What Is A Consecutive Odd Integer
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
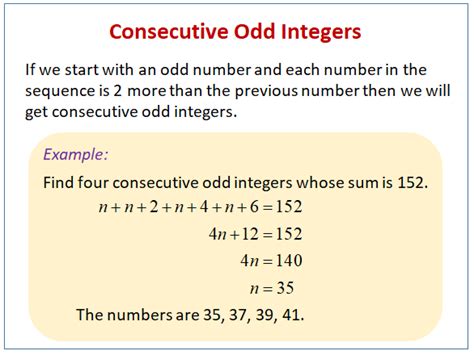
Table of Contents
What is a Consecutive Odd Integer? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Consecutive odd integers are a fundamental concept in number theory and algebra, forming the basis for numerous mathematical problems and applications. Understanding their properties and how to work with them is crucial for anyone pursuing mathematical studies or simply wanting to expand their mathematical knowledge. This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, properties, and applications of consecutive odd integers, providing clear explanations and examples to solidify your understanding.
Defining Consecutive Odd Integers
Simply put, consecutive odd integers are a sequence of odd numbers where each number is two more than the preceding number. Odd integers are whole numbers that are not divisible by 2. They can be represented in the form 2n + 1, where 'n' is any integer (0, 1, 2, 3,...).
Therefore, a sequence of consecutive odd integers can be expressed as:
2n + 1, 2n + 3, 2n + 5, 2n + 7,...
Where 'n' is an integer. Let's illustrate this with an example:
If n = 1, the sequence becomes: 3, 5, 7, 9,...
If n = 0, the sequence becomes: 1, 3, 5, 7,...
If n = -1, the sequence becomes: -1, 1, 3, 5,...
This simple formula allows us to represent any sequence of consecutive odd integers, regardless of its starting point. This foundational understanding will be key to tackling more complex problems.
Properties of Consecutive Odd Integers
Consecutive odd integers exhibit several key properties that are useful in problem-solving:
1. The Difference is Always 2
The most fundamental property is that the difference between any two consecutive odd integers is always 2. This is a direct consequence of their definition; each subsequent integer is obtained by adding 2 to the previous one.
2. Sum of Consecutive Odd Integers
The sum of the first 'k' consecutive odd integers is always equal to k². This is a remarkable property that has a geometric interpretation and can be proven through mathematical induction. For instance:
- 1 = 1²
- 1 + 3 = 4 = 2²
- 1 + 3 + 5 = 9 = 3²
- 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 16 = 4²
And so on. This pattern holds true for any number of consecutive odd integers, starting from 1.
3. Representation using Algebra
As mentioned earlier, consecutive odd integers can be elegantly represented algebraically. This allows us to translate word problems into solvable equations. For example, if we have three consecutive odd integers, they can be expressed as:
- x
- x + 2
- x + 4
Where 'x' represents the first odd integer in the sequence.
4. Parity Considerations
All consecutive odd integers will, naturally, have odd parity. This means they are not divisible by 2 and leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 2. This property can be used to simplify or solve problems related to divisibility or remainders.
Solving Problems Involving Consecutive Odd Integers
Let's explore how these properties can be applied to solve various types of problems:
Problem 1: Finding Consecutive Odd Integers Given Their Sum
Problem: The sum of three consecutive odd integers is 57. Find the integers.
Solution:
- Represent the integers algebraically: Let the three consecutive odd integers be x, x + 2, and x + 4.
- Set up the equation: x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) = 57
- Solve for x: 3x + 6 = 57 => 3x = 51 => x = 17
- Find the integers: The three consecutive odd integers are 17, 19, and 21.
Problem 2: Finding Consecutive Odd Integers Given a Product
Problem: The product of two consecutive odd integers is 143. Find the integers.
Solution:
- Represent the integers algebraically: Let the two consecutive odd integers be x and x + 2.
- Set up the equation: x(x + 2) = 143
- Solve the quadratic equation: x² + 2x - 143 = 0. This factors to (x - 11)(x + 13) = 0.
- Find the integers: The solutions are x = 11 and x = -13. Therefore, the pairs of consecutive odd integers are 11 and 13, or -13 and -11.
Problem 3: Word Problem involving Consecutive Odd Integers
Problem: The sum of five consecutive odd integers is 125. What are the integers?
Solution:
- Representation: Let the five consecutive odd integers be x, x + 2, x + 4, x + 6, and x + 8.
- Equation: x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) + (x + 6) + (x + 8) = 125
- Simplification: 5x + 20 = 125
- Solution for x: 5x = 105; x = 21
- Integers: The integers are 21, 23, 25, 27, and 29.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The concept of consecutive odd integers extends beyond simple algebraic manipulations. They appear in various areas of mathematics and have interesting applications:
- Number Theory: Exploring the properties of sums, products, and other relationships between consecutive odd integers is a rich area of number-theoretic investigation.
- Geometric Progressions: While not directly forming a geometric progression themselves, consecutive odd integers can be manipulated to create sequences that exhibit geometric patterns.
- Combinatorics and Probability: Problems involving selecting odd numbers from a set, or determining the probability of obtaining odd numbers in certain events, often involve consecutive odd integers.
- Calculus: The sum of consecutive odd integers can be used to illustrate the power of summation notation and its relationship to calculus concepts.
Conclusion: Mastering Consecutive Odd Integers
Understanding consecutive odd integers is crucial for developing a strong foundation in algebra and number theory. By mastering their definition, properties, and problem-solving techniques, you equip yourself with powerful tools for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. From simple algebraic equations to advanced number-theoretic explorations, the versatility of consecutive odd integers makes them a fundamental concept worth thorough understanding. The examples provided here represent just a glimpse into the myriad ways these numbers can be applied and analyzed, opening up exciting avenues for further mathematical inquiry. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and explore different problem types to enhance your problem-solving skills.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Square
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Basic Building Block Of All Matter
Mar 14, 2025
-
Exercise For Active And Passive Voice
Mar 14, 2025
-
Glucose Starch And Cellulose Are All Examples Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
28 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Consecutive Odd Integer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
