What Are The Factors Of 125
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
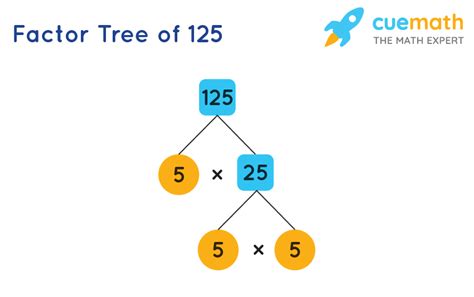
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of 125: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 125?", opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime factorization, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, a deeper investigation reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and their applications. This article delves into the factors of 125, exploring the methods used to find them and the broader mathematical context in which they reside.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we embark on our journey to find the factors of 125, let's establish a clear understanding of fundamental terms. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if we divide a number by one of its factors, the result is a whole number. Divisibility, therefore, refers to the property of one number being completely divisible by another.
For instance, the number 12 is divisible by 2, 3, 4, and 6 because these numbers divide 12 without leaving a remainder. Conversely, 12 is not divisible by 5 because 12 divided by 5 results in a remainder of 2. Therefore, 2, 3, 4, and 6 are factors of 12, while 5 is not.
Finding the Factors of 125: A Systematic Approach
Now, let's systematically determine the factors of 125. We can employ several approaches:
1. Trial Division: This is the most straightforward method. We systematically test each integer, starting from 1, to see if it divides 125 without leaving a remainder.
- 1 divides 125 (125/1 = 125)
- 2 does not divide 125 (125/2 = 62.5)
- 3 does not divide 125 (125/3 = 41.666...)
- 4 does not divide 125 (125/4 = 31.25)
- 5 divides 125 (125/5 = 25)
- 6 does not divide 125 (125/6 = 20.833...)
- ...and so on.
This process continues until we reach the square root of 125 (approximately 11.18). Once we exceed this value, any new factor we find will have a corresponding factor we've already identified. For example, if we find that 25 is a factor, we automatically know that 5 is also a factor (since 125 = 5 x 25).
2. Prime Factorization: This method is more efficient, particularly for larger numbers. It involves breaking down the number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
125 can be expressed as 5 x 25. However, 25 is not a prime number; it's 5 x 5. Therefore, the prime factorization of 125 is 5 x 5 x 5, or 5³.
This prime factorization reveals that the only prime factor of 125 is 5. This has significant implications for determining all factors.
3. Deriving Factors from Prime Factorization: Once we have the prime factorization (5³), we can systematically generate all factors. We consider all possible combinations of the prime factors:
- 5⁰ = 1
- 5¹ = 5
- 5² = 25
- 5³ = 125
Therefore, the factors of 125 are 1, 5, 25, and 125.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method highlights the fundamental importance of prime numbers in number theory. Prime numbers are the indivisible building blocks from which all other integers are constructed. Every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic). This unique factorization allows us to solve various problems in number theory, cryptography, and other fields.
In the context of 125, its prime factorization (5³) reveals its structural simplicity. The fact that it's a power of a single prime number simplifies the process of finding its factors.
Factors and their Properties
Let's examine the factors of 125 (1, 5, 25, 125) and some of their properties:
-
1 and 125: These are the trivial factors, always present for any integer. 1 is the multiplicative identity, and the number itself is always a factor.
-
5 and 25: These are non-trivial factors. They highlight the recursive nature of factorization: 5 is a factor, and 5 multiplied by itself (25) is also a factor.
-
Sum of Factors: The sum of the factors of 125 (1 + 5 + 25 + 125 = 156). This sum has relevance in various number theoretic contexts, such as determining perfect numbers and abundant numbers.
-
Number of Factors: 125 has four factors. The number of factors of a number can be easily calculated from its prime factorization. For a number with prime factorization p₁ᵃ¹ * p₂ᵃ² * ... * pₙᵃⁿ, the number of factors is (a₁ + 1)(a₂ + 1)...(aₙ + 1). In the case of 125 (5³), the number of factors is (3 + 1) = 4.
Applications and Extensions
Understanding factors extends beyond simple mathematical exercises. It has numerous applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization forms the backbone of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components underpins the security of these systems.
-
Computer Science: Concepts related to factors and divisibility are fundamental in algorithm design and optimization.
-
Abstract Algebra: Factors and divisibility are generalized in abstract algebra through the concepts of ideals and modules.
-
Real-world problem solving: Divisibility and factors play a role in problems involving distribution, grouping, and resource allocation. For instance, determining how many groups of 5 can be formed from 125 items is directly related to the factors of 125.
Beyond 125: Exploring Further
The exploration of the factors of 125 provides a solid foundation for understanding more complex concepts in number theory. Expanding on this, one can explore:
-
Factors of larger numbers: Applying the methods discussed above to larger numbers, possibly using computational tools for more efficient prime factorization.
-
Perfect numbers: Numbers whose sum of factors (excluding the number itself) equals the number.
-
Abundant and deficient numbers: Numbers where the sum of factors (excluding the number itself) is greater than (abundant) or less than (deficient) the number.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Understanding how to find the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers, which relies heavily on prime factorization.
Conclusion
Determining the factors of 125, while seemingly trivial at first glance, opens a window into the fascinating world of number theory. The seemingly simple act of finding these factors illuminates fundamental concepts like prime factorization, divisibility, and the building blocks of integers. This exploration provides a gateway to more advanced mathematical concepts and their diverse applications in various fields, underscoring the importance of even seemingly simple mathematical concepts. The journey from understanding the factors of 125 to grasping more complex number theoretic concepts is a testament to the interconnectedness and beauty of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 125 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
