What Are The Factors Of 168
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
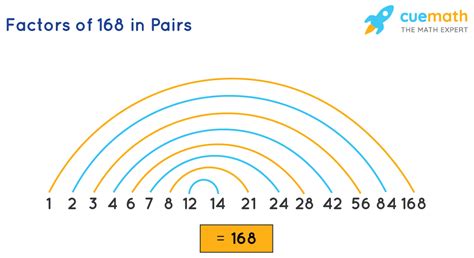
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 168? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory and its applications in various fields. This article delves deep into the factors of 168, exploring different methods to find them, their properties, and their relevance in mathematics and beyond. We'll cover everything from prime factorization to the significance of factors in higher-level mathematical concepts.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we dive into the specifics of 168, let's establish a solid foundation. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly, leaving no remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number. The process of finding these factors is closely tied to the concept of divisibility. Divisibility rules, while simple for smaller numbers, become increasingly complex as numbers grow larger.
Identifying Factors of 168: The Brute Force Method
The most straightforward way to find the factors of 168 is through systematic trial and error. We check each whole number, starting from 1, to see if it divides 168 without leaving a remainder. This method, while effective for smaller numbers, becomes impractical for larger ones.
Let's try it for 168:
- 1 divides 168 (168/1 = 168)
- 2 divides 168 (168/2 = 84)
- 3 divides 168 (168/3 = 56)
- 4 divides 168 (168/4 = 42)
- 6 divides 168 (168/6 = 28)
- 7 divides 168 (168/7 = 24)
- 8 does not divide 168
- 12 divides 168 (168/12 = 14)
- 14 divides 168 (168/14 = 12)
- 21 divides 168 (168/21 = 8)
- 24 divides 168 (168/24 = 7)
- 28 divides 168 (168/28 = 6)
- 42 divides 168 (168/42 = 4)
- 56 divides 168 (168/56 = 3)
- 84 divides 168 (168/84 = 2)
- 168 divides 168 (168/168 = 1)
Therefore, the factors of 168 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 21, 24, 28, 42, 56, 84, and 168.
Notice that the factors appear in pairs. This is because factors come in reciprocal pairs. For example, if 2 is a factor, then 168/2 = 84 is also a factor.
Prime Factorization: A More Efficient Approach
The brute force method is fine for smaller numbers, but prime factorization offers a much more efficient and elegant solution, especially for larger numbers. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors – numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
To find the prime factorization of 168, we can use a factor tree:
168
/ \
2 84
/ \
2 42
/ \
2 21
/ \
3 7
Therefore, the prime factorization of 168 is 2³ x 3 x 7.
Knowing the prime factorization is incredibly useful. It allows us to quickly determine all the factors of 168. We simply take combinations of the prime factors and their powers.
Deriving all factors from the Prime Factorization
From the prime factorization (2³ x 3 x 7), we can systematically generate all the factors:
- Using only 2: 2¹, 2², 2³ (2, 4, 8)
- Using 3: 3¹ (3)
- Using 7: 7¹ (7)
- Combinations:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 2 x 7 = 14
- 3 x 7 = 21
- 2² x 3 = 12
- 2² x 7 = 28
- 2 x 3 x 7 = 42
- 2³ x 3 = 24
- 2³ x 7 = 56
- 2² x 3 x 7 = 84
- 2³ x 3 x 7 = 168
- 1 (always a factor)
This method provides a complete and organized list of factors, avoiding the potential for missing any in the brute force approach.
Properties of Factors and Their Significance
The factors of 168, and factors in general, possess several interesting properties and hold significant importance in various mathematical contexts.
Sum of Factors: Abundant, Deficient, or Perfect?
We can calculate the sum of the factors of 168 (excluding 168 itself): 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 12 + 14 + 21 + 24 + 28 + 42 + 56 + 84 = 312. This sum (312) is greater than 168 itself. This classifies 168 as an abundant number. A number is abundant if the sum of its proper divisors (excluding itself) is greater than the number. If the sum is less than the number, it's a deficient number; if the sum equals the number, it's a perfect number.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Factors are crucial when finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) of numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides two or more integers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more integers. Prime factorization significantly simplifies the calculation of GCD and LCM.
For instance, to find the GCD of 168 and another number, say 252, we can use their prime factorizations:
- 168 = 2³ x 3 x 7
- 252 = 2² x 3² x 7
The GCD is found by taking the lowest power of each common prime factor: 2² x 3 x 7 = 84. Similarly, the LCM is found by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in either number: 2³ x 3² x 7 = 504.
Applications of Factors and Number Theory
The seemingly simple concept of factors and their properties extends far beyond basic arithmetic. They are fundamental building blocks in various advanced mathematical fields and practical applications:
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption, which relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms dealing with divisors and prime factorization are essential in optimization problems, data structures, and graph theory.
-
Music Theory: Number theory and its concepts like factors and divisors are surprisingly relevant in music theory, particularly in understanding musical intervals and harmonic relationships.
-
Engineering and Design: Understanding divisibility and factors is important in areas like designing structures with optimal dimensions and managing resources efficiently.
Conclusion: Beyond the Basics of 168's Factors
This comprehensive exploration of the factors of 168 has unveiled more than just a simple list of divisors. It has provided a gateway to understand the deeper concepts of number theory and its wide-ranging applications. From the basic brute force method to the elegant efficiency of prime factorization, finding the factors of a number, no matter how seemingly simple, reveals the intricate beauty and profound implications of fundamental mathematical concepts. Understanding these concepts provides a valuable foundation for tackling more advanced mathematical challenges and applications across various fields. The journey from identifying the factors of 168 to grasping the principles of number theory opens doors to a world of mathematical exploration and its powerful real-world applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Heavier Kilogram Or Pound
Mar 19, 2025
-
100 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 19, 2025
-
Latitude And Longitude Of Delhi India
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Is The Cell Membrane Said To Be Selectively Permeable
Mar 19, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Ending In Eat
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 168 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
