What Are The Factors For 62
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
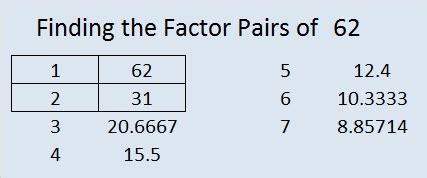
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Exploring the Factors of 62
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 62?" opens a door to a deeper understanding of number theory and its applications. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, delving into the concept of factors reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical relationships and their significance in various fields. This comprehensive article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the broader context of factors, their properties, and their importance in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we dive into the specific factors of 62, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. In mathematics, a factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving any remainder. For instance, if we consider the number 12, its factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Finding factors is a fundamental concept in arithmetic. It forms the basis for numerous operations, including simplifying fractions, solving equations, and understanding prime factorization – a cornerstone of number theory.
Finding the Factors of 62: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's determine the factors of 62. We can do this systematically by checking each whole number from 1 up to 62 to see if it divides 62 without leaving a remainder. Alternatively, we can use a more efficient method:
-
Start with 1: Every number has 1 as a factor.
-
Check for 2: Since 62 is an even number, it's divisible by 2. 62 ÷ 2 = 31. Therefore, 2 is a factor.
-
Check for 31: We found that 2 is a factor and the result of the division was 31. Thus, 31 is also a factor.
-
Check for other numbers: We need to check if any numbers between 2 and 31 are factors. We find no other whole numbers that divide 62 evenly.
Therefore, the factors of 62 are 1, 2, 31, and 62.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Prime Building Blocks
The concept of prime factorization is closely related to finding factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
In the case of 62, we can express it as a product of its prime factors as follows: 62 = 2 x 31. Both 2 and 31 are prime numbers. This representation is unique for every number, emphasizing the fundamental nature of prime factorization in number theory.
Applications of Factors and Prime Factorization: Beyond the Classroom
The seemingly simple concept of factors and prime factorization has far-reaching applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers play a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The security of these systems relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for finding prime factors are essential in computer science for tasks such as data compression, error correction codes, and hash functions.
-
Number Theory: Factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory. Many advanced mathematical theorems and conjectures are based on the properties of prime numbers and their factorization. For example, the Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, is related to the distribution of prime numbers.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concept of factors extends to abstract algebra, where it is generalized to the concept of divisors in various algebraic structures.
-
Real-World Applications: Understanding factors can be helpful in everyday situations. For instance, when dividing quantities, knowing the factors helps in determining even distribution. Consider dividing 62 candies equally among friends; the factors of 62 (1, 2, 31, 62) tell you the possible numbers of friends you can evenly distribute them to.
Exploring Related Concepts: Divisibility Rules and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
Understanding factors leads us to other important concepts:
-
Divisibility Rules: Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by another number without performing the division. For instance, a number is divisible by 2 if it's even, divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3, and so on. Knowing divisibility rules speeds up the process of finding factors.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD is useful in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems. For example, the GCD of 62 and 124 is 62.
Factors and Their Significance in Different Number Systems
The concept of factors extends beyond the realm of natural numbers. Factors can be explored in different number systems, such as complex numbers and integers modulo n. In these systems, the properties and relationships between factors can exhibit distinct characteristics, opening up new avenues of mathematical exploration.
The Importance of Practice: Mastering Factorization Skills
The ability to find factors and perform prime factorization is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Consistent practice is crucial for developing proficiency. There are numerous online resources, textbooks, and educational materials available to assist in learning and practicing factorization techniques. Start with smaller numbers and gradually progress to larger ones. The more you practice, the faster and more accurate you will become in determining factors.
Advanced Factorization Techniques: For the Curious Mind
While the methods described above are sufficient for finding factors of relatively small numbers, more advanced techniques are required for factoring very large numbers. These techniques, often used in cryptography, include algorithms such as the Pollard rho algorithm, the elliptic curve method, and the general number field sieve. These methods are computationally intensive and utilize sophisticated mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Factors – A Foundation of Mathematical Understanding
In conclusion, while the factors of 62 – 1, 2, 31, and 62 – might seem simple at first glance, they represent a gateway into a broader mathematical world. Understanding factors, prime factorization, and related concepts such as divisibility rules and GCD is essential not only for academic success but also for applications in various fields. This exploration should inspire further investigation into the fascinating world of number theory and its implications. The seemingly simple act of finding the factors of a number holds a deeper significance, showcasing the interconnectedness and power of mathematical principles. Continue exploring, continue learning, and continue to be amazed by the beauty and elegance of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Elbow Joint Is An Example Of A
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lcm Of 2 And 3 And 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Dna Have A Positive Or Negative Charge
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Find Square Root Of A Non Perfect Square
Mar 17, 2025
-
Intrinsic Carrier Concentration Of Silicon At 300k
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 62 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
