What Are The Factors Of 93
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
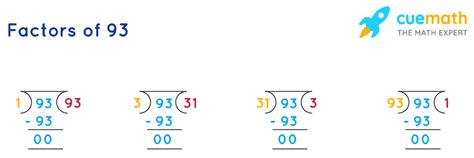
Table of Contents
- What Are The Factors Of 93
- Table of Contents
- What are the Factors of 93? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
- Understanding Factors and Divisibility
- Finding the Factors of 93: A Step-by-Step Approach
- The Significance of Factors in Mathematics
- Exploring Further: Beyond the Basics
- Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- Perfect Numbers and Abundant Numbers
- Applications in Real-World Scenarios
- Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factors
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What are the Factors of 93? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. Understanding factors is crucial in various mathematical fields, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations. This article will delve into the factors of 93, exploring the process of finding them, their properties, and their significance within the broader context of mathematics.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we embark on our journey to uncover the factors of 93, let's establish a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if you divide a number by its factor, the result is another whole number.
Divisibility rules offer shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by specific factors. For example:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
- Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if its last digit is 0.
These rules can significantly speed up the process of identifying potential factors.
Finding the Factors of 93: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's systematically find all the factors of 93. We'll begin by considering the divisibility rules and then use a methodical approach.
-
Check for Divisibility by Small Numbers: Let's start with the smallest prime numbers.
- Is 93 divisible by 2? No, because its last digit (3) is odd.
- Is 93 divisible by 3? Yes! The sum of its digits (9 + 3 = 12) is divisible by 3. Therefore, 3 is a factor of 93. 93 ÷ 3 = 31.
- Is 93 divisible by 5? No, because its last digit is not 0 or 5.
-
Identifying the Remaining Factors: Since we've found that 3 is a factor and 93 ÷ 3 = 31, we know that 31 is also a factor.
-
Prime Factorization: The prime factorization of a number is expressing it as a product of its prime factors. In this case, the prime factorization of 93 is 3 x 31. Both 3 and 31 are prime numbers (numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves).
-
Listing all Factors: Once we have the prime factorization, we can systematically list all the factors. The factors of 93 are: 1, 3, 31, and 93.
The Significance of Factors in Mathematics
The seemingly simple act of finding the factors of a number has far-reaching implications within various mathematical domains:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Factors are essential in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, if we have the fraction 93/186, we can find the greatest common factor (GCF) of 93 and 186, which is 93. Dividing both the numerator and denominator by 93 simplifies the fraction to 1/2.
-
Solving Equations: In algebra, finding the factors of a number or expression is crucial in solving equations. Factoring quadratic equations, for instance, relies heavily on finding the factors of the constant term.
-
Number Theory: The study of factors is a cornerstone of number theory, a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of integers. Concepts like prime numbers, composite numbers, and greatest common divisors all revolve around the idea of factors.
-
Cryptography: Factorization plays a vital role in cryptography, the science of secure communication. Modern encryption algorithms often rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems depends on the computational complexity of factorization.
Exploring Further: Beyond the Basics
Let's extend our understanding beyond the simple factorization of 93. We can explore related concepts to gain a more profound grasp of number theory.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides each of them without leaving a remainder. For instance, let's find the GCF of 93 and 186. Since 93 is a factor of 186 (186 ÷ 93 = 2), the GCF of 93 and 186 is 93.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all of them. To find the LCM of 93 and 186, we can use the formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a * b|) / GCF(a, b). In our case, LCM(93, 186) = (93 * 186) / 93 = 186.
Perfect Numbers and Abundant Numbers
Factors are also involved in the classification of numbers into categories like perfect numbers and abundant numbers:
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding the number itself). For example, 6 is a perfect number because its proper divisors are 1, 2, and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
-
Abundant Numbers: An abundant number is a number where the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number itself. For example, 12 is an abundant number because the sum of its proper divisors (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 = 16) is greater than 12.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of factors extends beyond theoretical mathematics and finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Dividing Resources: Factors are essential when dividing resources equally among a group of people. For example, if you have 93 apples to distribute evenly among a certain number of people, the factors of 93 will determine the possible group sizes.
-
Scheduling: Factors can help in scheduling tasks or events that need to be repeated at regular intervals. Finding the factors of a time duration helps determine possible scheduling patterns.
-
Geometry: Factors play a role in geometry when dealing with dimensions of shapes. For example, the factors of the area of a rectangle determine the possible integer values for its length and width.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factors
In conclusion, while the factors of 93 might seem like a minor detail in the vast landscape of mathematics, they reveal a deeper understanding of number theory's intricacies and its practical applications. From simplifying fractions to solving complex equations and even securing communications, the concept of factors remains an integral part of mathematical exploration. The systematic approach to finding factors, combined with an understanding of related concepts like GCF and LCM, empowers us to tackle more complex mathematical challenges and appreciate the elegance and utility of this fundamental concept. The journey of exploring the factors of 93 serves as a gateway to a broader understanding of the fascinating world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Function Of A Nucleus
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Positive Square Root Of 25
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Sides In A Parallelogram
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats The Lcm Of 9 And 15
Mar 16, 2025
-
Lowest Common Factor Of 7 And 9
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 93 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
