What Is The Electron Configuration For Barium
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
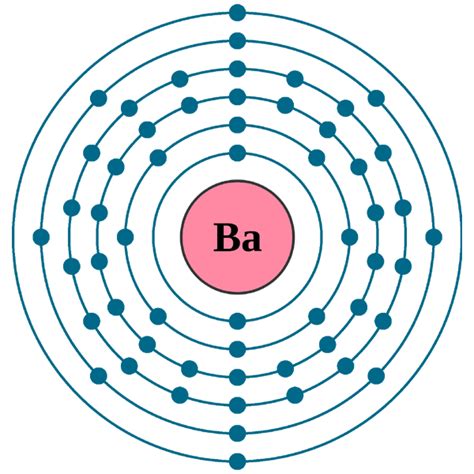
Table of Contents
What is the Electron Configuration for Barium? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Barium, a silvery-white alkaline earth metal, holds a significant place in various applications, from medical imaging to pyrotechnics. Understanding its properties begins with grasping its fundamental structure – its electron configuration. This article delves deep into the electron configuration of barium, exploring its implications for the element's reactivity, chemical behavior, and overall properties. We’ll also cover the underlying principles of electron configuration, and discuss how it’s determined.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before we dive into the specifics of barium, let's establish a foundational understanding of electron configuration. Electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in the various energy levels and sublevels within an atom. These arrangements determine an element's chemical properties and how it interacts with other elements.
The Basics: Shells, Subshells, and Orbitals
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. Electrons occupy specific energy levels, often visualized as concentric shells surrounding the nucleus. Each shell can accommodate a limited number of electrons. The shells are further divided into subshells (s, p, d, and f), each characterized by a specific shape and capable of holding a certain number of electrons:
- s subshell: Holds a maximum of 2 electrons.
- p subshell: Holds a maximum of 6 electrons.
- d subshell: Holds a maximum of 10 electrons.
- f subshell: Holds a maximum of 14 electrons.
Within each subshell are atomic orbitals, which represent regions of space where there's a high probability of finding an electron. Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins (Pauli Exclusion Principle).
The Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule
The arrangement of electrons within an atom follows specific rules:
-
Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. This means that electrons occupy the shells and subshells with the lowest energy before moving to higher energy levels.
-
Hund's Rule: Within a subshell, electrons fill orbitals individually before pairing up. This leads to the maximum number of unpaired electrons with parallel spins.
These rules are crucial for predicting the electron configuration of any element, including barium.
Determining the Electron Configuration of Barium (Ba)
Barium has an atomic number of 56, meaning it has 56 protons and 56 electrons in a neutral atom. Following the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, we can determine its electron configuration:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶ 6s²
Let's break this down shell by shell:
- First shell (n=1): Contains the 1s subshell with 2 electrons (1s²).
- Second shell (n=2): Contains the 2s and 2p subshells, holding a total of 8 electrons (2s² 2p⁶).
- Third shell (n=3): Contains the 3s, 3p, and 3d subshells, holding a total of 18 electrons (3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰).
- Fourth shell (n=4): Contains the 4s, 4p, and 4d subshells, holding a total of 18 electrons (4s² 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰).
- Fifth shell (n=5): Contains the 5s and 5p subshells, holding a total of 8 electrons (5s² 5p⁶).
- Sixth shell (n=6): Contains the 6s subshell with 2 electrons (6s²).
Therefore, the complete electron configuration of barium is [Xe] 6s². The [Xe] represents the electron configuration of Xenon, a noble gas, which is a shorthand notation for the filled inner shells. This noble gas core simplifies the representation while retaining all the necessary information.
Implications of Barium's Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of barium directly influences its chemical and physical properties. The two electrons in the 6s subshell are relatively loosely held, making barium highly reactive. This is characteristic of alkaline earth metals.
Reactivity and Chemical Behavior
The two outermost electrons (valence electrons) in the 6s orbital are readily lost, forming a Ba²⁺ ion. This tendency to lose electrons makes barium a highly reactive element, readily participating in redox reactions. It reacts vigorously with water, producing barium hydroxide and hydrogen gas:
Ba(s) + 2H₂O(l) → Ba(OH)₂(aq) + H₂(g)
It also reacts readily with oxygen, forming barium oxide:
2Ba(s) + O₂(g) → 2BaO(s)
Physical Properties and Applications
The electron configuration also contributes to barium's physical properties. Its metallic character is evident in its silvery-white appearance and its ability to conduct electricity. Its relatively low ionization energy allows for the easy loss of valence electrons, contributing to its reactivity.
The unique properties stemming from its electron configuration make barium crucial in several applications:
-
Medical Imaging: Barium sulfate (BaSO₄) is widely used as a contrast agent in X-ray imaging of the digestive system, due to its high opacity to X-rays and low toxicity.
-
Pyrotechnics: Barium compounds impart a bright green color to fireworks, leveraging the electron transitions within the barium atom.
-
Vacuum Tubes: Barium is sometimes used as a "getter" in vacuum tubes to remove residual gases, enhancing the tube's performance.
-
Lubricants: Barium compounds are used in lubricating greases to improve their high-temperature performance.
Comparing Barium's Configuration to Other Elements
Understanding barium's electron configuration allows us to compare it to other elements within the periodic table, particularly those in the same group (alkaline earth metals) and period (period 6).
Alkaline Earth Metals
Barium belongs to Group 2 (alkaline earth metals), which are characterized by having two valence electrons in their outermost s subshell. All alkaline earth metals exhibit similar reactivity due to this common electron configuration pattern. However, the reactivity increases as you move down the group because the outer electrons are further from the nucleus and more easily lost.
Period 6 Elements
Barium is a member of period 6. Elements in the same period share the same highest principal quantum number (n), indicating that their outermost electrons are in the same shell. However, within the same period, elements show diverse properties reflecting the filling of different subshells (s, p, d, f). For instance, while barium readily loses two electrons, the elements to its right (lanthanides and transition metals) exhibit more complex behaviors due to the involvement of d and f electrons in bonding.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
This article provides a comprehensive overview of barium's electron configuration. However, for a more in-depth understanding, further exploration into these concepts is recommended:
-
Quantum Mechanics: A deeper understanding of quantum mechanics provides a more nuanced view of electron behavior and the underlying principles governing electron configuration.
-
Spectroscopy: Techniques like atomic spectroscopy provide experimental confirmation of electron configurations by analyzing the light emitted or absorbed by atoms.
-
Relativistic Effects: For heavier elements like barium, relativistic effects become more significant, influencing the energy levels and electron distribution.
-
Computational Chemistry: Advanced computational methods can be used to model and predict the electron configurations and properties of complex atoms and molecules.
Conclusion
The electron configuration of barium ([Xe] 6s²) is a cornerstone to understanding its chemical and physical properties. This simple notation encapsulates a wealth of information, informing us about its reactivity, its tendency to form Ba²⁺ ions, and its applications in various fields. By understanding the fundamental principles governing electron configuration and its implications, we unlock a deeper understanding of the behavior of barium and its place within the broader world of chemistry. Further exploration into related topics will enhance your comprehension of atomic structure and the underlying principles that govern the behavior of matter.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Two Angles Form A Linear Pair
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In A Circle
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Was The Byzantine Empire Different From The Roman Empire
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is 68 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many 0 In 20 Million
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electron Configuration For Barium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
