What Is The Difference Between A Habitat And A Niche
Juapaving
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
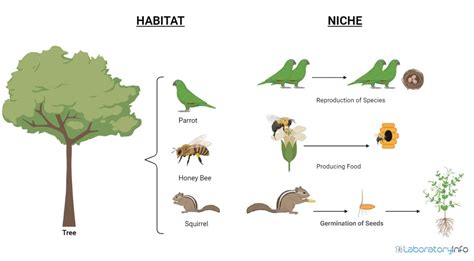
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between a Habitat and a Niche? Understanding Ecological Roles
The terms "habitat" and "niche" are frequently used in ecology, and while closely related, they represent distinct aspects of an organism's existence. Understanding the difference between a habitat and a niche is crucial for comprehending the complexities of ecosystems and the interactions between species. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the definitions, explore the key distinctions, and provide examples to clarify the concepts.
Defining Habitat: Where an Organism Lives
A habitat is simply the physical environment where an organism lives. It encompasses all the biotic and abiotic factors that influence an organism's survival and reproduction. Think of it as the organism's "address" in the ecosystem. A habitat provides the basic necessities for life, including:
Key Components of a Habitat:
- Shelter: Protection from predators, harsh weather conditions, and other environmental stressors. This could be a burrow, a tree hollow, a coral reef, or even a specific microclimate within a larger area.
- Food and Water: Essential resources for sustenance and metabolic processes. The availability of these resources directly influences the carrying capacity of a habitat.
- Space: Sufficient area for foraging, breeding, and avoiding competition. The size and quality of the available space significantly impact an organism's success.
- Appropriate Climate: Temperature, humidity, rainfall, and other climatic factors that are compatible with the organism's physiological tolerance.
Defining Niche: How an Organism Lives
A niche, on the other hand, is much more complex than a habitat. It defines an organism's functional role within its ecosystem. It's not just where an organism lives, but how it lives and interacts with its environment. Consider it the organism's "profession" within the ecosystem. A niche encompasses several crucial aspects:
Dimensions of a Niche:
- Resource Utilization: This involves the specific types of food an organism consumes, how it obtains that food, and the timing of its foraging activity. It also includes the resources it uses for shelter, breeding, and other activities. For example, two bird species might inhabit the same tree (habitat), but one might feed on insects in the canopy while the other feeds on seeds on the ground.
- Interactions with other organisms: This includes predation (being eaten), competition (for resources or mates), parasitism (living on or in another organism), mutualism (a mutually beneficial relationship), and commensalism (one organism benefits while the other is unaffected). Understanding these interactions is critical for understanding the dynamics of the ecosystem.
- Influence on the environment: Organisms actively shape their environment through their activities. A beaver building a dam fundamentally alters the flow of a river, creating a new habitat for various species. Similarly, a decomposer plays a vital role in nutrient cycling, impacting the entire ecosystem.
- Tolerance Limits: Every organism has limits to the environmental conditions it can tolerate. These limits define the boundaries of its niche. For example, a desert cactus has a high tolerance for drought but a low tolerance for frost.
Key Differences: Habitat vs. Niche
The most crucial distinction lies in their scope:
- Habitat: A habitat is a physical space. It's the address.
- Niche: A niche is a functional role. It's the profession.
A habitat can be described simply by its physical characteristics (e.g., "tropical rainforest," "coral reef," "alpine meadow"). Defining a niche requires a far more detailed analysis of the organism's interactions within its environment.
The Fundamental Niche vs. the Realized Niche
In reality, the concept of a niche is often divided into two parts:
-
Fundamental Niche: This represents the potential niche that an organism could occupy if there were no limiting factors such as competition or predation. It describes the full range of conditions and resources an organism could theoretically use.
-
Realized Niche: This describes the actual niche an organism occupies in the presence of limiting factors. It's often smaller than the fundamental niche due to interactions with other species.
Examples to Illustrate the Difference
Let's consider some examples to make the difference between habitat and niche clearer:
Example 1: Two species of Warbler Birds
Habitat: Both the Cape May Warbler and the Bay-breasted Warbler may share the same habitat – a coniferous forest.
Niche: However, their niches differ. The Cape May Warbler feeds primarily on insects high in the canopy, while the Bay-breasted Warbler forages lower in the trees, specializing on different insect species and avoiding direct competition. This difference in foraging behavior defines their distinct niches within the same habitat.
Example 2: Lions and Hyenas
Habitat: Both lions and hyenas inhabit the African savanna. Their habitat is the same.
Niche: However, their niches overlap significantly, leading to competition. Both are apex predators, feeding on similar prey. However, lions are generally more social and hunt cooperatively, while hyenas are more opportunistic scavengers, exhibiting different hunting strategies and social structures. Their overlapping yet distinct niches illustrate the complexity of ecological relationships.
Example 3: Different Plant Species in a Meadow
Habitat: All plants in a meadow share the same habitat—the meadow itself.
Niche: However, different plant species have different niches. Some are adapted to full sun, others to shade. Some have deep roots to access water, others shallow roots. Some might be early bloomers, while others bloom later. These differences allow various plants to coexist within the same habitat, utilizing different resources and occupying distinct niches.
The Importance of Understanding Habitat and Niche
Understanding the distinctions between habitat and niche is essential for:
-
Conservation Biology: Protecting habitats is crucial, but understanding the niches of endangered species allows for more effective conservation strategies. Protecting a habitat without considering the niche of a species is insufficient; the species may still fail if key resources or interactions are missing.
-
Ecosystem Management: Managing ecosystems effectively requires knowledge of the complex interactions between species, which are defined by their niches. Understanding how species interact helps predict the consequences of human intervention or environmental changes.
-
Predicting Invasive Species: Understanding the niches of both native and invasive species helps predict how invasive species might impact native communities. Invasive species often succeed because they exploit unused resources or outcompete native species for crucial resources within the same niche.
Conclusion: Intertwined yet Distinct Concepts
While habitat and niche are interconnected concepts, they represent distinct aspects of an organism's life within an ecosystem. A habitat is the organism's address, its physical location. The niche, on the other hand, is the organism's profession – its role and interactions within that environment. Understanding both is essential for comprehending the intricacies of ecological communities and for developing effective conservation and management strategies. By considering the habitat and niche simultaneously, we gain a far richer and more accurate understanding of how organisms thrive, interact, and shape the world around them.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Electric Field Due To Infinite Line Charge
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Does Gametes Have
Mar 26, 2025
-
Whats The Greatest Common Factor Of 12 And 18
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is 34 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 15
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between A Habitat And A Niche . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
