some edible flower petals are used in culinary creations, adding both flavor and visual appeal to dishes. Certain petals also possess medicinal properties and are used in traditional medicine.
- Religious and Ceremonial Uses: Flowers and their petals are frequently used in religious ceremonies and celebrations, symbolizing various aspects of life, love, and spirituality.
Conclusion
Petals are far more than just aesthetically pleasing components of flowers. They are essential structures that play a crucial role in plant reproduction, attracting pollinators through visual and olfactory cues, protecting reproductive structures, and even providing support. The extraordinary diversity of petal forms reflects the intricate evolutionary relationships between plants and their pollinators, showcasing the remarkable adaptations that have evolved over millions of years. Understanding the function of petals provides a richer appreciation for the beauty and complexity of the plant world and the essential role flowers play in our ecosystem. Further research into the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying petal development and evolution continues to unravel the secrets behind this vital floral component.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 25 Cm In Inches
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Describes The Process Of Globalization
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are The Greatest Common Factors Of 48
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Unit Of Energy In S I Units Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Does Temperature Relate To Kinetic Energy
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Function Of Petals On A Flower . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
