What Does Instantaneous Rate Of Change Mean
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
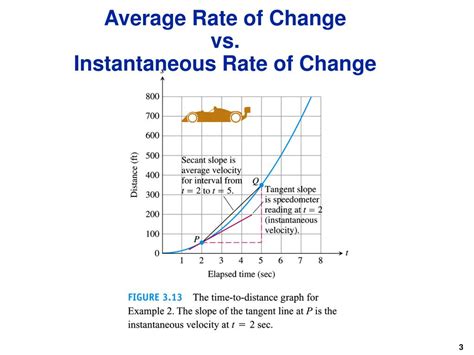
Table of Contents
What Does Instantaneous Rate of Change Mean? Unlocking the Secrets of Calculus
The concept of the instantaneous rate of change is a cornerstone of calculus, a branch of mathematics crucial for understanding how things change over time. While the average rate of change tells us the overall change over a period, the instantaneous rate of change focuses on the precise rate of change at a single moment. This seemingly subtle difference unlocks a powerful ability to analyze dynamic systems with remarkable accuracy. This article will delve deep into the meaning of instantaneous rate of change, exploring its applications, calculations, and significance across various fields.
Understanding the Average Rate of Change
Before diving into the instantaneous rate of change, let's solidify our understanding of its predecessor: the average rate of change. Imagine you're driving a car. You travel 100 miles in 2 hours. Your average speed is simply the total distance divided by the total time: 100 miles / 2 hours = 50 mph. This is the average rate of change of your distance with respect to time.
Mathematically, the average rate of change of a function f(x) over an interval [a, b] is given by:
(f(b) - f(a)) / (b - a)
This formula provides a straightforward calculation of the average change in the function's value across the specified interval. However, it doesn't tell us anything about the speed at any particular point within those two hours. Perhaps you were stopped at a red light for a while, or speeding down a highway at other times. The average hides these details.
The Limit Definition: Approaching the Instantaneous Rate of Change
To pinpoint the rate of change at a single instant, we need a more sophisticated approach. This is where the concept of a limit comes into play. Imagine shrinking the interval [a, b] in our driving example. As the time interval becomes smaller and smaller, the average speed increasingly reflects the speed at a specific moment. This is the essence of the instantaneous rate of change.
Let's consider a function f(x). To find the instantaneous rate of change at a specific point x = a, we take the limit of the average rate of change as the interval around 'a' shrinks to zero. This is expressed mathematically as:
lim (h→0) [(f(a + h) - f(a)) / h]
Here, 'h' represents the change in x. As 'h' approaches zero, the interval (a, a + h) becomes infinitesimally small, focusing our attention on the point 'a'. This limit, if it exists, represents the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x = a. It's also known as the derivative of f(x) at x = a, often denoted as f'(a) or df/dx|<sub>x=a</sub>.
Geometric Interpretation: The Tangent Line
The instantaneous rate of change has a powerful geometric interpretation. Consider the graph of a function. The average rate of change between two points on the graph represents the slope of the secant line connecting those points. As the interval between the points shrinks to zero, the secant line approaches the tangent line at the point of interest. Therefore, the instantaneous rate of change at a point is equivalent to the slope of the tangent line to the graph at that point.
Calculating Instantaneous Rate of Change: Differentiation Techniques
Calculating the instantaneous rate of change often involves finding the derivative of the function. Various techniques exist for differentiation, depending on the complexity of the function. Some common methods include:
- Power Rule: For functions of the form f(x) = x<sup>n</sup>, the derivative is f'(x) = nx<sup>n-1</sup>.
- Product Rule: For functions of the form f(x) = g(x)h(x), the derivative is f'(x) = g'(x)h(x) + g(x)h'(x).
- Quotient Rule: For functions of the form f(x) = g(x)/h(x), the derivative is f'(x) = [g'(x)h(x) - g(x)h'(x)] / [h(x)]<sup>2</sup>.
- Chain Rule: For composite functions of the form f(x) = g(h(x)), the derivative is f'(x) = g'(h(x))h'(x).
Mastering these rules allows for the efficient calculation of derivatives and, consequently, the instantaneous rate of change for a wide array of functions.
Applications of Instantaneous Rate of Change
The concept of instantaneous rate of change has far-reaching implications across various disciplines:
-
Physics: Velocity and acceleration are prime examples. Velocity is the instantaneous rate of change of displacement with respect to time, while acceleration is the instantaneous rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Analyzing projectile motion, oscillations, and fluid dynamics heavily relies on understanding instantaneous rates of change.
-
Engineering: Designing optimal structures, analyzing stress and strain on materials, and controlling systems all involve calculating instantaneous rates of change. For example, the rate of change of temperature in a chemical reaction or the rate of flow of a fluid through a pipe.
-
Economics: Marginal cost, marginal revenue, and marginal profit are all based on the instantaneous rate of change. Understanding how these factors change at a specific production level helps businesses make informed decisions.
-
Biology: Population growth rates, the spread of diseases, and reaction rates in biological systems are often modeled using differential equations, which heavily rely on the concept of instantaneous rate of change.
-
Computer Science: In areas like machine learning and artificial intelligence, optimization algorithms frequently use the concept of gradients, which are essentially vectors of instantaneous rates of change, to guide the learning process.
-
Finance: The instantaneous rate of change is essential for modeling stock prices, calculating the rate of return on investments, and managing financial risk. Options pricing models, for example, heavily rely on calculus concepts related to the instantaneous rate of change.
Beyond the Basics: Higher-Order Derivatives and Applications
The derivative itself can also have an instantaneous rate of change. This leads to the concept of higher-order derivatives. The second derivative, for instance, represents the instantaneous rate of change of the first derivative. In the context of motion, the second derivative of displacement with respect to time is acceleration. Higher-order derivatives find application in more complex scenarios requiring analysis of changes in rates of change.
Dealing with Non-Differentiable Functions
Not all functions are differentiable everywhere. A function may have sharp corners or discontinuities, making it impossible to define a tangent line, and therefore an instantaneous rate of change, at certain points. These situations require careful consideration and alternative approaches, often involving piecewise functions or other advanced techniques.
Conclusion: The Power of the Instantaneous
The instantaneous rate of change is a powerful mathematical concept that allows us to analyze dynamic systems with precision. Its applications span a vast range of disciplines, highlighting its significance in understanding how things change at a given moment in time. From analyzing the motion of objects to optimizing business strategies, the ability to calculate and interpret the instantaneous rate of change remains a crucial skill for anyone working with dynamic systems. While the initial concept might seem abstract, mastering its meaning and applications unlocks a deep understanding of the world around us. The journey into calculus, beginning with the instantaneous rate of change, opens doors to a wealth of knowledge and problem-solving capabilities. Understanding this fundamental concept lays the groundwork for further exploration of calculus and its profound implications across various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Organelle In A Plant Is Chlorophyll Found In
Mar 22, 2025
-
Takes The Shape Of Its Container
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not An Intensive Property
Mar 22, 2025
-
Distinguish Between Renewable And Non Renewable Energy
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Can 25 Be Divided By
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does Instantaneous Rate Of Change Mean . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
