How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Interrelated
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
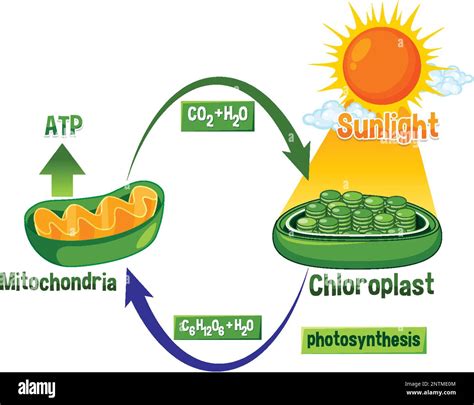
Table of Contents
How Are Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Interrelated?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental biological processes that are intricately linked and essential for life on Earth as we know it. While seemingly opposite processes, they are, in fact, complementary reactions that form a cyclical exchange of energy and matter within ecosystems. Understanding their interrelationship is crucial to grasping the delicate balance of life and the flow of energy through the biosphere. This article delves deep into the interconnectedness of these two vital processes, exploring their mechanisms, products, and significance in maintaining the Earth's ecological equilibrium.
The Fundamentals: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Before exploring their interconnectedness, let's briefly review each process individually.
Photosynthesis: Capturing Solar Energy
Photosynthesis is the remarkable process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This conversion occurs within chloroplasts, specialized organelles containing chlorophyll, the green pigment that absorbs sunlight. The process can be summarized as follows:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation illustrates that photosynthesis utilizes carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere and water (H₂O) to produce glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), a simple sugar that serves as the primary energy source for plants, and oxygen (O₂), a byproduct crucial for aerobic respiration in other organisms. The process is divided into two main stages:
-
Light-dependent reactions: These reactions capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). This stage also produces oxygen as a byproduct.
-
Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): This stage uses the ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions to convert CO₂ into glucose. This process does not directly require light but relies on the products of the light-dependent reactions.
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms break down glucose and other organic molecules to release the stored chemical energy. This energy is then used to power various cellular activities, including growth, movement, and reproduction. The process primarily occurs in the mitochondria, often called the "powerhouses" of the cell. The overall equation for cellular respiration is:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP
This equation demonstrates that cellular respiration consumes glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP, the energy currency of the cell. Cellular respiration is broadly categorized into several stages:
-
Glycolysis: The initial breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, a smaller molecule, occurs in the cytoplasm. This stage generates a small amount of ATP.
-
Pyruvate oxidation: Pyruvate is further processed to acetyl-CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle.
-
Krebs cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): This cycle further oxidizes acetyl-CoA, releasing CO₂ and generating more ATP and electron carriers (NADH and FADH₂).
-
Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation: This final stage utilizes the electron carriers from the Krebs cycle to generate a large amount of ATP through chemiosmosis. This process also requires oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
The Interdependence: A Cyclical Exchange
The beauty of photosynthesis and cellular respiration lies in their reciprocal relationship. They form a cyclical exchange of energy and matter, essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth.
Photosynthesis Provides the Fuel for Cellular Respiration
The glucose produced during photosynthesis serves as the primary fuel source for cellular respiration in plants and animals. Animals obtain glucose directly by consuming plants or other animals that consume plants. This glucose then undergoes cellular respiration to release the stored chemical energy in the form of ATP, powering various cellular processes.
Cellular Respiration Provides the Inputs for Photosynthesis
Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) as a byproduct. This CO₂ is then utilized by plants during photosynthesis, completing the cycle. Similarly, the water (H₂O) produced during cellular respiration is also essential for photosynthesis.
Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide: A Crucial Exchange
The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is vital for aerobic cellular respiration in most organisms. This oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling the efficient generation of ATP. Conversely, the carbon dioxide produced during cellular respiration is crucial for photosynthesis, providing the carbon source for glucose synthesis.
Ecological Significance of the Interrelationship
The interrelationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration has profound ecological implications:
-
Maintaining atmospheric composition: Photosynthesis replenishes oxygen in the atmosphere, while cellular respiration consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. This delicate balance is crucial for sustaining life as we know it. The disruption of this balance, for example through deforestation or excessive burning of fossil fuels, can lead to significant environmental consequences such as climate change.
-
Energy flow through ecosystems: Photosynthesis captures solar energy, converting it into chemical energy stored in glucose. This energy is then transferred to other organisms through the food chain as animals consume plants and other animals. Cellular respiration releases this stored energy, fueling the life processes of all organisms.
-
Carbon cycle regulation: Photosynthesis and cellular respiration play a critical role in the carbon cycle. Photosynthesis removes CO₂ from the atmosphere, while cellular respiration releases CO₂ back into the atmosphere. This cycle maintains the balance of carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, although human activities have disrupted this balance, leading to an increase in atmospheric CO₂ and global warming.
-
Nutrient cycling: Both processes contribute to nutrient cycling. Photosynthesis incorporates essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus into plant tissues, making them available to other organisms in the food chain. Cellular respiration releases some of these nutrients back into the environment, facilitating their reuse.
Variations and Adaptations
While the basic principles of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are conserved across most organisms, there are variations and adaptations depending on the specific environment and the organism's metabolic needs. For example:
-
C4 and CAM photosynthesis: These specialized photosynthetic pathways have evolved in plants adapted to hot, dry environments to minimize water loss while maximizing carbon dioxide uptake.
-
Anaerobic respiration: Some organisms can carry out cellular respiration in the absence of oxygen, using alternative electron acceptors. This process is less efficient than aerobic respiration but provides a means of energy generation in oxygen-poor environments.
-
Fermentation: This anaerobic process also produces energy from glucose in the absence of oxygen. However, it's significantly less efficient than cellular respiration and produces byproducts such as lactic acid or ethanol.
Conclusion: A Delicate Balance of Life
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes intricately linked, forming a cyclical exchange of energy and matter that sustains life on Earth. Understanding their interrelationship is crucial for appreciating the delicate balance of ecosystems and the importance of maintaining this balance for the continued health of our planet. The disruption of these processes, whether through human activities or natural events, can have far-reaching consequences. Continued research and efforts to understand and protect these essential biological processes are critical for securing the future of life on Earth. Further research into the intricacies of these processes and their interactions with other biological and environmental factors continues to reveal new insights into the complexity and interconnectedness of life on our planet. The ongoing exploration of these processes remains vital for addressing significant ecological challenges and ensuring a sustainable future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 31
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of Petals On A Flower
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Take Place In
Mar 25, 2025
-
Words With Ing At The End
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Are Characteristics Of A Prokaryotic Cell Select Three Options
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Interrelated . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
