What Are The Prime Factors Of 14
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
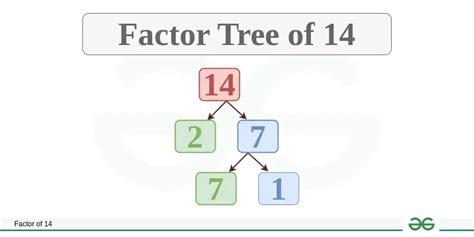
Table of Contents
What Are the Prime Factors of 14? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Finding the prime factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 14. However, understanding the process behind prime factorization is crucial for grasping fundamental concepts in number theory and algebra. This article will not only answer the question of what the prime factors of 14 are, but also explore the broader concept of prime factorization, its applications, and its significance in mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before delving into the prime factorization of 14, let's establish a solid understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In other words, a prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Uniqueness: Each prime number is unique and cannot be expressed as a product of other smaller numbers.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid centuries ago, a testament to their fundamental importance in mathematics.
Prime Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) as a product of its prime factors. This process is unique for every composite number. In essence, it's like finding the building blocks of a number, where the blocks are only prime numbers.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This theorem is the cornerstone of many mathematical concepts and proofs.
Finding the Prime Factors of 14
Now, let's address the central question: What are the prime factors of 14?
To find the prime factors of 14, we need to systematically break it down into its prime components. We can do this using a factor tree or by repeated division.
Method 1: Factor Tree
- Start with the number 14.
- Find two factors of 14. The most obvious pair is 2 and 7.
- Since 2 is a prime number, we circle it.
- Since 7 is also a prime number, we circle it.
The factor tree will look like this:
14
/ \
2 7
Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
Method 2: Repeated Division
- Start by dividing 14 by the smallest prime number, 2. 14 / 2 = 7.
- Now, we have 7, which is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has far-reaching implications across various mathematical fields. Here are some key applications:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization is essential for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
Example: Find the GCD and LCM of 14 and 21.
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
- Prime factorization of 21: 3 x 7
GCD(14, 21) = 7 (the common prime factor) LCM(14, 21) = 2 x 3 x 7 = 42 (all prime factors, with the highest power of each)
2. Cryptography
Prime numbers play a pivotal role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption. RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of many online transactions depends on the strength of this cryptographic algorithm.
3. Modular Arithmetic and Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental to many concepts in modular arithmetic and number theory. It helps solve problems related to congruences, divisibility, and other essential properties of integers.
4. Simplifying Fractions
Prime factorization is a powerful tool for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. By finding the prime factors of the numerator and denominator, you can identify common factors and cancel them out.
5. Abstract Algebra
The concept of prime factorization extends to more abstract algebraic structures, such as rings and ideals, providing insights into the properties and relationships within these structures.
Advanced Topics Related to Prime Factorization
While the prime factorization of 14 is straightforward, the process can become significantly more complex for larger numbers. Here are some advanced topics related to prime factorization:
- Trial Division: A basic but time-consuming method for finding prime factors by sequentially testing divisibility by prime numbers.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: An efficient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
- Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm used for factoring large composite numbers.
- General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): Currently, the most efficient algorithm for factoring very large numbers used in cryptography.
The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is a crucial aspect of modern cryptography. The development of efficient factorization algorithms is an ongoing area of research in computer science and mathematics.
Conclusion
While the prime factors of 14 are simply 2 and 7, understanding the process of prime factorization opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts and applications. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, prime factorization is a fundamental building block of many mathematical and computational processes. Its significance extends far beyond the simple example of 14, illustrating the elegance and power of prime numbers in the fabric of mathematics. Further exploration of prime numbers and their properties will undoubtedly reveal even more fascinating aspects of this fundamental area of number theory. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of prime factorization, serving as a foundation for further exploration of this essential mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Kirchhoffs Junction Rule Is A Statement Of
Mar 24, 2025
-
Is Dry Ice A Mixture Compound Or Element
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Characteristic Could Help You Distinguish Between Plants And Fungi
Mar 24, 2025
-
Coin Tossed 3 Times Sample Space
Mar 24, 2025
-
Are Polar Or Nonpolar Bonds Stronger
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factors Of 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
