What Is The Factors Of 54
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
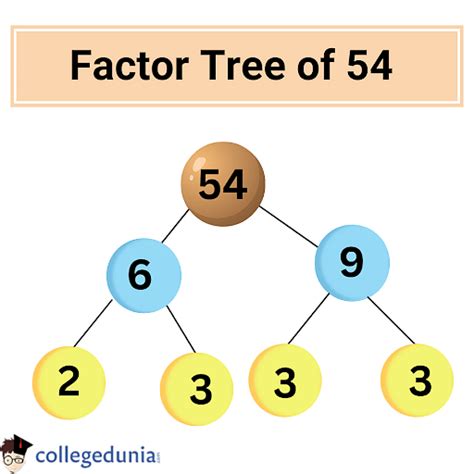
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of 54: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching implications in mathematics and computer science. This article delves into the fascinating world of factors, exploring not only how to find the factors of 54 but also the underlying principles and their broader significance. We'll explore various methods, discuss prime factorization, and touch upon the applications of factor analysis in diverse fields.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we jump into the specifics of 54, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. A factor (also known as a divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Identifying Factors: Methods and Strategies
Several methods can be employed to identify the factors of a number. Let's explore some common techniques:
1. The Division Method: This is the most straightforward approach. Systematically divide the number (in our case, 54) by each integer starting from 1, up to the square root of the number. If the division results in a whole number, both the divisor and the quotient are factors.
Let's apply this to 54:
- 54 ÷ 1 = 54 (1 and 54 are factors)
- 54 ÷ 2 = 27 (2 and 27 are factors)
- 54 ÷ 3 = 18 (3 and 18 are factors)
- 54 ÷ 6 = 9 (6 and 9 are factors)
Notice that after we reach the square root of 54 (approximately 7.35), we've already found all the factor pairs. This is because factors come in pairs.
2. Prime Factorization: This method breaks down the number into its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization is crucial because it provides a unique representation of any composite number (a number that is not prime).
To find the prime factorization of 54:
- We start by dividing 54 by the smallest prime number, 2: 54 ÷ 2 = 27
- 27 is not divisible by 2, so we move to the next prime number, 3: 27 ÷ 3 = 9
- 9 is divisible by 3: 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 54 is 2 x 3 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3³.
Once you have the prime factorization, you can find all the factors by systematically combining the prime factors. For 54:
- Combinations of the prime factors: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54
3. Factor Trees: A visual approach to prime factorization. You start with the number and branch out, dividing it by its prime factors until you reach only prime numbers at the ends of the branches.
The Factors of 54: A Complete List
Based on the methods above, the complete list of factors for 54 is: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, and 54.
Beyond the Basics: Applications and Significance of Factors
The seemingly simple task of finding factors has profound implications across various mathematical and computational fields:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM):**
Factors are essential for determining the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. These concepts are crucial in simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and performing various calculations.
2. Cryptography:**
Factorization plays a vital role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption. RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors. The security of many online transactions depends on this computational challenge.
3. Modular Arithmetic:**
Modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus), heavily utilizes factors. Congruence relations and other modular operations depend on the divisibility properties of numbers.
4. Computer Science:**
Factorization algorithms are fundamental in computer science, particularly in areas like algorithm optimization and data structure design. Efficient factorization methods are critical for improving the performance of various computational tasks.
5. Algebra and Number Theory:**
Factors underpin many concepts in algebra and number theory, including polynomial factorization, Diophantine equations, and the study of algebraic structures.
Exploring Further: Advanced Concepts Related to Factors
The concept of factors extends into more advanced areas of mathematics:
-
Divisibility Rules: These rules provide shortcuts for determining if a number is divisible by certain prime factors without performing long division. For instance, a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding itself). 6 is the smallest perfect number (1 + 2 + 3 = 6).
-
Abundant and Deficient Numbers: Abundant numbers have a sum of proper divisors greater than the number itself, while deficient numbers have a sum of proper divisors less than the number.
-
Highly Composite Numbers: These are numbers that have more divisors than any smaller positive integer.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factors
Finding the factors of 54, while seemingly a simple exercise, opens a door to a vast and fascinating realm of mathematical concepts. Understanding factors is crucial not only for basic arithmetic but also for advanced applications in cryptography, computer science, and various branches of mathematics. The principles of factorization are deeply interwoven with the fabric of number theory, providing the foundation for many important concepts and applications. From simple division to complex algorithms, the significance of factors extends far beyond the classroom, shaping the technological landscape and deepening our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Mixed Number To Decimal Conversion Calculator
Mar 21, 2025
-
Volume Of One Drop Of Water
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 2
Mar 21, 2025
-
2 Cubic Feet Is How Many Quarts
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is A Row In The Periodic Table
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factors Of 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
