What Element Has 4 Valence Electrons
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
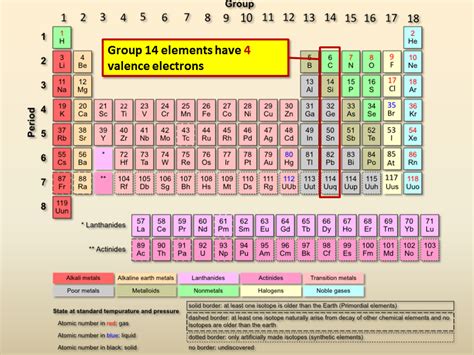
Table of Contents
What Element Has 4 Valence Electrons? Exploring Group 14
The question, "What element has 4 valence electrons?" points to a fascinating group of elements crucial to various aspects of our lives, from the silicon in our computers to the carbon in our bodies. This article delves deep into the characteristics of elements possessing four valence electrons, exploring their properties, applications, and the significance of their unique electron configuration.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we dive into the specifics of elements with four valence electrons, let's clarify the concept of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (or energy level) of an atom. These electrons are the most crucial in determining an element's chemical behavior and reactivity. They are the electrons involved in forming chemical bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons directly influences an element's ability to form bonds, the type of bonds it forms (ionic, covalent, metallic), and its overall chemical properties.
Group 14: The Family of Four-Valence-Electron Elements
Elements with four valence electrons are primarily found in Group 14 of the periodic table, also known as the carbon group or tetragonal group. This group includes:
- Carbon (C): The cornerstone of organic chemistry and the basis of all known life on Earth.
- Silicon (Si): A vital component in the semiconductor industry, forming the foundation of modern electronics.
- Germanium (Ge): Used in semiconductors, fiber optics, and certain alloys.
- Tin (Sn): A widely used metal found in numerous alloys, coatings, and solders.
- Lead (Pb): Though historically used extensively, its toxicity has led to a decrease in its applications. However, it still finds use in specific niche applications.
- Flerovium (Fl): A synthetic, highly radioactive element with limited known properties.
The Unique Chemistry of Group 14 Elements
The four valence electrons allow elements in Group 14 to exhibit diverse bonding behavior. They can form:
1. Covalent Bonds:
This is the most common bonding type for Group 14 elements. They share their four valence electrons with other atoms to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in their outermost shell). This leads to the formation of strong, stable covalent bonds, as seen in:
- Carbon: Forms the basis of countless organic molecules, exhibiting a remarkable ability to form long chains and complex structures. The diversity of organic compounds stems from carbon's ability to form single, double, and triple covalent bonds.
- Silicon: Forms strong covalent bonds with oxygen, leading to the formation of silicon dioxide (SiO2), the main component of sand and quartz. It also forms covalent bonds with other elements in semiconductors, leading to the creation of complex electronic structures.
2. Ionic Bonds:
While less common than covalent bonding, elements in Group 14 can form ionic bonds under specific circumstances. This typically involves the loss of four valence electrons to form a +4 cation, although this is less energetically favorable than covalent bond formation. This is more likely to occur with heavier elements in the group.
3. Metallic Bonds:
The heavier elements in Group 14, such as tin and lead, exhibit metallic bonding characteristics. This is due to the weaker attraction between the valence electrons and the nucleus, leading to the formation of a "sea" of delocalized electrons that contribute to the metallic properties like conductivity and malleability.
Applications of Group 14 Elements: A Diverse Landscape
The unique properties of Group 14 elements translate into a wide range of applications, impacting various industries.
Carbon: The Foundation of Life and Industry
- Organic Chemistry: Carbon's ability to form diverse bonds underpins the entire field of organic chemistry, responsible for the creation of plastics, polymers, pharmaceuticals, and countless other materials.
- Materials Science: Carbon-based materials such as diamond and graphite exhibit exceptional properties, making them valuable in industrial applications. Diamonds are known for their hardness and are utilized in cutting and drilling tools, while graphite is a good conductor of electricity and is found in batteries and lubricants.
- Energy: Carbon plays a significant role in fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), though their use is increasingly scrutinized due to environmental concerns.
Silicon: The Heart of Electronics
- Semiconductors: Silicon's semiconductor properties are crucial for the electronics industry. Silicon-based transistors and integrated circuits are the foundation of modern computers, smartphones, and countless other electronic devices.
- Solar Cells: Silicon is also a key component in solar cells, converting sunlight into electricity.
- Glass and Ceramics: Silicon dioxide is a primary ingredient in glass and various ceramics, contributing to their durability and other properties.
Germanium: Specialized Applications
- Semiconductors: Germanium, while less prevalent than silicon, finds applications in specific semiconductor devices and optoelectronic components.
- Fiber Optics: Germanium is used in fiber optic cables, enhancing their light transmission capabilities.
- Alloys: It is also used in certain alloys to improve their properties.
Tin and Lead: Traditional Uses and Modern Challenges
- Alloys: Tin is a vital component in various alloys, particularly bronze and solder, renowned for its corrosion resistance and ability to fuse metals.
- Coatings: Tin coatings protect metal surfaces from corrosion, extending their lifespan.
- Lead: Despite its toxicity, lead is still used in specialized applications, such as lead-acid batteries and radiation shielding. However, its use is increasingly restricted due to health and environmental concerns. Alternatives are actively being sought.
Environmental and Health Considerations
While Group 14 elements are essential for various applications, environmental and health concerns are associated with some members of this group.
- Lead: Lead's toxicity is well-established, causing developmental problems and other health issues, leading to stringent regulations on its use.
- Carbon Dioxide: The burning of fossil fuels (containing carbon) releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and greenhouse gas emissions. This is a significant environmental challenge demanding innovative solutions for cleaner energy production.
The Future of Group 14 Elements
Research continues to explore the potential of Group 14 elements, especially in developing sustainable technologies.
- Novel Materials: Scientists are developing new materials using carbon nanotubes, graphene, and other carbon-based structures with exceptional mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties.
- Silicon-based Photonics: Research focuses on integrating silicon photonics into electronics, aiming to combine the advantages of silicon-based electronics with the speed and efficiency of light-based communication.
- Sustainable Alternatives: The search for lead-free alternatives and strategies for reducing carbon emissions continues to drive innovation in materials science and energy technology.
Conclusion: A Diverse and Vital Group
In conclusion, elements with four valence electrons, predominantly found in Group 14 of the periodic table, are a diverse and vital group. Their unique chemical properties, particularly their ability to form covalent bonds, have led to their widespread use in various industries, from electronics and materials science to life sciences and energy production. While concerns remain about the environmental and health impacts of some elements, ongoing research and innovation continue to expand the applications of Group 14 elements, while striving for more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives. The future holds exciting possibilities for discovering and utilizing these elements in new and groundbreaking ways.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Conjugate Of A Complex Number In Polar Form
May 09, 2025
-
Arteries And Veins Fill In The Blank
May 09, 2025
-
48 As A Product Of Prime Factors
May 09, 2025
-
What Is Absolute Zero On The Celsius Scale
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 50 Square Meters
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Element Has 4 Valence Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.