What Is A Common Multiple Of 3 And 5
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
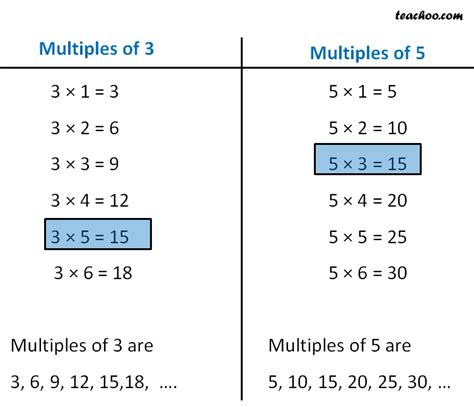
Table of Contents
What is a Common Multiple of 3 and 5? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common multiples of 3 and 5 might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but it opens a door to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory, crucial for various mathematical applications. This article will explore this seemingly simple question in depth, covering the basics, delving into advanced concepts, and providing practical examples along the way.
Understanding Multiples
Before we tackle common multiples, let's solidify our understanding of what a multiple is. A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any whole number (integer). For example:
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36... and so on to infinity.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60... and so on to infinity.
Notice that both lists extend infinitely. This is true for the multiples of any whole number greater than 1.
Identifying Common Multiples
A common multiple is a number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. Looking at the multiples of 3 and 5 listed above, we can already spot some common multiples:
- 15 is a multiple of 3 (3 x 5 = 15) and a multiple of 5 (5 x 3 = 15).
- 30 is a multiple of 3 (3 x 10 = 30) and a multiple of 5 (5 x 6 = 30).
- 45 is a multiple of 3 (3 x 15 = 45) and a multiple of 5 (5 x 9 = 45).
These are just a few examples. There are infinitely many common multiples of 3 and 5.
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Among the infinite common multiples, there's one that holds special significance: the Least Common Multiple (LCM). The LCM is the smallest positive common multiple of two or more numbers. In the case of 3 and 5, the LCM is 15.
There are several ways to find the LCM:
1. Listing Multiples Method:
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple. While simple for small numbers, it becomes inefficient for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method:
This is a more efficient method, especially for larger numbers. It involves:
-
Finding the prime factorization of each number:
- 3 = 3 (3 is a prime number)
- 5 = 5 (5 is a prime number)
-
Identifying the highest power of each prime factor:
- The prime factors are 3 and 5. The highest power of 3 is 3<sup>1</sup>, and the highest power of 5 is 5<sup>1</sup>.
-
Multiplying the highest powers together:
- LCM(3, 5) = 3<sup>1</sup> x 5<sup>1</sup> = 15
This method is more robust and works effectively even with larger numbers that have multiple prime factors.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a * b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method utilizes the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD). The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. For 3 and 5, the GCD is 1 (since 1 is the only common divisor).
Therefore:
LCM(3, 5) = (|3 * 5|) / GCD(3, 5) = 15 / 1 = 15
Applications of LCM and Common Multiples
Understanding common multiples and the LCM has practical applications across various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses arrive at a stop at different intervals. One arrives every 3 minutes, and the other every 5 minutes. The LCM (15 minutes) determines when both buses will arrive simultaneously.
-
Fraction Arithmetic: Finding the LCM is crucial for adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators. You need a common denominator (which is a common multiple) to perform these operations.
-
Cyclic Patterns: Many real-world phenomena exhibit cyclic patterns. The LCM helps determine when these patterns will align or repeat simultaneously.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Scenarios
The concept of common multiples expands beyond just two numbers. You can find common multiples for any set of numbers, no matter how large. The process involves similar techniques: listing multiples (inefficient for larger sets), prime factorization (more efficient), or utilizing algorithms designed for finding the LCM of multiple numbers.
Consider finding the LCM of 3, 5, and 7:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 3 = 3
- 5 = 5
- 7 = 7
-
Highest Powers: The highest power of each prime factor is simply the factor itself (3, 5, and 7).
-
Multiplication: LCM(3, 5, 7) = 3 x 5 x 7 = 105
Therefore, 105 is the least common multiple of 3, 5, and 7.
The Infinite Nature of Common Multiples
It’s crucial to remember that the set of common multiples for any given set of numbers is infinite. Once you've found the LCM, you can generate all other common multiples by multiplying the LCM by successive whole numbers.
For example, for 3 and 5:
- LCM = 15
- Other common multiples: 30 (15 x 2), 45 (15 x 3), 60 (15 x 4), and so on infinitely.
Advanced Concepts and Related Topics
The exploration of common multiples touches upon several advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Modular Arithmetic: This branch of number theory deals with remainders after division. Understanding common multiples is vital in solving modular arithmetic problems.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concepts of LCM and GCD extend to more abstract algebraic structures, such as rings and ideals.
-
Diophantine Equations: These are equations where only integer solutions are sought. The LCM and GCD play significant roles in solving certain types of Diophantine equations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Common Multiples
While the question of finding a common multiple of 3 and 5 might seem elementary, it serves as a gateway to understanding core concepts in number theory. From finding the LCM to applying these concepts in various contexts, the significance of common multiples extends far beyond basic arithmetic. Mastering these concepts provides a solid foundation for tackling more advanced mathematical challenges and offers practical solutions in numerous real-world scenarios. The journey from a simple question to a deeper understanding of number theory highlights the interconnectedness and beauty of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
8 Millimeters Equals How Many Centimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Words Starting With S For Kindergarten
May 09, 2025
-
Shapes With 3 Lines Of Symmetry
May 09, 2025
-
Is 1 Cc The Same As 1 Ml
May 09, 2025
-
A Fully Loaded Slow Moving Freight Elevator
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Common Multiple Of 3 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.