100 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
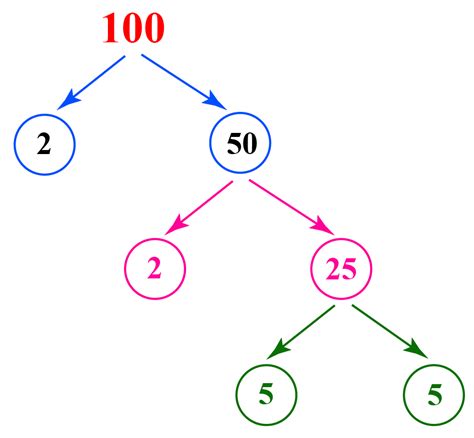
Table of Contents
100 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, the process of breaking down a number into its prime number components, is a fundamental concept in number theory with wide-ranging applications in mathematics, cryptography, and computer science. This article will explore the prime factorization of 100, illustrating the process and delving into the broader implications of this seemingly simple concept. We'll go beyond a simple answer, exploring various methods, practical applications, and related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before diving into the prime factorization of 100, let's solidify our understanding of the key terms.
-
Prime Number: A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other whole numbers.
-
Composite Number: A composite number is a whole number greater than 1 that is not a prime number. It can be divided by numbers other than 1 and itself. For example, 4, 6, 9, and 10 are composite numbers.
-
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This representation is unique for every composite number (except for the order of the factors).
Finding the Prime Factors of 100: Methods and Approaches
There are several ways to find the prime factors of 100. Let's explore a couple of common methods:
Method 1: The Factor Tree
The factor tree is a visual method that's particularly helpful for beginners. We start by expressing 100 as a product of any two factors. Then we continue factoring each factor until we're left only with prime numbers.
100
/ \
10 10
/ \ / \
2 5 2 5
From the factor tree, we can clearly see that the prime factorization of 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5, or 2² x 5².
Method 2: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly. We continue this process until the quotient is 1.
- Divide 100 by 2: 100 ÷ 2 = 50
- Divide 50 by 2: 50 ÷ 2 = 25
- Divide 25 by 5: 25 ÷ 5 = 5
- Divide 5 by 5: 5 ÷ 5 = 1
Therefore, the prime factorization of 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5, or 2² x 5².
The Significance of 2² x 5²
The prime factorization of 100, 2² x 5², holds significance beyond a simple mathematical exercise. It highlights several key aspects of number theory:
-
Uniqueness: Every composite number has a unique prime factorization (ignoring the order of the factors). This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This uniqueness is crucial in various mathematical proofs and applications.
-
Building Blocks: Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all whole numbers. Just as atoms form molecules, prime numbers combine to form all other composite numbers. Understanding the prime factorization allows us to analyze the properties of a number based on its constituent prime factors.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization is essential for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all given numbers.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, despite its seemingly simple nature, has numerous practical applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Public-key cryptography, which secures online transactions and communications, heavily relies on prime numbers and their properties. RSA encryption, one of the most widely used cryptographic algorithms, relies on the difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers are used in hash tables, which are data structures essential for efficient data retrieval in computer systems. They also play a significant role in algorithms related to network routing and data compression.
-
Coding Theory: Prime factorization is used in error-correcting codes which help ensure the reliable transmission and storage of digital data.
-
Number Theory Research: Prime factorization is a central topic in number theory research, with ongoing efforts to develop more efficient algorithms for factoring large numbers. This includes exploring the distribution of prime numbers, identifying patterns in prime numbers, and addressing unsolved problems such as the Riemann Hypothesis.
Beyond 100: Exploring Other Prime Factorizations
Let's briefly examine the prime factorizations of some related numbers to further illustrate the concept:
- 1000: 1000 = 10³ = (2 x 5)³ = 2³ x 5³
- 200: 200 = 2 x 100 = 2 x (2² x 5²) = 2³ x 5²
- 50: 50 = 2 x 25 = 2 x 5²
These examples demonstrate how the prime factorization of a number can help us understand its relationship to other numbers. For instance, we can easily see that 200 is a multiple of 100 (and 50) by examining their prime factorizations.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
The prime factorization of 100, while seemingly straightforward, opens the door to many more advanced concepts within number theory:
-
Modular Arithmetic: This branch of number theory deals with remainders after division. Understanding prime factorizations can be helpful in solving problems related to modular arithmetic.
-
Diophantine Equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions. Prime factorization plays a crucial role in solving certain types of Diophantine equations.
-
The Riemann Hypothesis: This unsolved problem in mathematics concerns the distribution of prime numbers and is one of the most important unsolved problems in modern mathematics.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple prime factorization of 100—2² x 5²—is far more significant than it might appear at first glance. It serves as a foundational concept in number theory, with far-reaching applications in cryptography, computer science, and other fields. Understanding prime factorization not only helps us break down numbers but also reveals fundamental properties of numbers and their relationships. Exploring this concept further unlocks a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty and power of mathematics. The unique prime factorization of each composite number underpins countless mathematical theories and practical applications, emphasizing its importance in both theoretical and applied contexts. It's a concept worth exploring further, uncovering its rich connections throughout the world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is The Surface Area The Same As Area
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are Advantages Of Fossil Fuels
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Zeros For 10 Lakhs
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 28 And 35
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 8 And 3
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 100 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
