What Is Larger 3/8 Or 1/2
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
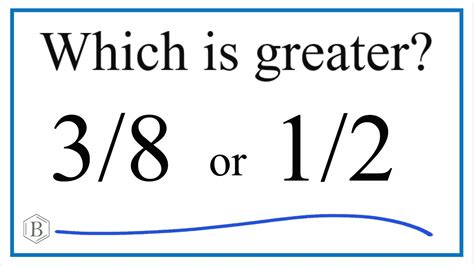
Table of Contents
What's Larger: 3/8 or 1/2? A Deep Dive into Fraction Comparison
Determining which fraction is larger, 3/8 or 1/2, might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the underlying principles of fraction comparison is crucial for developing a strong foundation in mathematics. This article will not only answer the question definitively but also explore various methods for comparing fractions, providing you with the tools to tackle similar problems with confidence. We'll delve into visual representations, equivalent fractions, decimal conversion, and even touch upon the application of these concepts in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Refresher
Before we embark on comparing 3/8 and 1/2, let's refresh our understanding of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two key components:
- Numerator: The top number indicates the number of parts you have.
- Denominator: The bottom number represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For example, in the fraction 3/8, 3 is the numerator (the number of parts we have) and 8 is the denominator (the total number of equal parts).
Visualizing the Fractions: The Pizza Analogy
One of the simplest ways to compare fractions is through visualization. Imagine two pizzas, both of the same size.
- Pizza 1 (representing 1/2): Cut this pizza into two equal slices. You take one slice. You have 1/2 of the pizza.
- Pizza 2 (representing 3/8): Cut this pizza into eight equal slices. You take three slices. You have 3/8 of the pizza.
Which pizza has a larger portion? Looking at the two pizzas, it's visually apparent that 1/2 is larger than 3/8. Half of a pizza is clearly bigger than three-eighths of a pizza.
Finding a Common Denominator: The Key to Comparison
While visualization is helpful, it's not always practical for larger or more complex fractions. A more robust method involves finding a common denominator. A common denominator is a number that is a multiple of both denominators.
For 3/8 and 1/2, the denominators are 8 and 2. The least common multiple (LCM) of 8 and 2 is 8. We can convert both fractions to have a denominator of 8:
- 1/2: To convert the denominator from 2 to 8, we multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 4: (1 x 4) / (2 x 4) = 4/8
Now we can easily compare:
- 3/8
- 4/8
Since 4/8 is greater than 3/8, we confirm that 1/2 (which is equivalent to 4/8) is larger than 3/8.
Converting to Decimals: Another Approach
Another effective method for comparing fractions is converting them to decimals. To convert a fraction to a decimal, simply divide the numerator by the denominator.
- 3/8 = 0.375
- 1/2 = 0.5
By comparing the decimal values, it's evident that 0.5 (1/2) is larger than 0.375 (3/8).
Real-World Applications: Where Fraction Comparison Matters
The ability to compare fractions isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often require precise measurements, necessitating the ability to compare fractions of cups or teaspoons. Knowing whether 1/4 cup is more or less than 2/8 cup is crucial for achieving desired results.
-
Construction and Engineering: In construction and engineering, accurate measurements are essential for safety and functionality. Comparing fractions of inches or meters is commonplace in blueprints and construction plans.
-
Finance: Understanding fractions is vital for managing budgets, calculating interest rates, and comprehending financial statements. Analyzing stock market performance often involves comparing fractions or percentages.
-
Data Analysis: Many fields, including science, statistics, and business, involve analyzing data expressed as fractions or percentages. The ability to accurately compare and interpret these data points is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Beyond the Basics: Comparing More Complex Fractions
The techniques discussed above – visualization, common denominators, and decimal conversion – provide a strong foundation for comparing fractions. However, let's extend our understanding to handle more complex scenarios.
Consider comparing 5/12 and 7/18. Finding the least common denominator (LCM) becomes slightly more challenging but follows the same principle:
- Find the prime factorization of each denominator: 12 = 2 x 2 x 3; 18 = 2 x 3 x 3
- Identify the highest power of each prime factor: The highest power of 2 is 2², and the highest power of 3 is 3².
- Multiply the highest powers together: 2² x 3² = 4 x 9 = 36. Therefore, the LCM of 12 and 18 is 36.
Now, convert both fractions to have a denominator of 36:
- 5/12 = (5 x 3) / (12 x 3) = 15/36
- 7/18 = (7 x 2) / (18 x 2) = 14/36
Therefore, 15/36 (5/12) is larger than 14/36 (7/18).
Mastering Fraction Comparison: Tips and Tricks
-
Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering fraction comparison. Work through various examples, starting with simple fractions and gradually progressing to more complex ones.
-
Utilize Visual Aids: Diagrams, charts, and other visual aids can help solidify your understanding and make comparing fractions more intuitive.
-
Embrace Different Methods: Become comfortable using various methods—common denominators, decimal conversion, and visualization—to compare fractions. The best method often depends on the specific fractions you're working with.
-
Check Your Work: Always double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy. Errors in calculations can lead to incorrect conclusions.
-
Seek Help When Needed: Don't hesitate to ask for help from teachers, tutors, or online resources if you're struggling with a particular concept.
Conclusion: A Solid Foundation in Fractions
The ability to compare fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics with far-reaching applications in various aspects of life. By mastering the techniques discussed in this article—visualization, finding common denominators, and converting to decimals—you'll develop a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and confidently navigating real-world scenarios involving fractions. Remember, practice and a willingness to explore different approaches are key to achieving proficiency in fraction comparison. So, grab a pizza, some paper, and start practicing! You'll be amazed at how quickly your skills improve.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Letter Words Beginning With Pra
Mar 25, 2025
-
Alternation Of Generations Means That Plants Produce
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Factors Of 225
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Does Lv Mean In Roman Numerals
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Interrelated
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Larger 3/8 Or 1/2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
