What Is The Factors Of 44
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
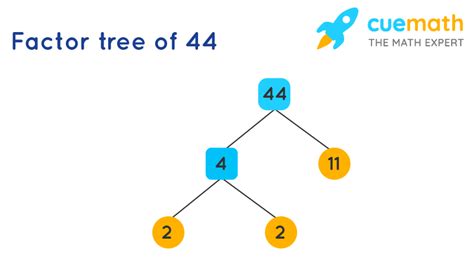
Table of Contents
Unpacking the Prime Factorization of 44: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 44?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of arithmetic. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, delving deeper reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts that are crucial for understanding more complex mathematical structures. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the underlying mathematical principles involved, demonstrating how seemingly simple concepts form the foundation for more advanced mathematical ideas.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before diving into the factors of 44, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms involved. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's a number that can be multiplied by another whole number to produce the original number. Divisibility, therefore, is the property of a number being perfectly divisible by another number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder. 1 x 12 = 12, 2 x 6 = 12, and 3 x 4 = 12.
Finding the Factors of 44: A Systematic Approach
To find the factors of 44, we can use a systematic approach:
- Start with 1: Every number has 1 as a factor.
- Consider 2: Since 44 is an even number, it's divisible by 2 (44/2 = 22). This gives us the factor pair (2, 22).
- Check 3: 44 is not divisible by 3 (4+4=8, and 8 is not divisible by 3).
- Check 4: 44 is divisible by 4 (44/4 = 11). This gives us the factor pair (4, 11).
- Check 5: 44 is not divisible by 5 (it doesn't end in 0 or 5).
- Check 6: 44 is not divisible by 6 (it's not divisible by both 2 and 3).
- Check 7: 44 is not divisible by 7.
- Check 8: 44 is not divisible by 8.
- Check 9: 44 is not divisible by 9.
- Check 10: 44 is not divisible by 10.
- Check 11: 44 is divisible by 11 (44/11 = 4). This gives us the factor pair (11, 4), which we already found.
We've now identified all the factors: 1, 2, 4, 11, 22, and 44.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
The concept of prime factorization takes our understanding a step further. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two distinct divisors: 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. This is a unique representation for every number (excluding 1, which has no prime factors).
To find the prime factorization of 44, we can use a factor tree:
44
/ \
2 22
/ \
2 11
This shows that 44 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 11, or 2² x 11. This is the prime factorization of 44. Each of these numbers (2 and 11) is a prime factor. This representation is unique to 44; no other combination of prime numbers will multiply to give 44.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number is crucial in various areas of mathematics:
- Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms by canceling out common factors in the numerator and denominator.
- Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): The GCD and LCM are fundamental concepts in arithmetic, and prime factorization provides an efficient method for calculating them.
- Cryptography: Prime numbers and factorization play a vital role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptosystems like RSA. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the basis for the security of these systems.
- Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization forms the foundation for many advanced concepts in abstract algebra, such as modular arithmetic and ring theory.
- Number Theory: Prime factorization is a cornerstone of number theory, a branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of integers. The distribution of prime numbers, the search for large primes, and the study of their relationships are active areas of research.
Exploring Further: Related Concepts
The analysis of factors and prime factorization leads to many related mathematical concepts:
- Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding itself). For example, 6 is a perfect number (1 + 2 + 3 = 6).
- Abundant Numbers: An abundant number is a positive integer where the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number itself.
- Deficient Numbers: A deficient number is a positive integer where the sum of its proper divisors is less than the number itself.
- Composite Numbers: These are whole numbers greater than 1 that are not prime. They can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. 44 is a composite number.
Practical Applications of Factorization
Beyond the theoretical realm, factorization finds numerous practical applications:
- Division and Simplification: In everyday calculations, understanding factors simplifies division and reduces complexity.
- Measurement and Units: Factors are essential when converting units of measurement (e.g., converting inches to feet).
- Scheduling and Optimization: In project management and scheduling, understanding factors can help in optimizing resource allocation and task assignments.
- Data Structures and Algorithms: Concepts related to factorization are used in computer science for designing efficient data structures and algorithms.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factorization
The simple question of finding the factors of 44 has led us on a journey through fundamental mathematical concepts, revealing the interconnectedness of seemingly disparate areas. From basic arithmetic to advanced cryptography, the importance of understanding factors and prime factorization cannot be overstated. The exploration of this topic highlights the beauty and power of mathematics, demonstrating how seemingly simple concepts can form the basis for complex and profound ideas with far-reaching implications across various fields. The seemingly simple number 44, with its factors 1, 2, 4, 11, 22, and 44, and its prime factorization 2² x 11, serves as a powerful reminder of the rich mathematical landscape waiting to be explored. This journey underscores the value of persistent inquiry and the profound impact of fundamental mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Letter Words End With Er
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Cm Is 14 Inches
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Feet In A 100 Yards
Mar 25, 2025
-
Difference Between Nuclear Reaction And Chemical Reaction
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is Water A Mixture Or A Compound
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factors Of 44 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
