What Is Area Model In Math
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
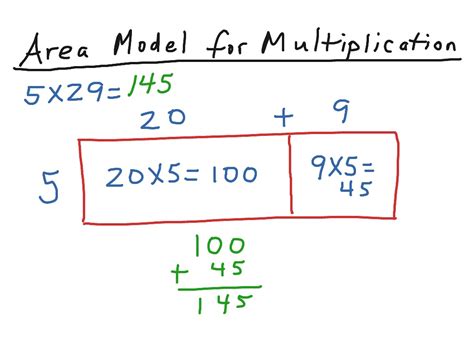
Table of Contents
What is the Area Model in Math? A Comprehensive Guide
The area model in math is a visual and intuitive method for representing multiplication and division problems, particularly useful for understanding the distributive property and working with multi-digit numbers. Unlike traditional algorithms, which can sometimes feel abstract, the area model offers a concrete, geometric representation that makes mathematical concepts easier to grasp. This guide delves deep into the area model, explaining its applications, benefits, and how it can be used to tackle various mathematical challenges.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Area and Multiplication
At its core, the area model leverages the concept of area—the space inside a two-dimensional shape. We know that the area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length and width. This simple geometric principle forms the bedrock of the area model's effectiveness.
The Area Model as a Visual Representation of Multiplication:
Imagine you need to multiply 12 by 15. Instead of using the standard algorithm, we can represent this problem as a rectangle with dimensions 12 units by 15 units. We then break down both numbers into their place values (tens and ones):
- 12 becomes 10 + 2
- 15 becomes 10 + 5
Now, we divide our rectangle into four smaller rectangles:
- A rectangle with dimensions 10 x 10 (representing 10 x 10 = 100)
- A rectangle with dimensions 10 x 5 (representing 10 x 5 = 50)
- A rectangle with dimensions 2 x 10 (representing 2 x 10 = 20)
- A rectangle with dimensions 2 x 5 (representing 2 x 5 = 10)
By adding the areas of these smaller rectangles (100 + 50 + 20 + 10), we get the total area, which represents the product of 12 and 15: 180.
This visual breakdown makes it easier to understand how the distributive property works in multiplication. The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. In our example:
12 x 15 = 12(10 + 5) = (12 x 10) + (12 x 5) = 120 + 60 = 180
The area model perfectly illustrates this process.
Visualizing the Process: A Step-by-Step Example
Let's multiply 23 by 34 using the area model:
-
Break down the numbers: 23 becomes 20 + 3, and 34 becomes 30 + 4.
-
Draw a rectangle: Draw a rectangle and divide it into four smaller rectangles based on the decomposed numbers. Label the sides of the rectangles with the decomposed parts (20 and 3 on one side, 30 and 4 on the other).
-
Calculate the area of each smaller rectangle:
- 20 x 30 = 600
- 20 x 4 = 80
- 3 x 30 = 90
- 3 x 4 = 12
-
Add the areas: Add the areas of the four smaller rectangles: 600 + 80 + 90 + 12 = 782.
Therefore, 23 x 34 = 782.
Beyond Basic Multiplication: Extending the Area Model's Use
The versatility of the area model extends far beyond basic multiplication. It's a powerful tool that can be applied to:
1. Multiplication of Larger Numbers:
The area model effortlessly handles larger numbers, making multiplication less daunting. For example, multiplying 123 by 456 can be visualized by breaking down each number into hundreds, tens, and ones, creating a larger rectangle divided into nine smaller rectangles. Each smaller rectangle represents a simpler multiplication problem that can be solved easily. The sum of the areas of these nine smaller rectangles provides the final answer.
2. Multiplication with Decimals:
The area model adapts seamlessly to multiplication with decimals. Treat the decimal parts as fractions of the whole numbers and incorporate them into the area model. The resulting calculation remains consistent with the principles already outlined.
3. Multiplication of Polynomials (Algebra):
The area model proves particularly useful in algebra for multiplying polynomials. For instance, consider the expression (x + 2)(x + 3). This can be represented by a rectangle with sides (x + 2) and (x + 3). The areas of the smaller rectangles would represent the product of the individual terms, providing a visual understanding of how to expand the expression into x² + 5x + 6.
4. Division:
While primarily known for multiplication, the area model can also effectively represent division. Instead of starting with the area, we start with the product (the total area) and work backwards to find the missing dimensions. This approach aids in building conceptual understanding of division as the inverse of multiplication. This method is particularly helpful in visualizing problems with remainders.
5. Understanding Fractions:
The area model can be used to visualize fractions, particularly useful in operations such as fraction multiplication and addition. By representing fractions as parts of a whole (the area), students can intuitively grasp the concepts of equivalent fractions, simplifying fractions, and performing operations involving fractions.
Benefits of Using the Area Model
The area model offers numerous advantages over traditional algorithms:
-
Visual Representation: The visual nature of the area model makes abstract mathematical concepts more concrete and easier to understand.
-
Improved Conceptual Understanding: Instead of rote memorization, the area model promotes conceptual understanding of multiplication and division, fostering deeper learning.
-
Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: It provides a systematic approach to solving complex multiplication and division problems.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: It applies to a wide range of mathematical problems, from simple multiplication to complex polynomial multiplication.
-
Reduced Errors: The structured approach reduces the likelihood of errors commonly made with traditional algorithms.
Addressing Common Challenges and Misconceptions
While the area model is highly effective, some misconceptions can arise:
-
Incorrect Decomposition: Students might incorrectly decompose the numbers, leading to inaccurate calculations. Careful attention to place value is essential.
-
Misalignment of Rectangles: Inaccurate drawing or labeling of rectangles can lead to errors. Encouraging neat and labelled diagrams is crucial.
-
Difficulty with Larger Numbers: When dealing with very large numbers, the area model might become unwieldy. Teachers should guide students in breaking down larger problems into smaller, manageable chunks.
Conclusion: Empowering Students with Visual Math
The area model offers a potent alternative to traditional methods, transforming the often-abstract concepts of multiplication and division into concrete, manageable tasks. Its visual nature, inherent flexibility, and intuitive approach to problem-solving make it an invaluable tool for educators and students alike. By embracing the area model, educators can foster a deeper understanding of mathematical principles and empower students to confidently navigate the world of numbers and equations. Its use extends beyond elementary arithmetic, providing a solid foundation for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts in algebra and beyond. The area model is not just a method; it's a powerful visualization tool that facilitates genuine mathematical understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Area Model In Math . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
