What Are The Factors For 59
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
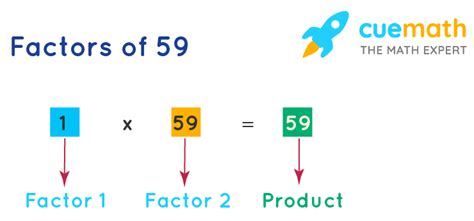
Table of Contents
Decoding the Factors of 59: A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
The number 59 holds a unique position in the world of mathematics. Understanding its factors requires exploring the concepts of prime numbers, divisibility rules, and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. This article will delve into these concepts, providing a comprehensive understanding of why 59 is a fascinating number and what makes its factors so distinct.
Understanding Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we examine the factors of 59, it's crucial to grasp the definition of a prime number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it cannot be evenly divided by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. Examples of prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on.
Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers. This is because of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every whole number greater than 1 can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers. This decomposition is often called the prime factorization of the number.
Exploring Divisibility Rules: A Shortcut to Factor Identification
Divisibility rules are handy shortcuts that help us determine if a number is divisible by another number without performing long division. While there aren't specific divisibility rules for all numbers, understanding common rules helps narrow down potential factors. For instance:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
- Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if its last digit is 0.
Applying these rules to 59, we can quickly eliminate several potential divisors. 59 is not divisible by 2 (its last digit is 9), 3 (5 + 9 = 14, which isn't divisible by 3), or 5 (its last digit is 9). This process of elimination helps us focus on the prime numbers.
The Unique Factorization of 59: Why it's a Prime Number
Now, let's tackle the core question: What are the factors of 59? Using the divisibility rules and a bit of trial and error, we find that 59 is not divisible by any whole number other than 1 and itself. This directly confirms that 59 is a prime number.
Therefore, the only factors of 59 are 1 and 59. This makes its prime factorization incredibly simple: 59 = 1 x 59. There are no other prime numbers that multiply together to equal 59.
Prime Number Distribution and the Sieve of Eratosthenes
The distribution of prime numbers among whole numbers is a fascinating area of mathematical study. While there's no simple formula to predict exactly where prime numbers will appear, various methods help identify them. One such method is the Sieve of Eratosthenes, a historical algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
The Sieve of Eratosthenes works by systematically eliminating multiples of prime numbers. We start by listing all whole numbers up to our target (in this case, a range that includes 59). Then, we mark 2 as prime and eliminate all its multiples. Next, we find the next unmarked number (3), mark it as prime, and eliminate its multiples. We continue this process until we reach the square root of our target number. All the remaining unmarked numbers are prime. This process efficiently identifies prime numbers like 59.
The Significance of Prime Numbers in Cryptography
Prime numbers have significant practical applications, especially in cryptography. Many encryption algorithms rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems depends on the fact that it is computationally extremely difficult to factor very large numbers, even with powerful computers. This is why prime numbers are crucial in securing online transactions and sensitive data.
Exploring Related Concepts: Composite Numbers and Factorization
In contrast to prime numbers, composite numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that have more than two divisors. They can be factored into smaller whole numbers. For example, 12 is a composite number because its factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. The process of breaking down a composite number into its prime factors is called prime factorization. This concept is fundamental in many areas of mathematics.
Prime Factorization and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: A Deeper Look
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which we mentioned earlier, is a cornerstone of number theory. It guarantees that every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers, regardless of the order of the factors. This uniqueness is essential in various mathematical proofs and algorithms. For instance, finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) and the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers relies heavily on prime factorization.
Conclusion: 59 – A Simple Prime Number with Significant Implications
In conclusion, the factors of 59 are simply 1 and 59. Its simplicity as a prime number belies its significance within the broader context of number theory and its applications. Understanding prime numbers, divisibility rules, and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic provides a solid foundation for exploring more complex mathematical concepts and appreciating the intricate beauty of number systems. The unique properties of 59 highlight the fundamental role that prime numbers play in mathematics and its real-world applications, particularly in the realm of cryptography and secure data transmission. The seemingly simple number 59, therefore, reveals a depth of mathematical significance that underscores its importance in our understanding of numbers and their properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Letter Words Starting With H A I
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Mm Are In One Meter
Mar 31, 2025
-
Does A Flatworm Have A Coelom
Mar 31, 2025
-
An Automobile Engine Converts Energy Into Energy
Mar 31, 2025
-
Is Chlorine A Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 59 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
