What Is A Polygon That Has 9 Sides
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
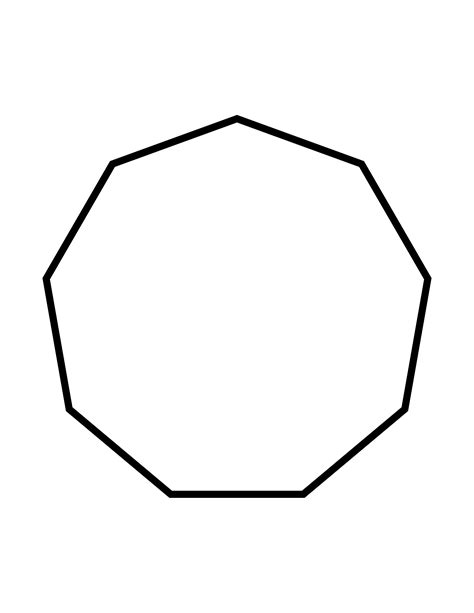
Table of Contents
What is a Nonagon? A Deep Dive into the 9-Sided Polygon
A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting straight line segments. We encounter polygons of various shapes and sizes in our everyday lives, from the squares of a chessboard to the triangles of a traffic sign. But what about a polygon with nine sides? This fascinating shape, known as a nonagon, holds a unique place in the world of geometry. This comprehensive article will delve into the properties, characteristics, types, and applications of nonagons, providing a complete understanding of this often-overlooked polygon.
Understanding the Basics: Defining a Nonagon
A nonagon, also known as an enneagon, is a nine-sided polygon. This means it's a two-dimensional shape with nine straight edges and nine vertices (points where the edges meet). Like other polygons, nonagons can be classified based on their properties, specifically their angles and side lengths.
Key Characteristics of a Nonagon
- Number of Sides: 9
- Number of Vertices: 9
- Number of Angles: 9
- Sum of Interior Angles: 1260 degrees (calculated using the formula (n-2) * 180°, where 'n' is the number of sides)
- Sum of Exterior Angles: 360 degrees (This is true for all polygons)
Types of Nonagons: Regular vs. Irregular
Nonagons, like other polygons, are categorized into two main types: regular and irregular.
Regular Nonagon
A regular nonagon is a nonagon with all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure. Each interior angle of a regular nonagon measures 140 degrees (1260° / 9 = 140°). The symmetry of a regular nonagon makes it aesthetically pleasing and frequently used in design. Its perfectly balanced form is often seen in architectural and artistic contexts. Constructing a perfect regular nonagon using only a compass and straightedge is, however, impossible. This is because 9 is not a Fermat prime.
Irregular Nonagon
An irregular nonagon is a nonagon where the sides and angles are not all equal. This means the lengths of its sides and the measures of its interior angles can vary significantly. Irregular nonagons are far more common than regular ones in the natural world and in everyday objects. Their diverse shapes allow them to adapt to various situations and contexts.
Exploring the Geometry of Nonagons: Angles and Sides
The geometry of a nonagon is governed by the relationships between its sides and angles. Understanding these relationships is crucial for solving problems involving nonagons.
Interior Angles
As mentioned earlier, the sum of the interior angles of any nonagon is 1260 degrees. In a regular nonagon, each interior angle measures 140 degrees. In irregular nonagons, the individual angles can vary, but their sum will always remain 1260 degrees.
Exterior Angles
The exterior angles of a nonagon, like all polygons, always add up to 360 degrees. An exterior angle is formed by extending one side of the polygon and measuring the angle between the extended side and the adjacent side.
Diagonals
A diagonal is a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. A nonagon has a significant number of diagonals. The formula for calculating the number of diagonals in an n-sided polygon is n(n-3)/2. Therefore, a nonagon has 27 diagonals (9(9-3)/2 = 27). These diagonals divide the nonagon into numerous smaller triangles and quadrilaterals, which can be useful in solving geometric problems.
Constructing a Nonagon: Methods and Challenges
Constructing a regular nonagon using only a compass and straightedge is impossible. This is a consequence of the fact that a regular nonagon cannot be constructed using only compass and straightedge constructions. While approximate constructions are possible, achieving perfect accuracy is not feasible with these basic tools. More advanced methods, such as using specialized tools or employing trigonometric calculations, are necessary for precise construction.
Applications of Nonagons in Real Life and Design
Despite its complexity, the nonagon finds applications in various fields.
Architecture and Design
Nonagons are less common in architecture compared to polygons with fewer sides, but they can be found in some unique designs, especially in more modern buildings where unconventional shapes are embraced. Often, aspects of a nonagon’s shape are incorporated rather than a perfect nonagon.
Art and Nature
While not as prevalent as some other shapes in nature, certain natural formations might exhibit approximate nonagonal symmetry. More often, the nonagon features in artistic design where the balance and visual interest of its shape can be creatively exploited. Tessellations using nonagons, though not easily created, can create stunning visual patterns.
Engineering and Technology
In engineering, the nonagon may find application in the design of certain mechanical components or structures where the unique properties of this shape offer advantages. However, this is less common compared to simpler polygons.
Games and Puzzles
Nonagons can feature in puzzles and games, offering an interesting challenge due to their complex angles and sides.
Nonagons in Advanced Mathematics: Further Exploration
Beyond basic geometry, nonagons play a role in more advanced mathematical concepts.
Trigonometry and Geometry
The trigonometric ratios and geometric properties of nonagons provide opportunities for deeper exploration and mathematical problem-solving. Analyzing the angles, areas, and relationships within a nonagon provides insights into broader mathematical principles.
Group Theory and Symmetry
The symmetries of a regular nonagon are studied in group theory, a branch of abstract algebra. Understanding the symmetries reveals valuable information about the nonagon's structure and properties.
Number Theory and Constructions
The impossibility of constructing a regular nonagon with a compass and straightedge is linked to number theory and the specific mathematical properties of the number nine.
Conclusion: The Underrated Charm of the Nonagon
The nonagon, while often overlooked compared to more familiar polygons, offers a unique and fascinating exploration into the world of geometry. Its characteristics, from its interior angles and side lengths to its numerous diagonals, present a rich field for mathematical investigation. Though constructing a perfect regular nonagon presents certain challenges, its irregular forms are abundantly present in various aspects of our lives, often subtly influencing design and structure. By understanding the properties and applications of nonagons, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty and complexity found within this often-unsung nine-sided polygon. Its role in advanced mathematical concepts further emphasizes its importance in a broader mathematical context, demonstrating its relevance well beyond basic geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Conservative And Non Conservative Forces Examples
Mar 17, 2025
-
In Math The Word Dilate Means To
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is Square Root Of 9 A Rational Number
Mar 17, 2025
-
5 Letter Word With Er At The End
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Quadrilateral With Parallel Opposite Sides
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Polygon That Has 9 Sides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
