What Is A Factor Of 98
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
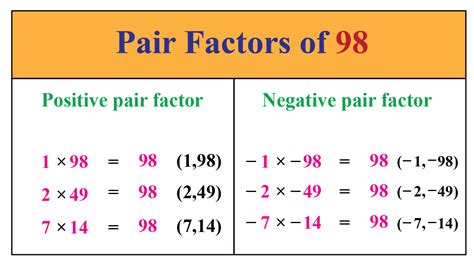
Table of Contents
What is a Factor of 98? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 98. However, understanding the concept of factors goes beyond simple division; it delves into the fundamental principles of number theory, offering insights into prime factorization, divisibility rules, and the very structure of our number system. This article will explore what constitutes a factor of 98, explain the methods for finding all its factors, and extend the discussion to broader concepts within number theory.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we pinpoint the factors of 98, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental terms. A factor (or divisor) of a number is an integer that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number and get a whole number as the result, the number you divided by is a factor. Divisibility, then, is the property of one number being completely divisible by another.
For instance, 2 is a factor of 10 because 10 ÷ 2 = 5 (a whole number). Similarly, 5 is also a factor of 10. Numbers that have only two factors, 1 and themselves, are known as prime numbers. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, and 11. Numbers with more than two factors are called composite numbers. 98, as we will see, falls into this category.
Finding the Factors of 98: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several approaches to identify all the factors of 98. Let's explore the most common and effective methods:
1. The Trial Division Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We systematically test each integer, starting from 1, to see if it divides 98 without leaving a remainder. If it does, we've found a factor.
- 1: 98 ÷ 1 = 98 (1 is a factor)
- 2: 98 ÷ 2 = 49 (2 is a factor)
- 3: 98 ÷ 3 = 32.666... (3 is not a factor)
- 4: 98 ÷ 4 = 24.5 (4 is not a factor)
- 5: 98 ÷ 5 = 19.6 (5 is not a factor)
- 6: 98 ÷ 6 = 16.333... (6 is not a factor)
- 7: 98 ÷ 7 = 14 (7 is a factor)
- 8: 98 ÷ 8 = 12.25 (8 is not a factor)
- 9: 98 ÷ 9 = 10.888... (9 is not a factor)
- 10: 98 ÷ 10 = 9.8 (10 is not a factor)
- 11: 98 ÷ 11 = 8.909... (11 is not a factor)
- 12: 98 ÷ 12 = 8.166... (12 is not a factor)
- 13: 98 ÷ 13 = 7.538... (13 is not a factor)
- 14: 98 ÷ 14 = 7 (14 is a factor)
- And so on...
Notice that after 14, the factors will start to repeat (as 14 x 7 = 98, mirroring the earlier 7 x 14). Therefore, we've found all the factors.
2. Prime Factorization
This is a more elegant and efficient method, especially for larger numbers. Prime factorization involves breaking down a number into its prime factors – the prime numbers that multiply together to give the original number.
To find the prime factorization of 98, we start by dividing by the smallest prime number, 2:
98 ÷ 2 = 49
Now, 49 is not divisible by 2, 3, or 5. However, it is divisible by 7:
49 ÷ 7 = 7
7 is a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 98 is 2 x 7 x 7, or 2 x 7².
Once we have the prime factorization, finding the factors becomes easier. We can systematically combine the prime factors in different ways:
- 1 (always a factor)
- 2
- 7
- 7 x 7 = 49
- 2 x 7 = 14
- 2 x 7 x 7 = 98 (always a factor)
Therefore, the factors of 98 are 1, 2, 7, 14, 49, and 98.
3. Using Factor Pairs
This method utilizes the concept that factors always come in pairs. If 'a' is a factor of a number 'n', then 'n/a' is also a factor. We find one factor and immediately know its pair.
We start with 1 (which always pairs with the number itself):
- 1 and 98
Then we try other numbers:
- 2 and 49
- 7 and 14
We've found all the factor pairs, hence all the factors.
Extending the Concept: Applications and Significance of Factors
Understanding factors has numerous applications across various mathematical fields and real-world scenarios:
- Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator allows for fraction simplification. For instance, if we need to simplify 98/196, finding that the GCF is 98 allows us to simplify it to 1/2.
- Solving Equations: Factors are crucial in solving algebraic equations, especially when factoring quadratic expressions or finding roots of polynomials.
- Number Theory: Factors are at the heart of many number theory concepts such as perfect numbers (whose factors add up to the number itself), amicable numbers (pairs of numbers where the sum of factors of one equals the other, and vice versa), and highly composite numbers (numbers with more factors than any smaller positive integer).
- Cryptography: Factorization plays a significant role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption, where the security relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
- Computer Science: Efficient algorithms for factoring large numbers are essential in various computer science applications, including cryptography and primality testing.
Divisibility Rules and their Relevance to Finding Factors
Divisibility rules are shortcuts for determining if a number is divisible by certain integers without performing long division. Knowing these rules can significantly speed up the process of finding factors. Here are some relevant divisibility rules:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8). 98 is divisible by 2.
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. 9 + 8 = 17, which is not divisible by 3, so 98 is not divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5. 98 is not divisible by 5.
- Divisibility by 7: There isn't a simple divisibility rule for 7, but we can perform the division directly. 98 is divisible by 7.
- Divisibility by 11: A number is divisible by 11 if the alternating sum of its digits is divisible by 11. (9 - 8 = 1), not divisible by 11.
Conclusion: Beyond the Factors of 98
Finding the factors of 98, while seemingly a basic arithmetic exercise, opens a gateway to a deeper understanding of number theory. The various methods explored—trial division, prime factorization, and using factor pairs—illustrate different approaches to problem-solving and highlight the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts. The applications of factors extend far beyond simple division, impacting fields from cryptography to computer science. Mastering the art of finding factors lays a strong foundation for tackling more advanced mathematical challenges and appreciating the underlying structure of our number system. Remember, every number holds a unique story, and understanding its factors is key to unlocking that story.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Differences Between Vertebrae Cervical Thoracic Lumbar
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Colour Is An Animal Cell
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Degrees Are In A Parallelogram
Mar 20, 2025
-
Words That End In I N G
Mar 20, 2025
-
Group Of Baboons Is Called What
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Factor Of 98 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
