What Is Lcm Of 6 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
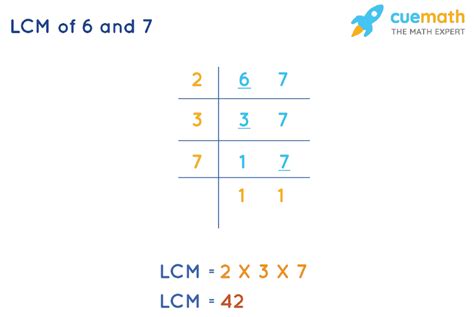
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 6 and 7? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. This article will thoroughly explore the concept of LCM, focusing specifically on finding the LCM of 6 and 7, while also providing a broader understanding of the methods involved. We'll delve into different approaches, explaining the underlying principles clearly and concisely. This will equip you with the skills to calculate the LCM of any two numbers.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific case of 6 and 7, let's solidify our understanding of LCMs. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors.
Think of it like this: Imagine you have two gears, one with 6 teeth and the other with 7 teeth. The LCM represents the number of rotations it takes for both gears to simultaneously return to their starting position. This analogy helps visualize the concept of finding the smallest common multiple.
Key Differences Between LCM and GCD
It's important to distinguish the LCM from the greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF). While the LCM is the smallest common multiple, the GCD is the largest number that divides both integers without leaving a remainder. They are related but distinct concepts. For example, the GCD of 6 and 7 is 1 (as they share no common factors other than 1), whereas their LCM is, as we'll soon discover, 42.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
Several methods can efficiently determine the LCM of two numbers. Let's explore the most common ones, applying them to find the LCM of 6 and 7:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, particularly suitable for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
As we can see, the smallest number that appears in both lists is 42. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 7 is 42. This method is simple to visualize but becomes less efficient with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from these prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 × 3
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together:
LCM(6, 7) = 2 × 3 × 7 = 42
This method is more systematic and less prone to errors, especially when dealing with larger numbers or numbers with multiple prime factors.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a × b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and GCD. We already know that the GCD of 6 and 7 is 1. Therefore:
LCM(6, 7) = (6 × 7) / GCD(6, 7) = 42 / 1 = 42
This formula provides a very efficient way to calculate the LCM once the GCD is known. Finding the GCD can be done using the Euclidean algorithm, which is particularly efficient for larger numbers.
Applications of LCM
Understanding LCMs has practical applications in numerous areas:
- Fraction Simplification: Finding the LCM of the denominators is essential when adding or subtracting fractions.
- Scheduling Problems: Determining when events will coincide (like the gear analogy mentioned earlier). For example, if two buses leave a depot at different intervals, the LCM helps determine when they will depart at the same time.
- Music Theory: The LCM plays a role in understanding musical intervals and harmonies.
- Modular Arithmetic: It is utilized extensively in cryptography and computer science.
- Unit Conversion: LCM aids in converting between different units of measurement smoothly.
Beyond the Basics: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, you simply include all prime factors from all numbers, using the highest power of each. For the formula method, you would need to iteratively calculate the LCM of pairs of numbers. Listing multiples becomes increasingly less practical with more than two numbers.
For example, to find the LCM of 6, 7, and 8:
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 × 3
- Prime factorization of 7: 7
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
LCM(6, 7, 8) = 2³ × 3 × 7 = 8 × 3 × 7 = 168
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM
Calculating the least common multiple is a fundamental skill in mathematics with far-reaching applications. While the listing method is intuitive for small numbers, the prime factorization and formula methods are more efficient and powerful, especially for larger numbers. Understanding the concept of LCM and the various methods for calculating it empowers you to solve a wide range of mathematical problems, from basic arithmetic to more complex scenarios. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for mastering LCM calculations and applying this essential mathematical concept effectively. Remember to choose the method that best suits the situation and the numbers involved. With practice, you'll find calculating LCMs becomes second nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 18 And 48
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is A Multiple Of 3
Mar 04, 2025
-
Six Words To Describe Your Child
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is One Singular Comon Noun
Mar 04, 2025
-
Whoch Of The Following Has The Units Og G Mol
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Lcm Of 6 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
