What Are The Factors For 85
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
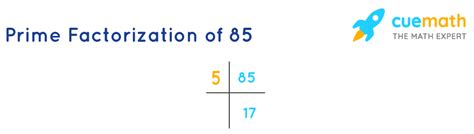
Table of Contents
Decoding the Factors of 85: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 85?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, exploring the concept of factors, their properties, and the methods for finding them unveils a rich mathematical landscape. This article delves into the factors of 85, expanding on the fundamental concepts and providing a broader understanding of factorisation in mathematics.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we delve into the specific factors of 85, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. In mathematics, a factor (or divisor) of a number is an integer that divides the number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if we divide a number by one of its factors, the result is a whole number. This concept is intrinsically linked to divisibility. A number is divisible by another number if the result of their division is an integer.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder. Finding factors is a crucial part of many mathematical operations, including simplification of fractions, solving equations, and exploring more advanced concepts like prime factorisation.
Finding the Factors of 85: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's focus on the number 85. To find its factors, we systematically check which integers divide 85 without leaving a remainder. One efficient method involves considering pairs of numbers whose product is 85:
-
Start with 1: Every number has 1 as a factor. Therefore, 1 is a factor of 85.
-
Check the small prime numbers: Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Checking small primes is a common starting point as they often form the building blocks of larger numbers. We find that 85 is divisible by 5 (85 ÷ 5 = 17).
-
Identify the corresponding factor: Since 5 is a factor, we immediately know that 17 is also a factor (because 5 x 17 = 85).
-
Consider the larger factor: Having found 5 and 17, we've identified two factors.
-
Check for other factors: We can continue checking larger integers, but since 17 is already a factor, we know that no other integers between 17 and 85 will divide 85 evenly.
Therefore, the factors of 85 are 1, 5, 17, and 85.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
The process of finding factors is closely related to prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime factors are prime numbers that divide the number without leaving a remainder. Every composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers.
For 85, its prime factorization is 5 x 17. Both 5 and 17 are prime numbers. This factorization is unique; there is no other way to express 85 as a product of prime numbers.
Applications of Factors and Factorization
The concept of factors and factorization is not just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator allows for simplification of fractions to their lowest terms.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: Factorization is a critical technique in solving quadratic and higher-order polynomial equations.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography systems, such as RSA, which relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
-
Computer Science: Factorization algorithms are used in various computational tasks, such as data compression and code optimization.
-
Modular Arithmetic: The concept of factors is fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of mathematics that deals with remainders.
Beyond 85: Exploring Factorization Techniques
While finding the factors of 85 is relatively straightforward, dealing with larger numbers requires more efficient techniques. Here are some commonly used methods:
-
Division Method: Systematically dividing the number by integers starting from 1 and progressing upwards.
-
Prime Factorization Method: Finding the prime factors of the number. This method is particularly efficient for larger numbers.
-
Factor Trees: A visual representation of the factorization process, breaking down the number into smaller factors until all factors are prime.
-
Using Algorithms: For very large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are employed to efficiently find factors.
The Significance of Factors in Number Theory
The study of factors forms the bedrock of many concepts in number theory, a branch of mathematics that explores the properties of integers. Understanding factors is crucial for grasping more advanced concepts, such as:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The largest number that divides two or more integers without leaving a remainder.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest number that is a multiple of two or more integers.
-
Perfect Numbers: Numbers that are equal to the sum of their proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself).
-
Amicable Numbers: Two numbers where the sum of the proper divisors of one number is equal to the other number, and vice versa.
Conclusion: Factors – A Cornerstone of Mathematics
This exploration of the factors of 85 has revealed that seemingly simple questions can lead to a deep dive into the fascinating world of number theory. Understanding factors, factorization, and prime factorization provides a fundamental base for solving a wide variety of mathematical problems and has significant applications across numerous fields. The techniques and concepts discussed here are essential building blocks for more advanced mathematical pursuits and are vital for developing a strong understanding of number systems and their properties. From simplifying fractions to securing cryptographic systems, the influence of factors permeates many aspects of our mathematical and technological world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Distributive Property Calculator Step By Step
Mar 11, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Abiotic
Mar 11, 2025
-
What Do Arrows Mean In A Food Chain
Mar 11, 2025
-
Is Sugar Dissolving In Water A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 11, 2025
-
Which Step In Cellular Respiration Produces The Most Atp
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 85 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
