What Is The Factorization Of 8
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
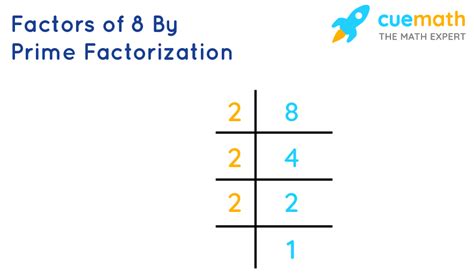
Table of Contents
What is the Factorization of 8? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Beyond
The seemingly simple question, "What is the factorization of 8?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the process and its implications reveals a wealth of knowledge applicable far beyond basic arithmetic. This article will explore the factorization of 8 in detail, covering various methods, exploring related concepts, and demonstrating its relevance in more advanced mathematical contexts.
Understanding Factorization
Factorization, in its simplest form, is the process of breaking down a number into smaller numbers that, when multiplied together, give the original number. These smaller numbers are called factors. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because 1 x 12 = 12, 2 x 6 = 12, and 3 x 4 = 12.
This seemingly simple concept forms the basis for many advanced mathematical operations and is crucial in fields like cryptography and computer science. The ability to efficiently factor large numbers is a cornerstone of modern security protocols.
Finding the Factors of 8
Let's apply the concept of factorization to the number 8. We are looking for numbers that, when multiplied together, result in 8. Here's a systematic approach:
- 1 x 8 = 8: 1 and 8 are factors of 8.
- 2 x 4 = 8: 2 and 4 are also factors of 8.
Therefore, the factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, and 8.
Prime Factorization: The Building Blocks
While the above lists all the factors, a more fundamental type of factorization is prime factorization. This involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization is unique for every number; it's like the number's DNA, providing a fundamental representation.
To find the prime factorization of 8, we can use a factor tree:
8
/ \
2 4
/ \
2 2
This shows that 8 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 2, or 2³. Therefore, the prime factorization of 8 is 2³. This means 8 is composed entirely of the prime number 2, repeated three times. This prime factorization is unique to 8; no other number has this specific prime factorization.
The Importance of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization isn't just an exercise in number manipulation; it has profound implications across mathematics and computer science. Here are some key reasons why it's so important:
-
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (disregarding the order of factors). This ensures consistency and provides a foundation for many other mathematical concepts.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization simplifies the calculation of the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers, and the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. By using prime factorization, finding the GCD and LCM becomes a straightforward comparison of prime factors.
-
Cryptography: The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors is the foundation of many modern encryption algorithms, such as RSA. The security of these algorithms relies on the computational infeasibility of factoring extremely large numbers with many prime factors. Breaking these codes would require an immense amount of computing power.
Beyond the Basics: Applications of Factorization
The concept of factorization extends far beyond finding factors of simple numbers like 8. Here are some advanced applications:
-
Polynomial Factorization: Factorization isn't limited to integers; it also applies to polynomials. Polynomial factorization involves expressing a polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials. This is a crucial tool in algebra and calculus, often used to solve equations and simplify complex expressions. For example, x² - 4 can be factored into (x - 2)(x + 2).
-
Matrix Factorization: In linear algebra, matrix factorization involves expressing a matrix as a product of simpler matrices. This has wide-ranging applications in data analysis, machine learning, and computer graphics. Techniques like Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Eigenvalue Decomposition are powerful matrix factorization methods with numerous practical applications.
-
Number Theory: Factorization is a central concept in number theory, a branch of mathematics that studies the properties of integers. It underpins many advanced theorems and conjectures, including the Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics.
Further Exploration: Factorization Algorithms
The process of factoring small numbers like 8 is simple, but factoring extremely large numbers is a computationally intensive task. Over the years, mathematicians and computer scientists have developed sophisticated algorithms to factor large numbers efficiently. Some notable algorithms include:
-
Trial Division: This is a basic method that involves trying to divide the number by all prime numbers up to its square root.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that is relatively efficient for finding small factors.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers, particularly those with hundreds of digits. This algorithm utilizes advanced mathematical techniques and requires substantial computational resources.
The development of efficient factorization algorithms is an ongoing area of research, with implications for both theoretical mathematics and practical applications in cryptography and computer security.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Factorization
While the factorization of 8 might seem trivial at first glance, it serves as a gateway to understanding profound mathematical concepts. The ability to factor numbers, particularly into their prime factors, is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications in various fields. From the simplicity of finding the factors of 8 to the complexity of factoring large numbers for cryptographic security, the concept of factorization remains a cornerstone of mathematics and computer science. Understanding prime factorization provides a deeper appreciation for the structure and beauty of numbers, highlighting the interconnectedness of seemingly disparate mathematical areas. The journey from the basic factorization of 8 to the advanced algorithms used for factoring large numbers demonstrates the continuous evolution and increasing sophistication of mathematical techniques, emphasizing the enduring power and elegance of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Factor Of 96
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Element Has The Highest Ionization Potential
Mar 06, 2025
-
Moment Of Inertia Of A Hollow Sphere
Mar 06, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 18 And 27
Mar 06, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 5
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factorization Of 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
