What Is Prime Factorization Of 88
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
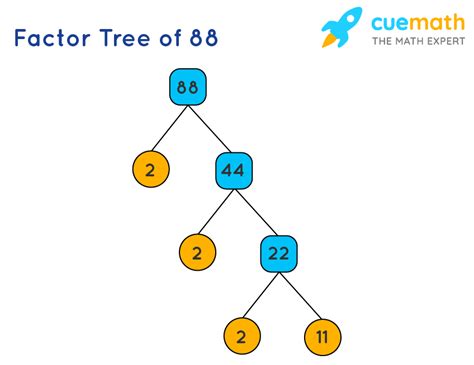
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 88? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory with wide-ranging applications in mathematics and computer science. It involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This article will explore the prime factorization of 88, providing a detailed explanation of the process and highlighting the importance of prime numbers and factorization in various fields. We'll also delve into related concepts and explore some practical examples.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we delve into the prime factorization of 88, let's refresh our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other integers, a concept that forms the basis of prime factorization.
Identifying Prime Numbers
Identifying prime numbers can be challenging for larger numbers. However, several methods exist to determine primality. One common approach is the trial division method, where we check for divisibility by all prime numbers less than the square root of the given number. If no prime number divides the given number without leaving a remainder, it's considered a prime number. More sophisticated algorithms, like the AKS primality test, exist for efficiently determining primality of larger numbers.
Prime Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) as a product of its prime factors. Each composite number has a unique prime factorization; this is a fundamental theorem in number theory. This unique factorization allows for various mathematical operations and calculations to be performed more easily.
The Prime Factorization of 88
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 88. We can use a method known as the factor tree.
-
Start with the number 88: We begin by finding the smallest prime number that divides 88. This is 2.
-
Divide by 2: 88 / 2 = 44.
-
Continue the process: Now we find the smallest prime factor of 44, which is also 2. 44 / 2 = 22.
-
Repeat until we reach a prime number: The smallest prime factor of 22 is 2. 22 / 2 = 11.
-
Final Prime Factor: 11 is a prime number. We've reached the end of our factorization.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 88 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 11, which can be written as 2³ x 11.
Visualizing Prime Factorization with a Factor Tree
A visual representation using a factor tree can make the prime factorization process easier to understand.
88
/ \
2 44
/ \
2 22
/ \
2 11
This tree clearly shows how we repeatedly divide by prime numbers until we are left only with prime numbers as the leaves of the tree.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization might seem like a purely theoretical concept, but it has several practical applications in various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime numbers and their factorization play a critical role in modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms, like RSA, rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring extremely large semiprimes (numbers that are the product of two large prime numbers).
2. Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental to many concepts in number theory, including modular arithmetic, Diophantine equations, and the distribution of prime numbers. Understanding the prime factorization of numbers is crucial for solving many problems in this area.
3. Computer Science
Prime factorization finds its application in algorithms related to data structures, such as hash tables and search algorithms. They also play a role in certain optimization techniques.
4. Mathematics Education
Understanding prime factorization is essential in early mathematics education. It builds a strong foundation in arithmetic, number sense, and algebraic manipulation. It helps students develop their problem-solving skills and lays the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Beyond 88: Exploring other Prime Factorizations
Let's explore the prime factorization of a few more numbers to solidify our understanding:
- Prime Factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
- Prime Factorization of 24: 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2³ x 3
- Prime Factorization of 36: 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
- Prime Factorization of 100: 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 = 2² x 5²
- Prime Factorization of 1000: 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 x 5 = 2³ x 5³
These examples demonstrate how different composite numbers can be broken down into their unique prime factors.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization is crucial for finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
Finding GCD and LCM using Prime Factorization:
To find the GCD of two numbers, we identify the common prime factors and multiply them with the lowest power present. For instance, let's find the GCD of 12 (2² x 3) and 18 (2 x 3²):
- Common prime factors: 2 and 3
- Lowest power of 2: 2¹
- Lowest power of 3: 3¹
- GCD(12, 18) = 2 x 3 = 6
To find the LCM, we identify all prime factors present in the numbers and multiply them with the highest power present. For the same numbers:
- All prime factors: 2 and 3
- Highest power of 2: 2²
- Highest power of 3: 3²
- LCM(12, 18) = 2² x 3² = 36
Conclusion
Prime factorization, though seemingly a simple concept, forms the bedrock of many advanced mathematical and computational applications. Understanding the prime factorization of a number like 88 (2³ x 11) provides insights into its structure and allows for efficient calculations in various contexts. The ability to break down numbers into their prime components offers a powerful tool for solving diverse problems across various disciplines. From cryptography securing our online transactions to simplifying complex mathematical calculations, prime factorization remains a vital concept in mathematics and computer science. Its understanding is fundamental not only for advanced mathematical studies but also for building a strong foundation in basic arithmetic.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Volume Of A Bcc Unit Cell
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is Kinetic Energy Scalar Or Vector
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Are Raw Materials For Photosynthesis
Mar 20, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 5 And 6
Mar 20, 2025
-
25000 Is What Percentage Of 127000
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 88 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
