What Is A Factor Of 34
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
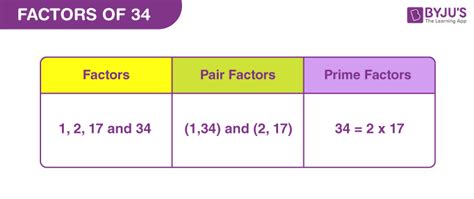
Table of Contents
What is a Factor of 34? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for a relatively small number like 34. However, understanding the concept of factors unlocks a gateway to a fascinating world of number theory, with implications far beyond basic arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will explore what factors are, how to find them, and delve into the mathematical concepts surrounding the factors of 34 and beyond. We'll explore the prime factorization, divisors, and the broader significance of these concepts in mathematics and computer science.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we dive into the specifics of 34, let's establish a firm understanding of what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any integer that divides that number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's a number that can be multiplied by another whole number to produce the original number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because:
- 1 x 12 = 12
- 2 x 6 = 12
- 3 x 4 = 12
These pairs represent all the ways we can multiply two whole numbers together to get 12. Notice that we include both 1 and the number itself as factors.
Finding the Factors of 34: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's focus on our target number: 34. To find its factors, we can systematically check each integer from 1 up to 34, looking for those that divide 34 evenly. Alternatively, a more efficient approach is to consider pairs of factors.
-
Start with 1: 1 is always a factor of any number. 1 x 34 = 34.
-
Check for 2: 34 is an even number, so 2 is a factor. 2 x 17 = 34.
-
Check for 3: 34 divided by 3 leaves a remainder, so 3 is not a factor.
-
Check for other numbers: We can continue checking, but since we've already found 17 (half of 34), we know that we've discovered all pairs of factors. Any number larger than 17 wouldn't be a factor of 34.
Therefore, the factors of 34 are 1, 2, 17, and 34.
Prime Factorization: Uncovering the Fundamental Building Blocks
The concept of prime factorization is crucial in number theory. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
Let's find the prime factorization of 34:
34 can be expressed as 2 x 17. Both 2 and 17 are prime numbers. Therefore, the prime factorization of 34 is 2 x 17.
This prime factorization is unique; every composite number (a number that is not prime) has only one unique prime factorization. This fundamental theorem of arithmetic is a cornerstone of number theory.
Divisors: Another Perspective on Factors
The term "divisor" is often used interchangeably with "factor." Both refer to a number that divides another number without leaving a remainder. Therefore, the divisors of 34 are the same as its factors: 1, 2, 17, and 34.
Applications of Factors and Number Theory
Understanding factors and prime factorization isn't just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers and factorization play a critical role in modern cryptography, forming the basis of encryption algorithms used to secure online communication. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the foundation of the security of many encryption systems.
-
Computer Science: Number theory concepts, including prime factorization, are essential in algorithm design and optimization. Many computational tasks can be efficiently performed by leveraging the properties of prime numbers and factors.
-
Mathematics: Factorization and related concepts underpin many areas of higher mathematics, including modular arithmetic, abstract algebra, and algebraic number theory.
-
Music Theory: Surprisingly, even music theory has connections to number theory. The relationships between different musical intervals can be understood using concepts related to factors and ratios.
Beyond 34: Exploring Factors of Larger Numbers
The techniques used to find the factors of 34 can be applied to larger numbers, although the process becomes more computationally intensive as the numbers get bigger. For larger numbers, efficient algorithms and computational tools are often used.
For example, finding the factors of a number like 123456789 would require more sophisticated methods than simple trial division. Advanced techniques involving sieve algorithms and other optimization strategies are employed for this purpose.
Conclusion: The Significance of Factors in Mathematics and Beyond
The seemingly simple task of finding the factors of 34 reveals a deeper understanding of number theory and its far-reaching implications. From the basic concept of divisibility to the sophisticated world of cryptography and computer science, the principles of factors and prime factorization form the foundation of many critical fields. Understanding these concepts opens a world of possibilities for exploring the intricate relationships within the realm of numbers and their applications in the wider world. The factors of 34—1, 2, 17, and 34—represent more than just simple divisors; they are building blocks that contribute to a larger mathematical structure with far-reaching consequences. Whether you're a student of mathematics, a computer scientist, or simply someone fascinated by numbers, grasping the significance of factors is an essential step towards a deeper appreciation of the mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Push Or A Pull Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Factor Of 34 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
