What Degree Is A Straight Line
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
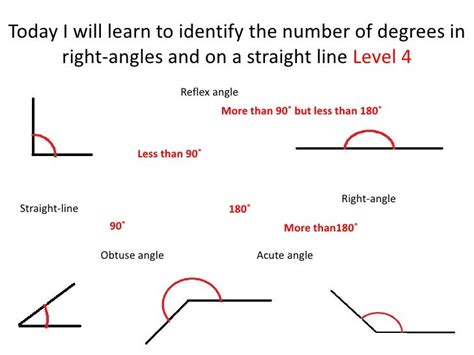
Table of Contents
What Degree is a Straight Line? Understanding Angles and Linearity
The question, "What degree is a straight line?" seems deceptively simple. It's a fundamental concept in geometry, yet understanding its nuances requires delving into the definitions of angles, lines, and the very nature of measurement. This article will explore this seemingly straightforward question in detail, clarifying the concept and expanding upon its implications in various fields.
Defining a Straight Line and Angles
Before we can determine the degree of a straight line, we must first establish clear definitions for our key terms:
Straight Line: A straight line is a fundamental geometric object defined as the shortest distance between two points. It extends infinitely in both directions. It has no curvature; it's perfectly linear. Imagine drawing a line with a perfectly sharpened pencil – that's the ideal representation of a straight line, though in reality, perfect straight lines only exist as abstract concepts.
Angle: An angle is formed by two rays (half-lines) that share a common endpoint, called the vertex. Angles are typically measured in degrees (°) or radians. The measure of an angle reflects the amount of rotation between the two rays.
The 180-Degree Angle: Understanding the Straight Angle
A straight line forms a straight angle, which measures 180 degrees. This is a crucial point. While a line itself doesn't possess a degree measure in the traditional sense, the angle formed by extending a line on both sides of a point creates a straight angle measuring 180°.
Think of it this way: Imagine a line segment. Now, extend that segment infinitely in both directions. This creates two rays emanating from a single point (the original segment's midpoint). The angle formed by these two rays is a straight angle, and its measure is 180°.
Visualizing the 180-Degree Angle
Consider these visual examples:
-
A perfectly folded piece of paper: When you fold a piece of paper perfectly in half, the crease forms a straight line, and the angle formed between the two halves is a straight angle, measuring 180°.
-
A straight road: Imagine a perfectly straight road extending to the horizon. The angle formed between the two directions the road extends to is a 180-degree angle.
-
A protractor: A protractor is designed to measure angles, and you'll notice that its straight edge represents a 180-degree angle.
Beyond the Basics: Angles and Lines in Geometry
Understanding the 180-degree angle is fundamental to several key concepts in geometry:
Supplementary Angles
Two angles are supplementary if their sum is 180°. A straight angle can be divided into two supplementary angles. For instance, if one angle is 60°, its supplementary angle is 120° (60° + 120° = 180°).
Linear Pairs
A linear pair is a pair of adjacent angles formed by intersecting lines. These angles are always supplementary; their sum is always 180°.
Vertically Opposite Angles
When two lines intersect, they form four angles. Vertically opposite angles are the angles opposite each other, and they are always equal. While not directly related to a straight angle's 180° measure, understanding the concept of vertically opposite angles highlights the interconnectedness of angles formed by intersecting lines.
Applications in Various Fields
The concept of a straight line and its associated 180-degree angle extends far beyond the realm of theoretical geometry. It has significant practical applications in many fields:
Engineering and Architecture
In engineering and architecture, understanding angles and straight lines is crucial for designing stable and functional structures. Calculations involving angles are essential for everything from bridge construction to building design. Precise measurements and calculations involving straight lines and 180-degree angles guarantee structural integrity and prevent collapse.
Computer Graphics and Game Development
In computer graphics and game development, straight lines and angles are fundamental to creating and manipulating 2D and 3D environments. Creating realistic models and simulations requires a detailed understanding of geometric principles, including the concept of the 180-degree angle.
Navigation and Surveying
Navigation and surveying rely heavily on the principles of geometry, especially the concepts of angles and straight lines. Understanding how to measure angles precisely using instruments like theodolites and compasses is critical for accurate surveying and navigation. In GPS technology, straight lines (geodesics) are used to calculate distances and positions on the Earth's curved surface.
Physics and Optics
In physics, particularly in optics, understanding the angles of incidence and reflection of light relies on the principles of straight lines and angles. The laws of reflection state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, both measured relative to a straight line perpendicular to the reflecting surface.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
Several common misconceptions surrounding the degree of a straight line need clarification:
-
A line has no degree: It's crucial to remember that a line itself doesn't have a degree measure. The 180-degree measurement refers to the angle formed by extending the line.
-
Infinite length doesn't imply infinite degrees: The infinite length of a line is independent of the 180-degree angle it forms. The angle remains constant regardless of how far the line extends.
-
Curved lines: Curved lines, by definition, do not form a 180-degree angle. They deviate from linearity, and the angles formed along their paths vary continuously.
Conclusion: The Significance of the 180-Degree Angle
The seemingly simple question, "What degree is a straight line?" leads to a deeper exploration of fundamental geometric principles. Understanding that a straight line forms a 180-degree angle is not just a matter of memorization; it's a cornerstone for understanding more complex geometric concepts and their applications in various fields. From structural engineering to computer graphics, the concept of the straight angle, and its relationship to lines and angles, remains an indispensable tool for problem-solving and innovation. This foundational knowledge allows us to build upon the principles of geometry to tackle more complex mathematical and real-world challenges. The 180-degree angle is a silent but powerful player in the world of mathematics and its countless applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cash Book And Petty Cash Book
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Multiples Of 24
Mar 10, 2025
-
Law Of Conservation Of Mass In A Sentence
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is A Triangle With Two Equal Sides
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Factorization Of 100
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Degree Is A Straight Line . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
