What Are The Prime Factorization Of 58
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
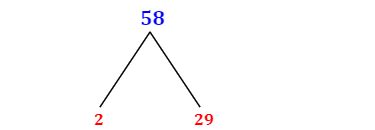
Table of Contents
What are the Prime Factorization of 58? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Finding the prime factorization of a number might seem like a simple mathematical exercise, but it underpins many crucial concepts in number theory and cryptography. This article will delve deep into the prime factorization of 58, explaining the process, its significance, and related mathematical concepts. We'll explore what prime numbers are, how to find the prime factorization of any number, and the practical applications of this fundamental mathematical operation.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 58, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means it's only divisible without a remainder by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid centuries ago.
- Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: Every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order). This theorem is the cornerstone of our exploration.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 58
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 58. The process involves systematically dividing the number by prime numbers until we're left with only prime numbers.
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 58 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 58 ÷ 2 = 29.
-
Check the next prime number: 29 is not divisible by 3 (2+9=11, not divisible by 3), 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, or 23.
-
Identify the prime number: We find that 29 is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 58 is 2 x 29. This means 58 can be expressed uniquely as the product of the prime numbers 2 and 29. No other combination of prime numbers will yield 58.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
While the prime factorization of 58 was relatively straightforward, larger numbers require more systematic approaches. Here are a few common methods:
1. Factor Tree Method
This is a visual method particularly useful for smaller numbers. You start with the original number and branch out, dividing by prime numbers until you reach only prime numbers at the ends of the branches. For 58:
58
/ \
2 29
2. Division Method
This is a more systematic approach, especially for larger numbers. You repeatedly divide the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly until you reach 1.
For 58:
- 58 ÷ 2 = 29
- 29 ÷ 29 = 1
The prime factors are 2 and 29.
3. Using Algorithms (for very large numbers)
For extremely large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are necessary. These algorithms are crucial in cryptography and other areas of computer science. Examples include:
- Trial division: A straightforward but time-consuming method for relatively small numbers.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: An efficient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified limit.
- Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm suitable for factoring large composite numbers.
- General number field sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers.
Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has profound implications across various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime factorization is at the heart of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components is the foundation of the RSA algorithm, widely used to secure online communication and data transmission.
2. Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental to number theory, a branch of mathematics exploring the properties of integers. Many important theorems and conjectures in number theory rely on the unique prime factorization property.
3. Computer Science
Efficient algorithms for prime factorization are crucial in computer science for applications like cryptography, data compression, and random number generation.
4. Other Applications
Prime factorization also finds applications in:
- Coding theory: Designing efficient error-correcting codes.
- Hashing: Generating unique fingerprints for data.
- Generating pseudo-random numbers: Creating sequences of numbers that appear random.
Beyond 58: Exploring Other Factorizations
Let's explore a few more examples to solidify our understanding:
Prime Factorization of 12:
12 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2: 12 ÷ 2 = 6. 6 is also divisible by 2: 6 ÷ 2 = 3. 3 is a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 or 2² x 3.
Prime Factorization of 75:
75 is divisible by 5: 75 ÷ 5 = 15. 15 is also divisible by 5: 15 ÷ 5 = 3. 3 is a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 75 is 3 x 5 x 5 or 3 x 5².
Prime Factorization of 100:
100 is divisible by 2: 100 ÷ 2 = 50. 50 is divisible by 2: 50 ÷ 2 = 25. 25 is divisible by 5: 25 ÷ 5 = 5. 5 is a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 or 2² x 5².
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factorization of a number, such as 58 (2 x 29), reveals a depth of mathematical significance and practical applications. From its role in securing online transactions to its foundational place in number theory, understanding prime factorization is crucial for anyone interested in mathematics, computer science, or cryptography. While finding the prime factors of small numbers like 58 is relatively straightforward, the challenge of factoring very large numbers continues to drive advancements in algorithms and computational power, shaping the landscape of modern technology. The journey of understanding prime factorization is a journey into the fundamental building blocks of numbers and their powerful influence on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 25 Cm In Inches
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Describes The Process Of Globalization
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are The Greatest Common Factors Of 48
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Unit Of Energy In S I Units Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Does Temperature Relate To Kinetic Energy
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factorization Of 58 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
