What Is Prime Factorization Of 66
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
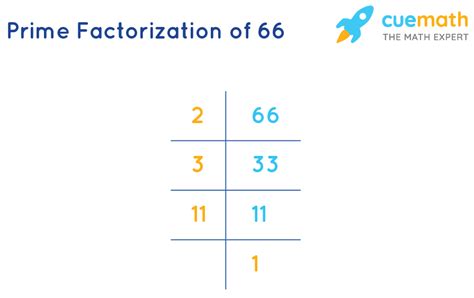
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 66? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Understanding this concept unlocks doors to various mathematical applications, from cryptography to simplifying complex fractions. This article delves deep into the prime factorization of 66, explaining the process, its significance, and extending the concept to more complex scenarios.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before embarking on the prime factorization of 66, it's crucial to define the key terms:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. In other words, it's a number that can be factored into smaller positive integers. For example, 6 is a composite number because it's divisible by 2 and 3.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This unique representation is the prime factorization.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 66
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 66. We can use a factor tree or repeated division to achieve this.
Method 1: Factor Tree
A factor tree visually represents the factorization process.
-
Start with 66: Write 66 at the top of your tree.
-
Find a pair of factors: Find two numbers that multiply to 66. A simple pair is 2 and 33. Branch out from 66 to 2 and 33.
-
Continue factoring: 2 is a prime number, so we stop branching from it. 33 is composite, so we find its factors: 3 and 11. Branch out from 33 to 3 and 11.
-
Identify the prime factors: Both 3 and 11 are prime numbers. The process ends here.
The prime factorization of 66 is therefore 2 x 3 x 11.
Method 2: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until you reach 1.
-
Start with 66: Divide 66 by its smallest prime factor, which is 2. 66 ÷ 2 = 33.
-
Continue dividing: The smallest prime factor of 33 is 3. 33 ÷ 3 = 11.
-
Final prime factor: 11 is a prime number. Dividing 11 by 11 gives 1.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 66 is 2 x 3 x 11.
Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number is more than just a mathematical exercise; it has significant implications in various areas:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization is essential for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
2. Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization helps simplify fractions to their lowest terms by canceling out common factors in the numerator and denominator.
3. Cryptography: Prime factorization forms the basis of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors is what makes these encryption methods secure.
4. Modular Arithmetic: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modular arithmetic, which is used in various fields like computer science and cryptography.
5. Number Theory Research: Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in advanced number theory research, with mathematicians continuously exploring properties and patterns of prime numbers and their factorizations.
Extending the Concept: Factorizing Larger Numbers
The methods used for factoring 66 can be applied to larger numbers, although the process might become more complex. Let's consider an example: finding the prime factorization of 360.
Using the factor tree method:
- Start with 360.
- Factor 360 into 2 and 180.
- Factor 180 into 2 and 90.
- Factor 90 into 2 and 45.
- Factor 45 into 3 and 15.
- Factor 15 into 3 and 5.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 360 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 5, or 2³ x 3² x 5.
Using repeated division:
- 360 ÷ 2 = 180
- 180 ÷ 2 = 90
- 90 ÷ 2 = 45
- 45 ÷ 3 = 15
- 15 ÷ 3 = 5
- 5 ÷ 5 = 1
Again, the prime factorization is 2³ x 3² x 5.
Dealing with Larger Composite Numbers: Advanced Techniques
For extremely large composite numbers, finding the prime factorization becomes computationally intensive. Specialized algorithms are required, and the search for efficient factorization algorithms is an ongoing area of research in computer science and cryptography. Some of these algorithms include:
- Trial division: A straightforward method, but becomes inefficient for large numbers.
- Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm, offering a good balance between speed and efficiency.
- General number field sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers.
These algorithms are far beyond the scope of a simple factorization problem like 66, but understanding their existence highlights the complexity and importance of prime factorization in advanced mathematics and computer science.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 66, while seemingly simple, serves as a gateway to understanding a fundamental concept in number theory with wide-ranging applications. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, the ability to break down numbers into their prime constituents remains a cornerstone of mathematics and its applications in the modern world. Whether you're a student grasping the basics or a researcher delving into the complexities of cryptography, a solid understanding of prime factorization is invaluable. The seemingly simple act of factoring 66 into 2 x 3 x 11 opens up a world of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
250 Square Meters To Square Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Millimeters Are In One Meter
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Milliseconds Are In A Minute
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Copper Have
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Mm In 1 M
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 66 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
