What Is The Difference Between A Kilo And A Pound
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
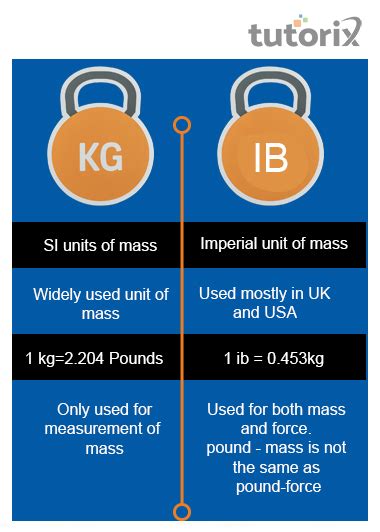
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between a Kilo and a Pound? A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple question, "What's the difference between a kilo and a pound?" delves deeper than a straightforward conversion factor. Understanding the nuances requires exploring the history, the science, and the practical implications of these two common units of mass. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the differences, offering clarity and context for anyone seeking a thorough understanding.
Understanding the Systems: Metric vs. Imperial
Before diving into the specifics of kilos and pounds, it's crucial to grasp the overarching systems they represent: the metric system and the imperial system (or US customary units). These are fundamentally different approaches to measuring mass, length, volume, and other physical quantities.
The Metric System: A Foundation of Ten
The metric system, officially known as the International System of Units (SI), is a decimal system based on powers of ten. This makes conversions remarkably straightforward. A kilometer is 1000 meters, a milliliter is one-thousandth of a liter, and so on. This elegant simplicity is one of the key reasons for its global adoption. The fundamental unit of mass in the metric system is the kilogram (kg).
The Imperial System: A Patchwork of History
The imperial system, prevalent in the United States and a few other countries, is a hodgepodge of historical units with less consistent relationships between them. It's characterized by its lack of a unified, logical structure, making conversions often more complex and requiring memorization of various conversion factors. The fundamental unit of mass in the imperial system is the pound (lb).
The Kilo: The Metric Standard Bearer
The kilogram (kg) is the base unit of mass in the SI system. It's defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram (IPK), a platinum-iridium cylinder kept under highly controlled conditions at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) in Sèvres, France. While this definition is being updated to a more fundamental physical constant, the practical implications for everyday use remain largely unchanged. A kilo is a substantial amount; think of a large bag of sugar or a small child.
Uses of the Kilogram:
- Grocery Shopping: Many grocery items, from fruits and vegetables to grains and meat, are sold by the kilogram.
- Scientific Research: The kilogram is essential in scientific experiments, measurements, and calculations across various fields.
- Industrial Applications: In manufacturing and engineering, the kilogram is a crucial unit for measuring materials and components.
- International Trade: The kilogram facilitates consistent measurements in international trade and commerce.
The Pound: A Legacy of History
The pound (lb), a unit of mass in the imperial system, has a rich and complex history tracing back to ancient civilizations. Its origins are intertwined with various systems of weights and measures, evolving over centuries. Unlike the kilogram's relatively straightforward definition, the pound’s definition has changed over time, reflecting the historical evolution of measurement standards. Today, the pound is defined in terms of the kilogram, offering a clear link to the SI system.
Understanding the Pound's Variations:
While the pound is a common unit, it’s essential to note that there are slight variations depending on the specific system used:
- Avoirdupois pound: This is the most common type of pound used in everyday life and commerce in countries that still use the imperial system. It is the pound referenced in most everyday conversions.
- Troy pound: This type of pound is primarily used in the precious metals industry, and it’s crucial to distinguish it from the avoirdupois pound as its mass is different.
Uses of the Pound:
- Everyday Measurements: In countries that still primarily use the imperial system, the pound is frequently used for measuring various goods, especially in cooking and baking.
- Specific Industries: Certain industries, like food packaging and some manufacturing sectors, may still use pounds as their primary unit of mass.
- Historical Context: The pound's use often reflects a legacy of measurement practices and historical conventions.
Kilo vs. Pound: Direct Conversion and Practical Implications
The fundamental difference between a kilo and a pound lies in their mass:
1 kilogram (kg) ≈ 2.20462 pounds (lb)
1 pound (lb) ≈ 0.453592 kilograms (kg)
This seemingly simple conversion masks the deeper implications:
- Scale Differences: A kilogram is significantly heavier than a pound, meaning a kilogram of an item will feel noticeably heavier than a pound of the same item.
- Conversion Complexity: The inconsistent nature of the imperial system makes converting between pounds and other units, like ounces or tons, more complicated than equivalent metric conversions.
- Global Standardization: The widespread adoption of the metric system globally underscores its efficiency and ease of use in scientific research, international trade, and everyday applications.
Beyond Mass: Exploring Units of Weight
While the terms "kilo" and "pound" are often used interchangeably in everyday conversations, it's essential to distinguish between mass and weight.
- Mass: A measure of the amount of matter in an object. Mass remains constant regardless of location.
- Weight: A measure of the force of gravity on an object. Weight varies depending on the gravitational field (e.g., an object weighs less on the moon than on Earth).
Strictly speaking, kilograms measure mass, while pounds can refer to both mass and weight, depending on the context. However, in most everyday contexts, the distinction is often blurred.
The Ongoing Shift Towards Metric: Global Standardization
The global trend shows an increasing adoption of the metric system. Its consistent and logical structure offers significant advantages in scientific research, engineering, manufacturing, and international trade. Even in countries that primarily use the imperial system, the metric system is often used alongside or in specific contexts (e.g., scientific publications, medical settings). This shift underscores the advantages of standardization and consistency in measurement.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Unit
The choice between using kilograms or pounds often depends on cultural norms, established practices within specific industries, and regional conventions. However, the advantages of the metric system's simplicity, ease of conversion, and global adoption are undeniable. While understanding the differences between kilos and pounds is important, appreciating the broader context of the metric and imperial systems reveals a deeper understanding of measurement and its evolution. For clarity, consistency, and ease of use, the metric system offers a more streamlined and universally accepted approach. As globalization continues, the prevalence of the metric system is expected to increase further, solidifying its position as the dominant system of measurement worldwide.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Structural And Functional Unit Of The Kidney Is The
May 09, 2025
-
What Chemical Is Inside A Battery
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 1 5 Cm In Mm
May 09, 2025
-
How Does A Subsidy Affect Supply
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Purpose Of A Contractile Vacuole
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between A Kilo And A Pound . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.